Scientists Reveal Immunoglobulins' Dual Role in Aging
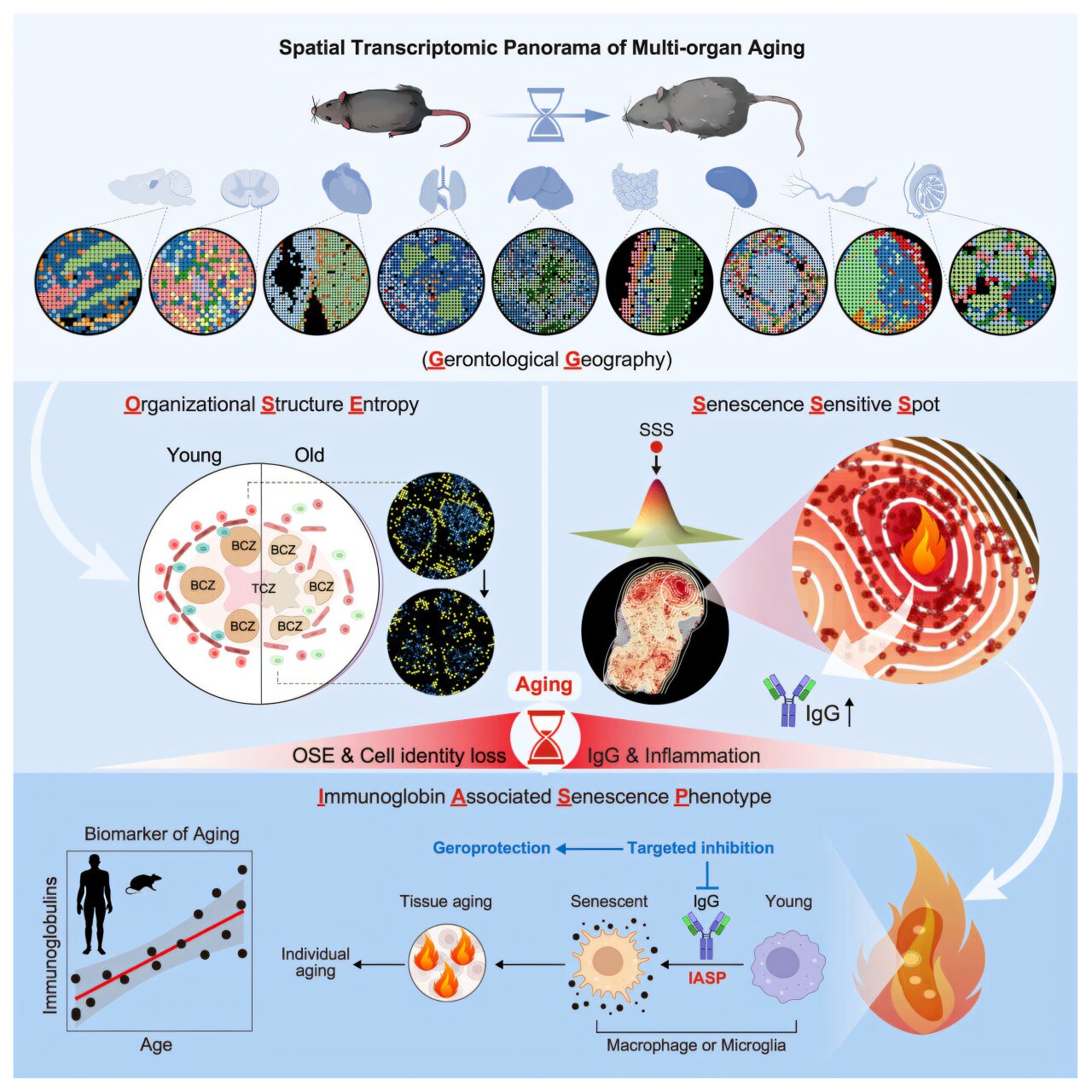
Scientists from the Chinese Academy of Sciences and BGI Research have discovered that immunoglobulins play a dual role in the aging process, potentially reshaping our understanding of aging. By creating high-precision spatial transcriptomic maps of nine organs in mice, the study identified immunoglobulin G (IgG) as a key driver of aging, which accumulates in tissues and induces aging effects. The research suggests IgG levels could serve as biomarkers for aging and introduces an intervention using antisense oligonucleotides to reduce IgG and delay aging.