Disease Rebound Fears Post-COVID-19 Unfounded
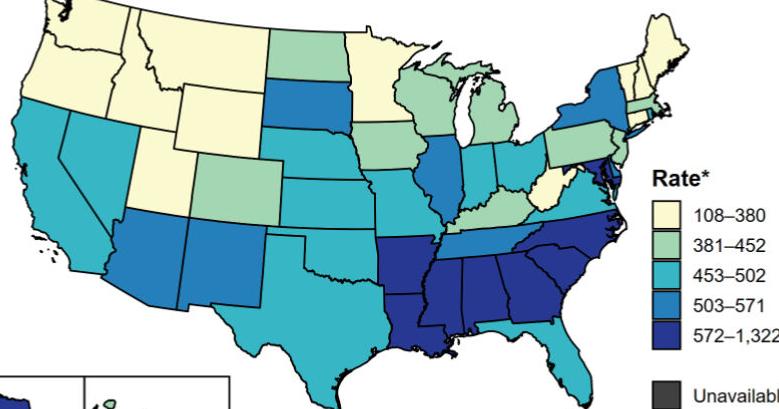
A study published in Science found that fears of a rebound in infectious diseases after COVID-19 lockdowns were largely unfounded, with airborne diseases like influenza slightly increasing but not offsetting the overall decline during the pandemic, and sexually transmitted infections remaining low post-pandemic, highlighting the complex effects of public health measures.