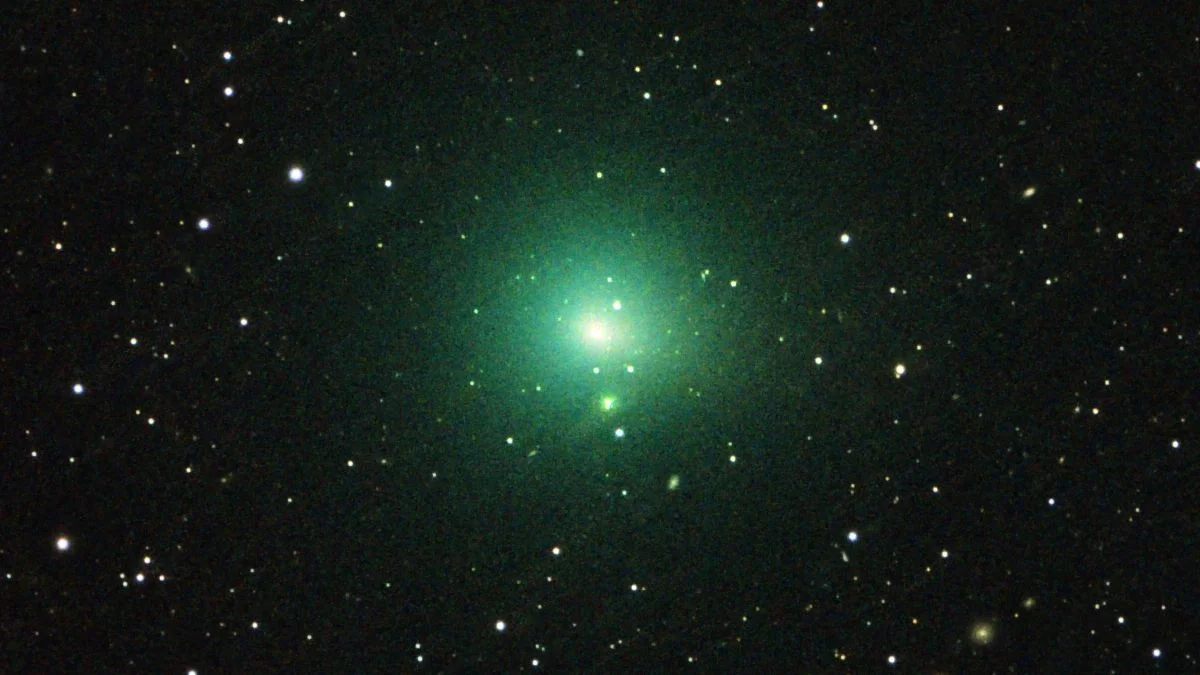
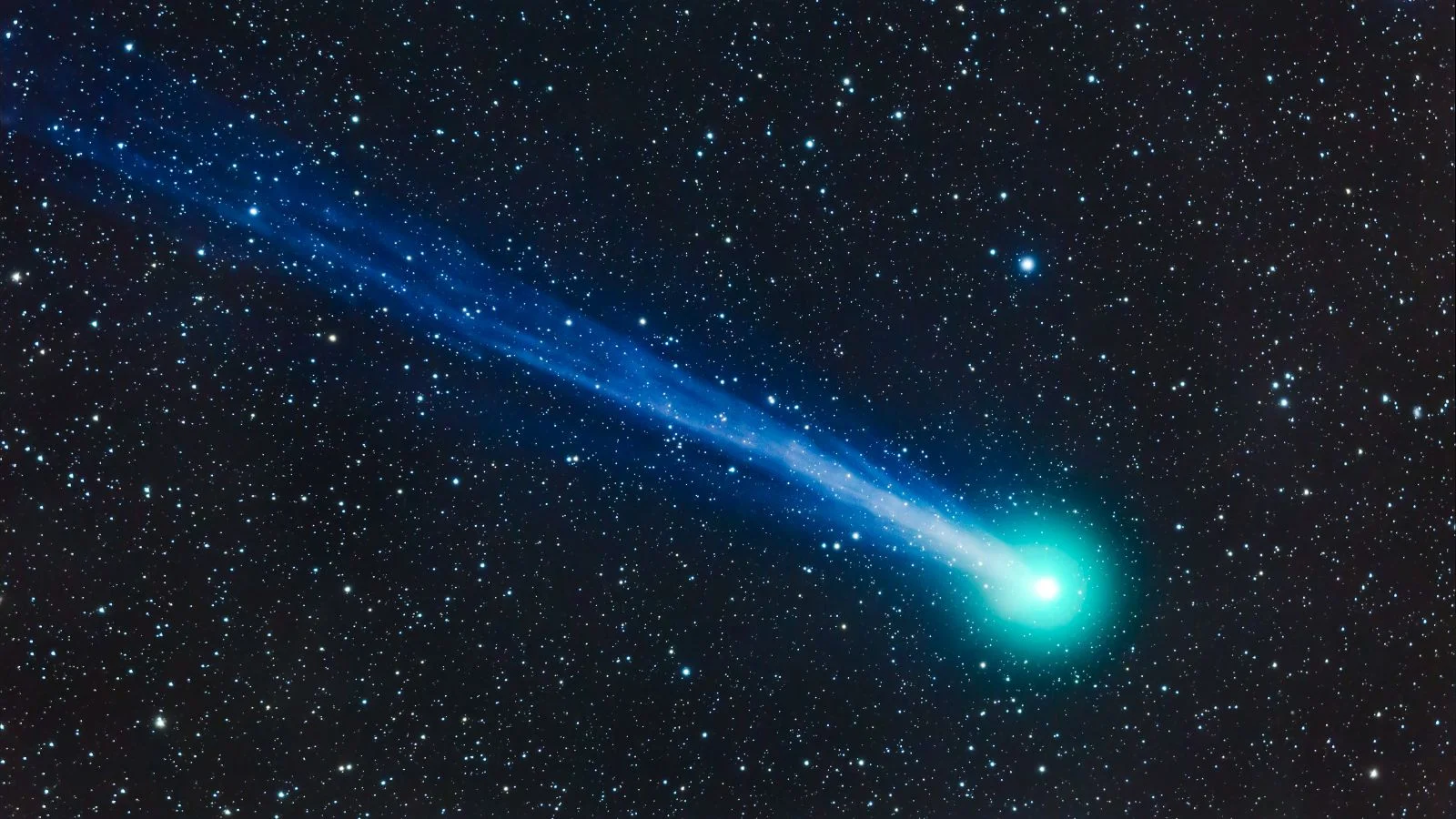
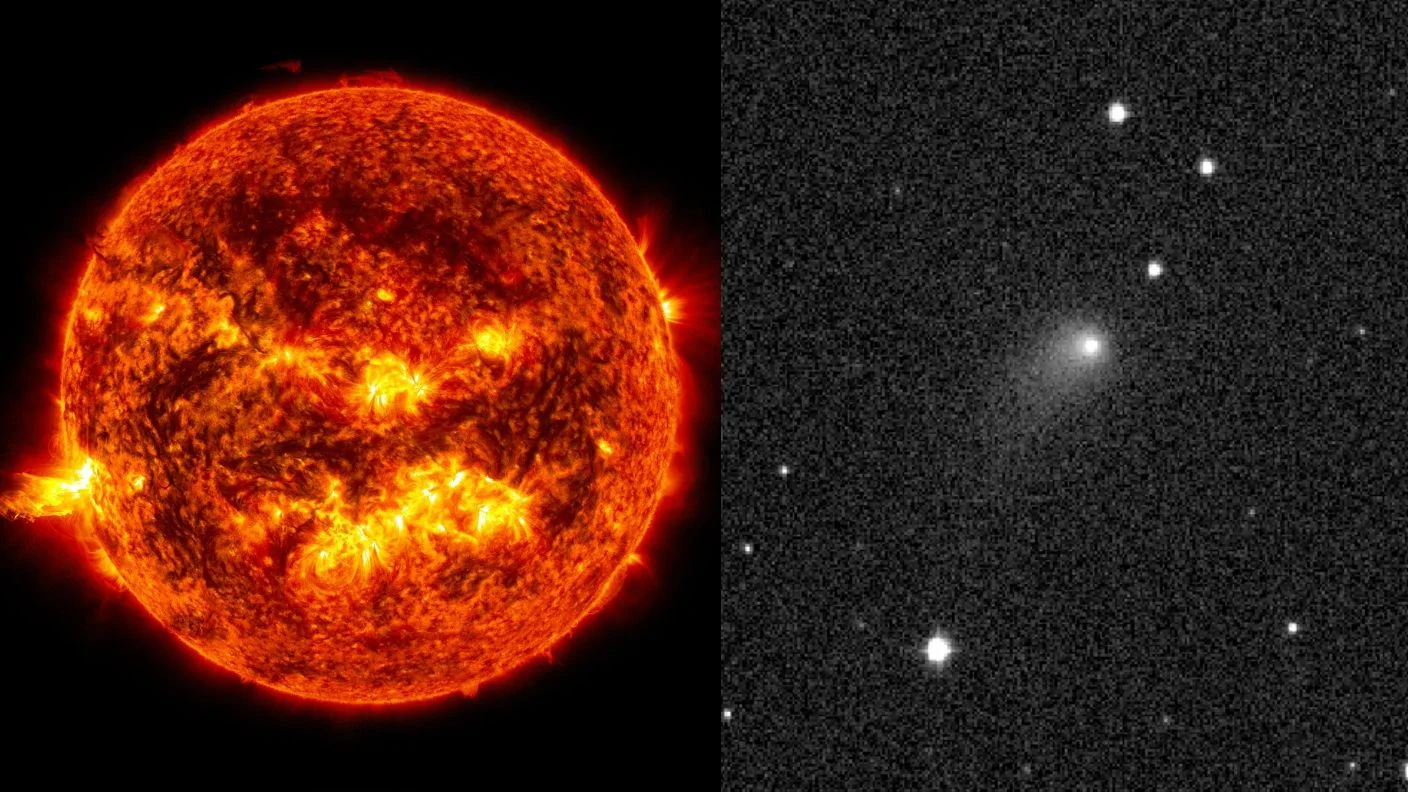
Tiny Comet 41P Flips Its Spin After Near-Sun Pass
Analysis of comet 41P/Tuttle-Giacobini-Kresák from its 2017 close solar approach shows a dramatic spin-down followed by an apparent spin reversal, inferred from light curves and Hubble data. The rapid change, likely driven by torques from outgassed jets on its ~1‑km nucleus, exceeds previous records and could spin the comet apart if it continues; the finding is in an arXiv preprint and not yet peer‑reviewed, with the next spin measurements expected at the 2028 perihelion.