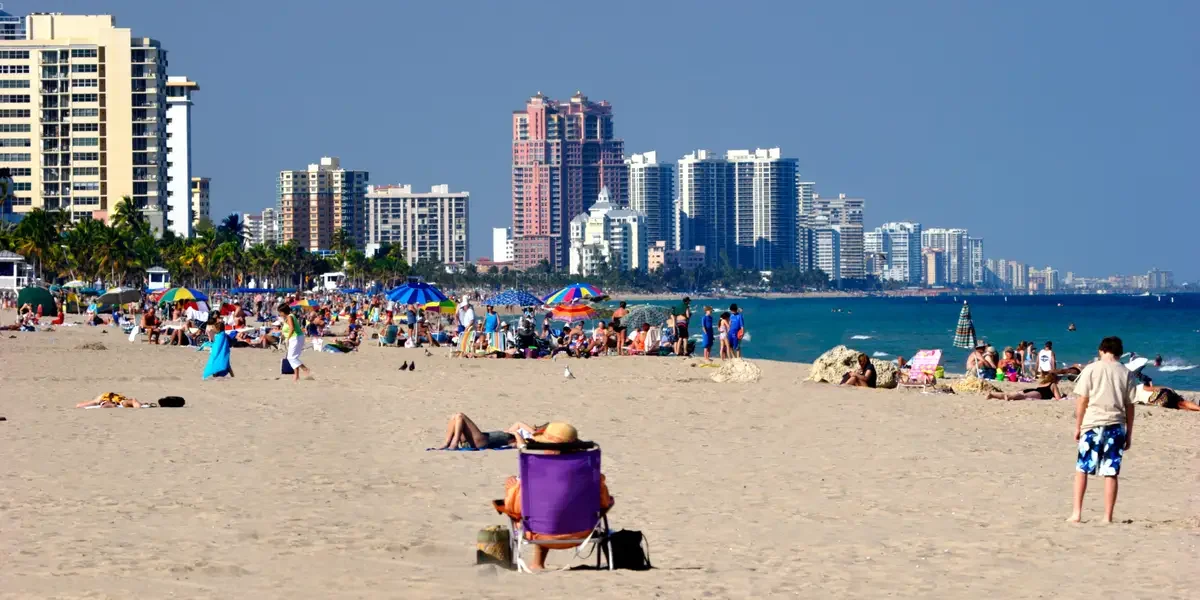
Florida's Domestic Migration Slows as Costs Rise
Florida still draws newcomers, but net domestic migration has slowed due to rising home prices and insurance costs, pushing some longtime residents to relocate while international and wealthier buyers keep inflows.