Space Baby Era Emerges as Private Spaceflight Tests Reproduction
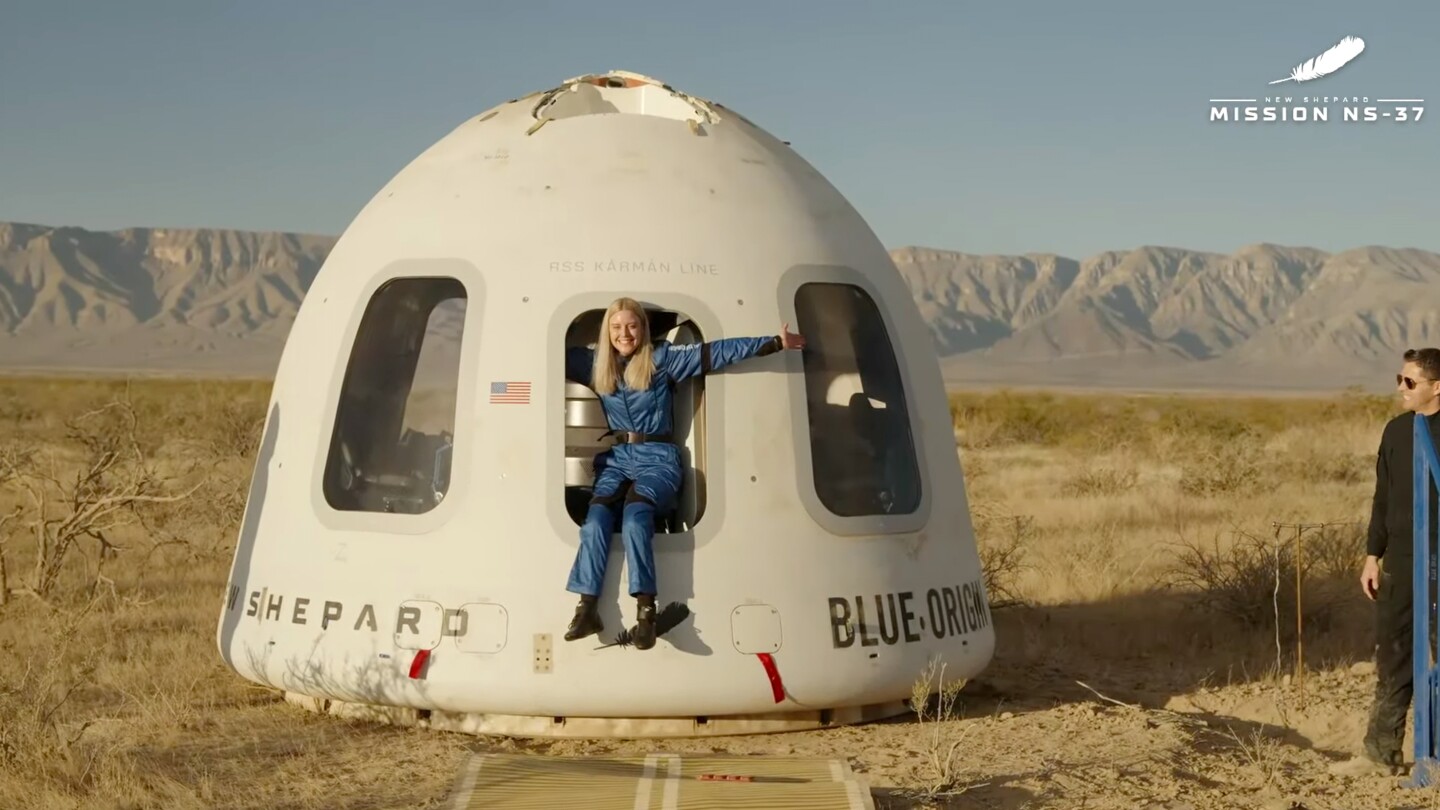
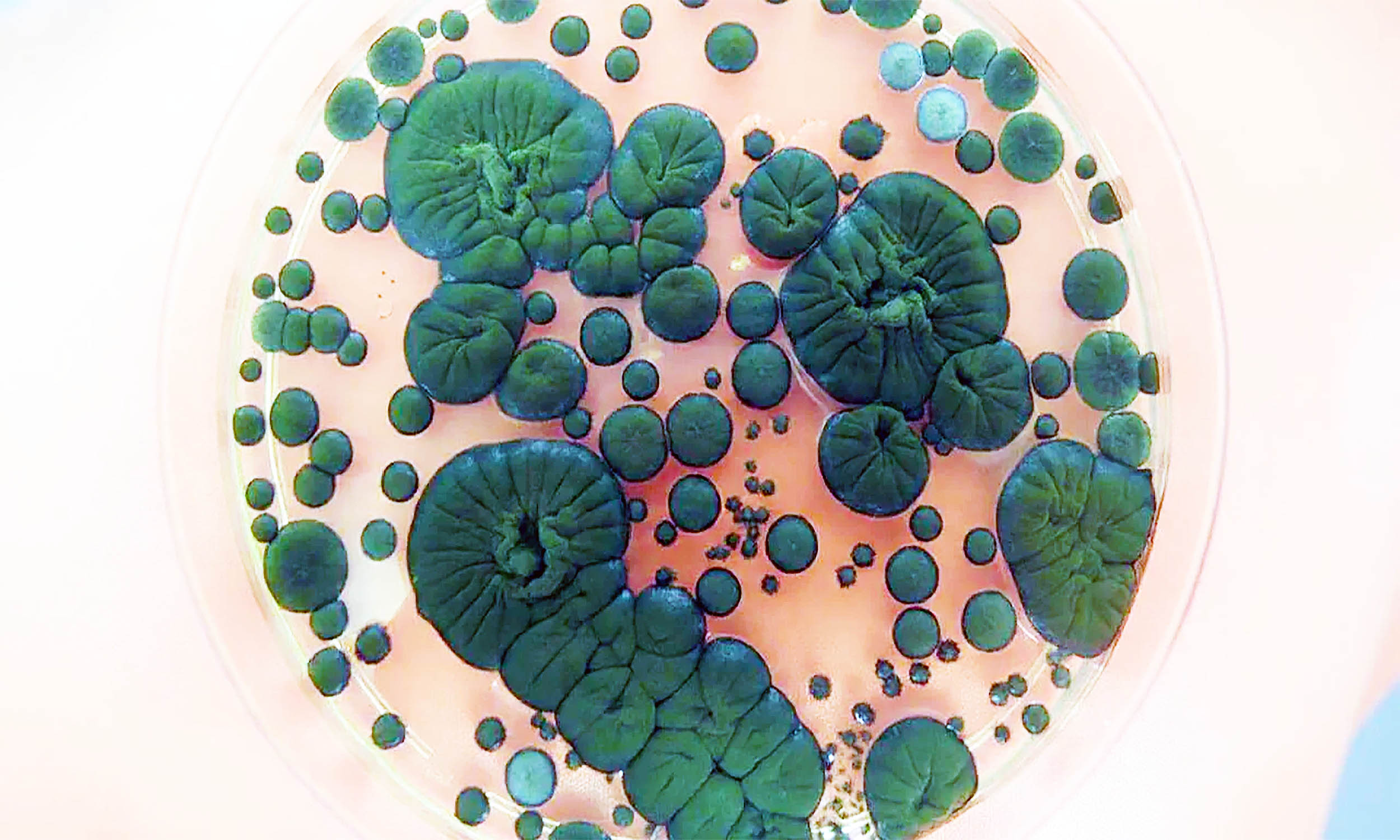
Researchers and startups are exploring space fertility, from microgravity experiments on embryos to plans for private crews on Virgin Galactic’s Delta-class plane, signaling early steps toward space-enabled reproduction and the broader potential of space colonization.