Hidden Brain Drain Path Discovered Along the Dura Near a Key Artery
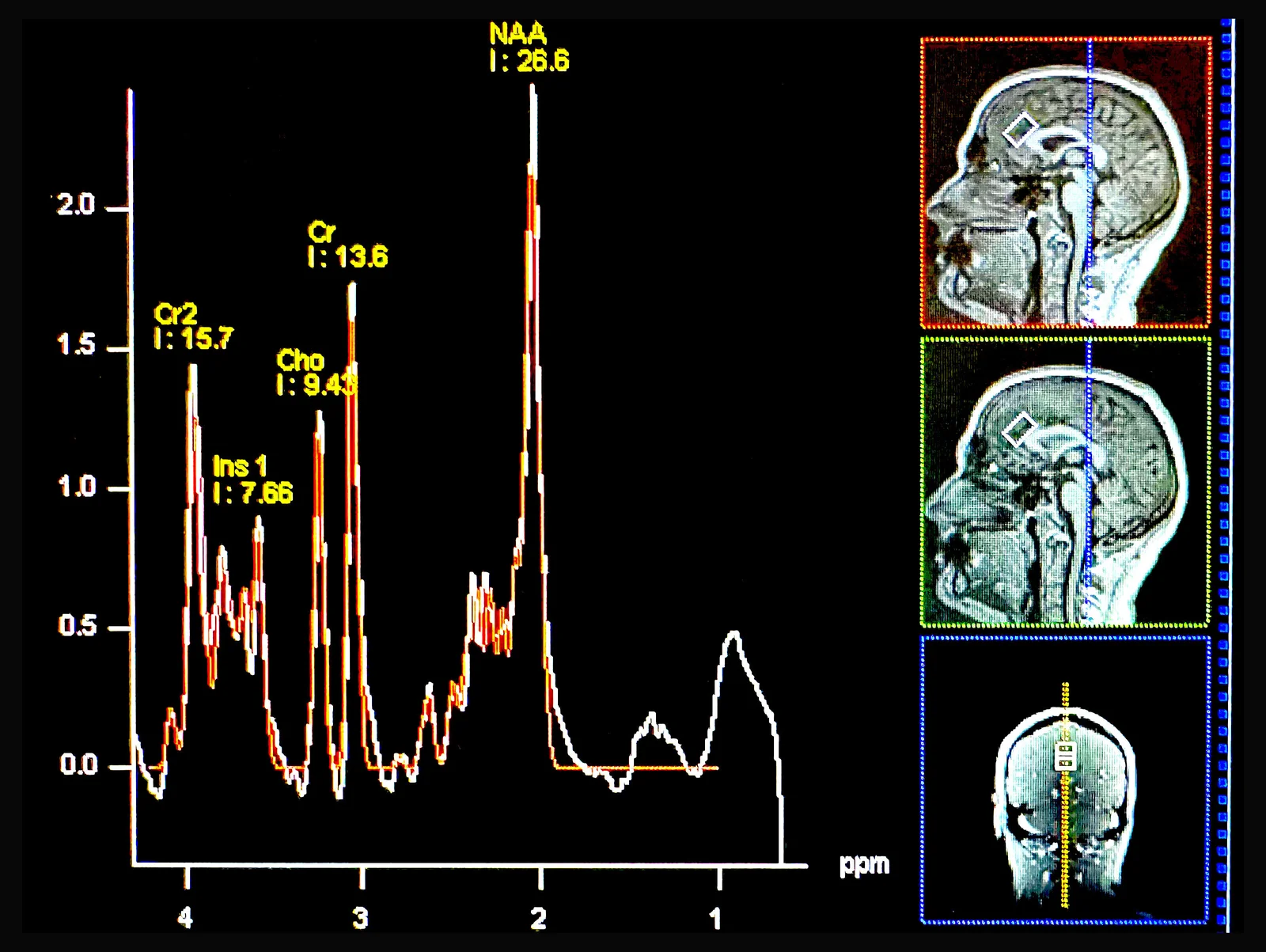
Researchers identified a slow, lymphatic-like drainage channel in the dura surrounding the middle meningeal artery in healthy adults, using dynamic MRI and postmortem tissue with lymphatic markers PROX1, PDPN, LYVE1. This pathway could help clear cerebrospinal and interstitial fluids, reshaping how we understand brain waste clearance and potentially impacting aging and diseases like Alzheimer’s, while reinforcing the dura as an active immune interface rather than a static barrier.