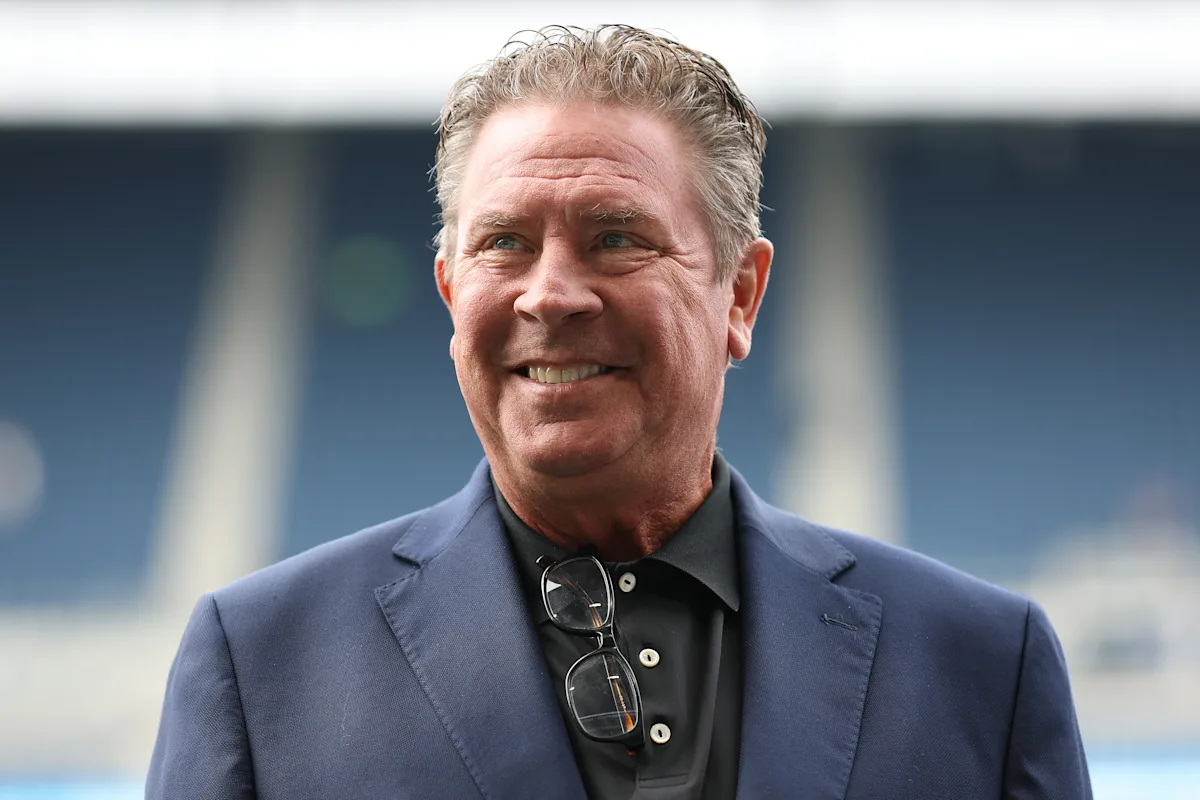
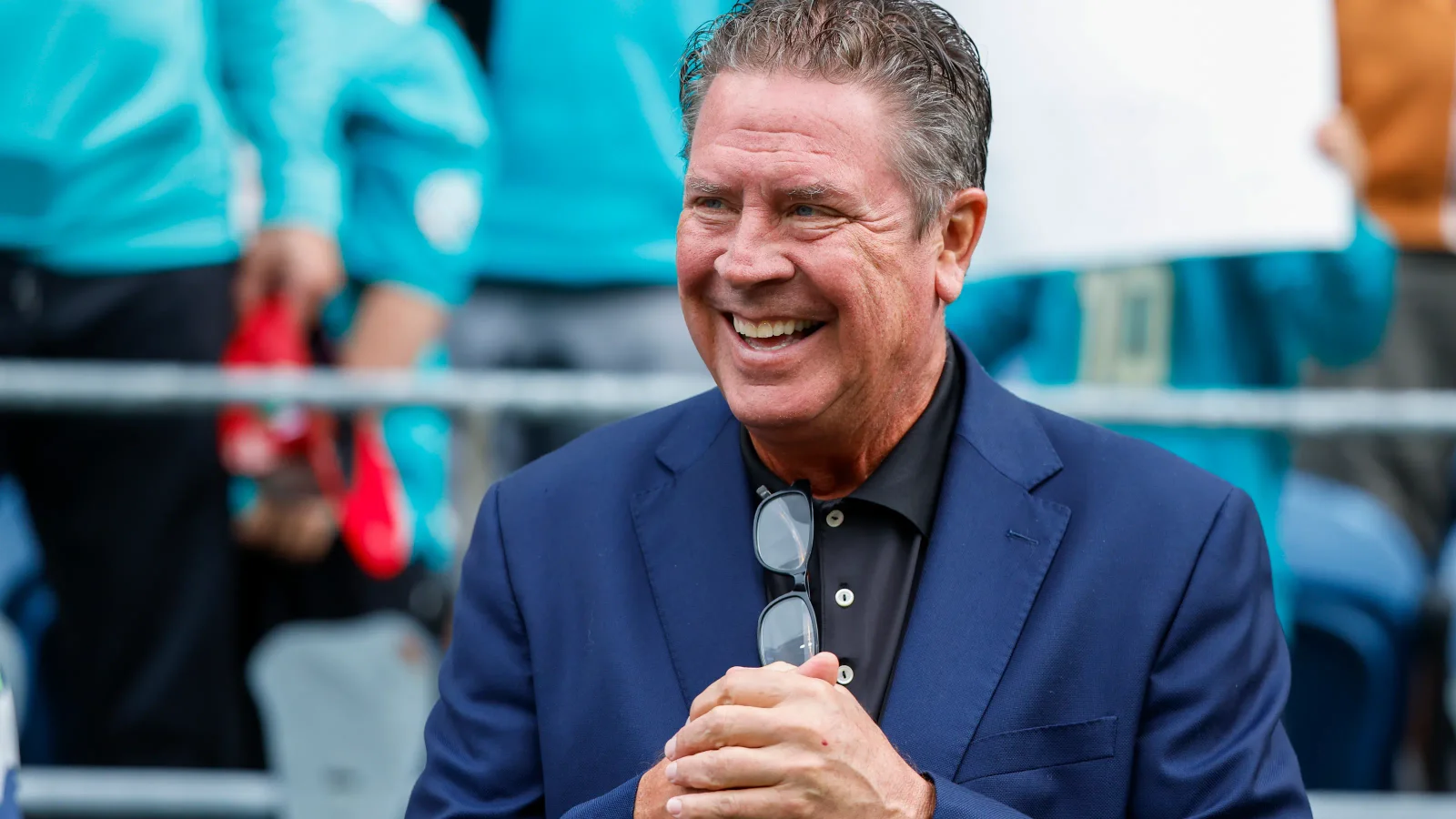
Dan Marino Opens Up About Liver Disease Diagnosis and His Health Journey
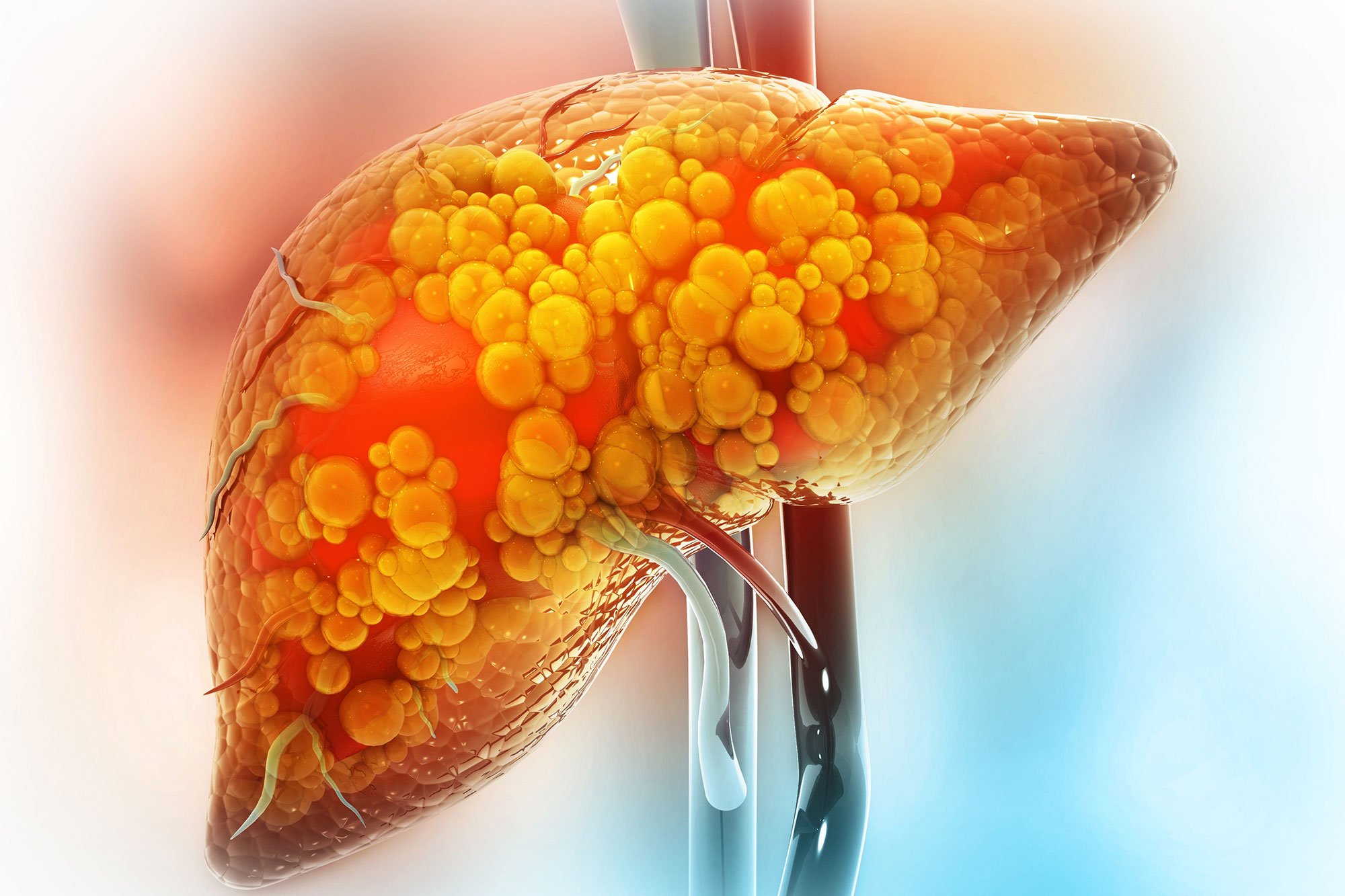
NFL legend Dan Marino was diagnosed with fatty liver disease (MASH) in 2007, which he attributes to lifestyle changes after retirement. He is now sharing his story to raise awareness about the importance of diet and exercise in managing the condition, emphasizing support from loved ones and the potential for reversal through healthy habits.