Brain Imaging Reveals Dopamine's Main Action in the Striatum
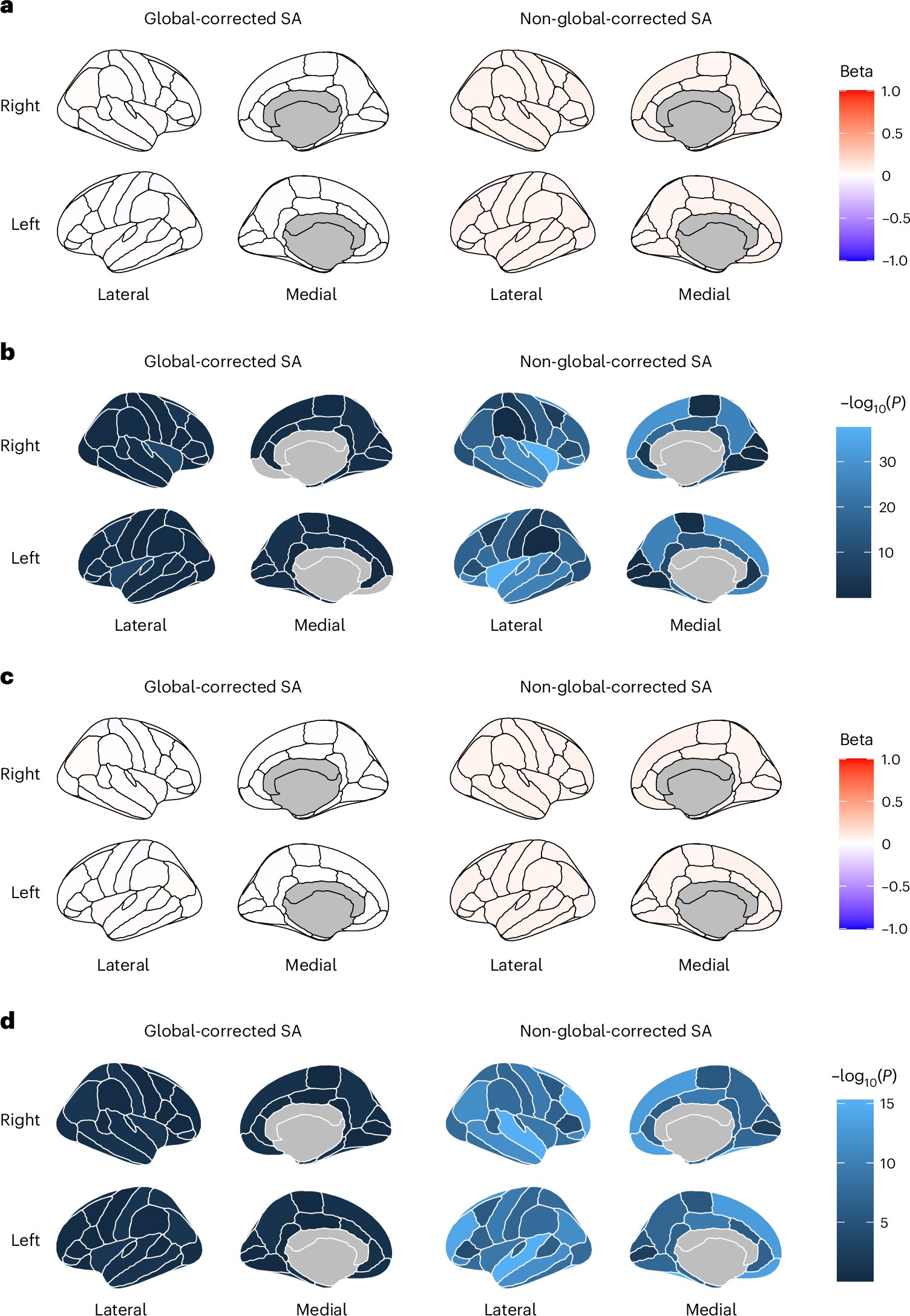
A brain imaging study in mice shows that dopamine is predominantly concentrated in the striatum rather than the cortex, challenging previous assumptions and highlighting the importance of the striatum in movement and psychiatric disorders like Parkinson's and schizophrenia.