Essential Hydration Tips for Optimal Health and Mental Clarity
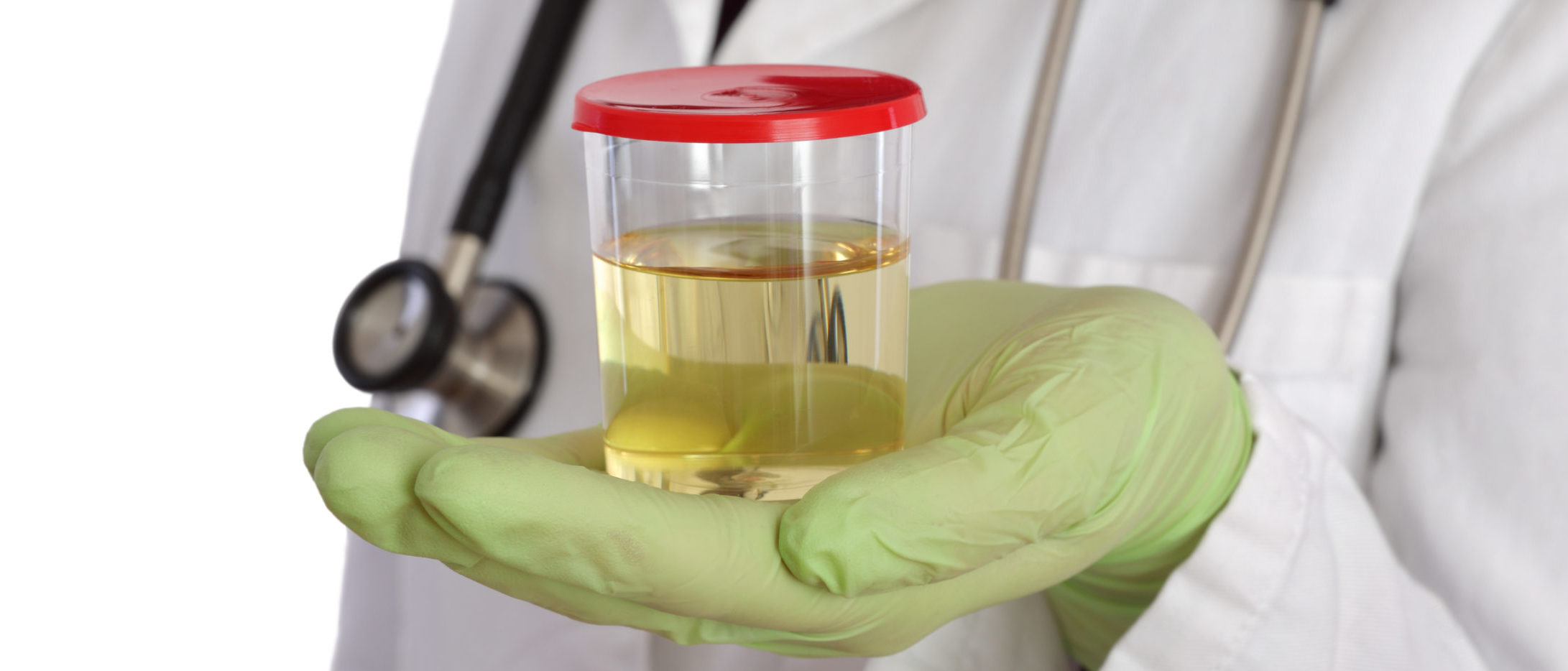
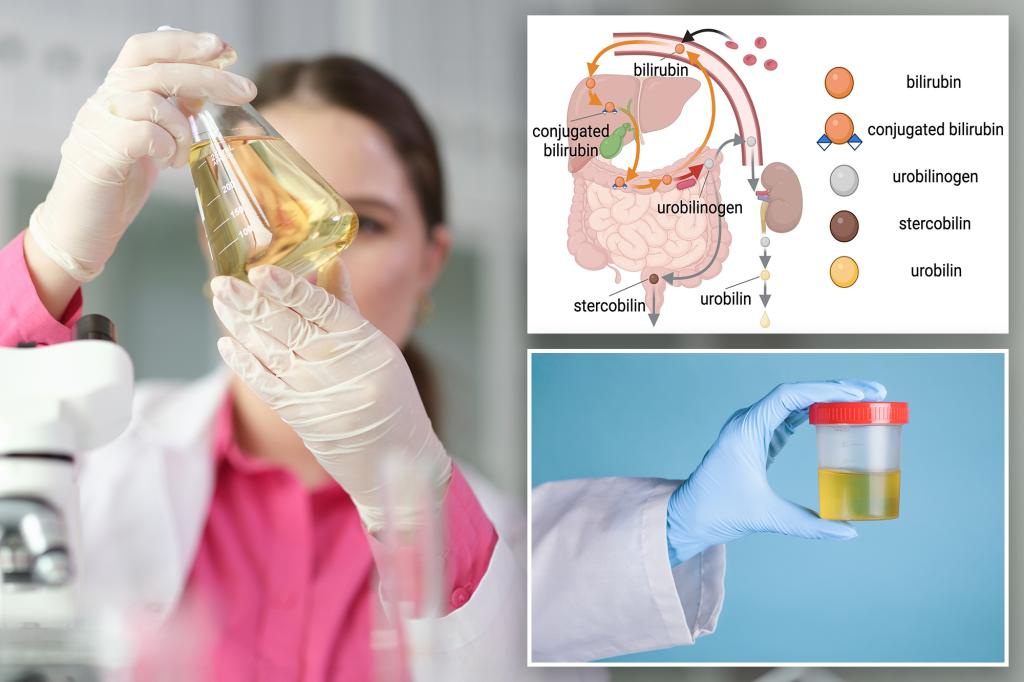
Dr. Jamin Brahmbhatt emphasizes that maintaining proper hydration is crucial for health, advocating for monitoring urine color as a simple way to gauge hydration levels, and highlights that water intake needs vary based on individual factors, with a focus on balancing water and electrolytes to prevent dehydration and overhydration.