The at-home HPV self-test that unlocked my cervical cancer screening
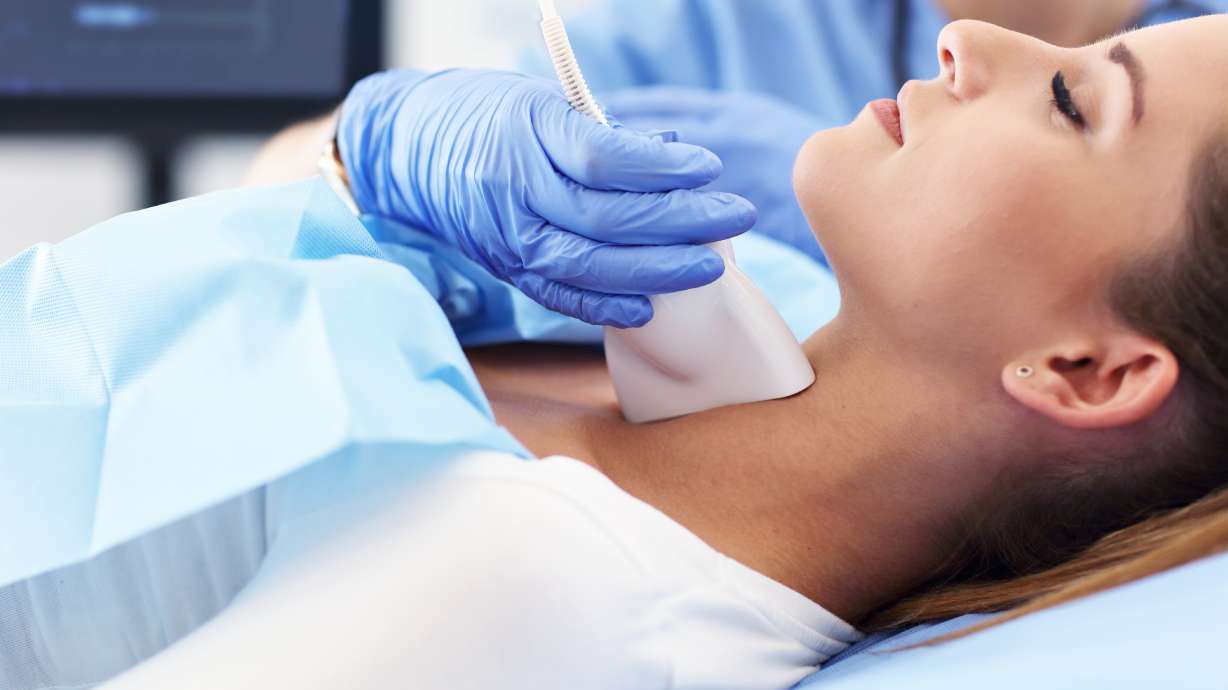
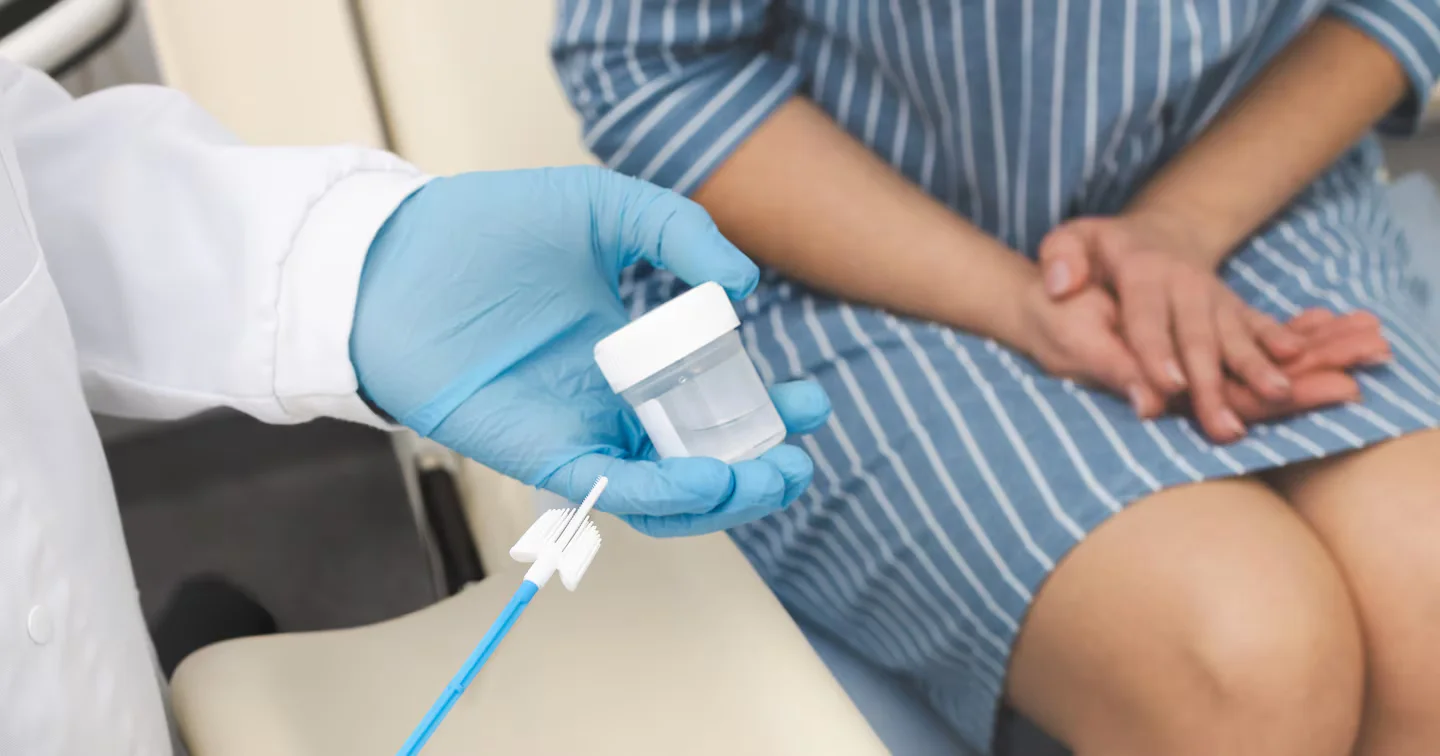
A Washington Post Well+Being guest column by Kami Rieck explains how the American Cancer Society’s updated guidelines allowing a self-collected HPV test finally let her get cervical cancer screening, despite vaginismus that made traditional clinician exams nearly impossible, illustrating how at-home sampling can expand access to a lifesaving screening for people with screening barriers.