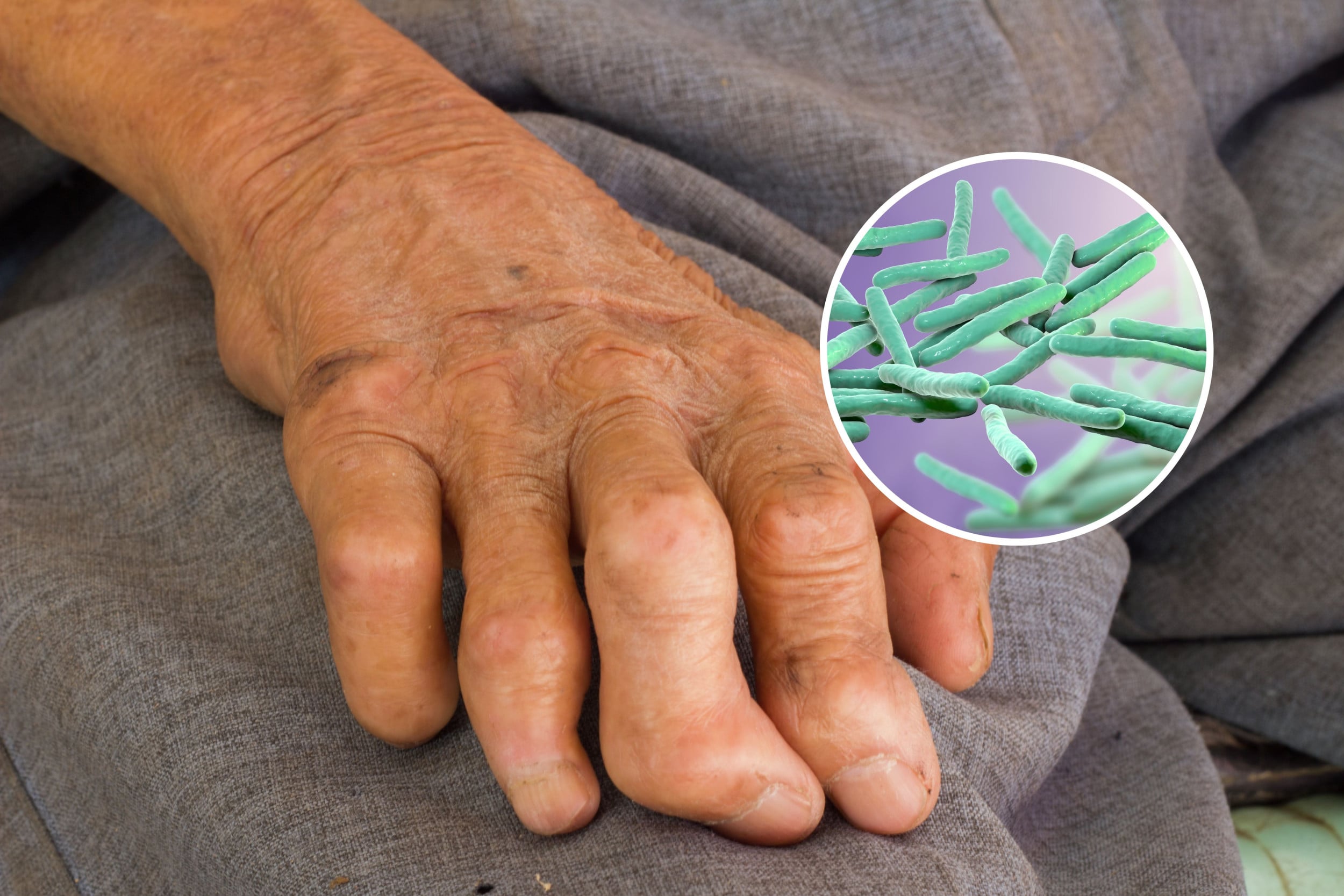
Global push to end leprosy gains momentum ahead of World Leprosy Day
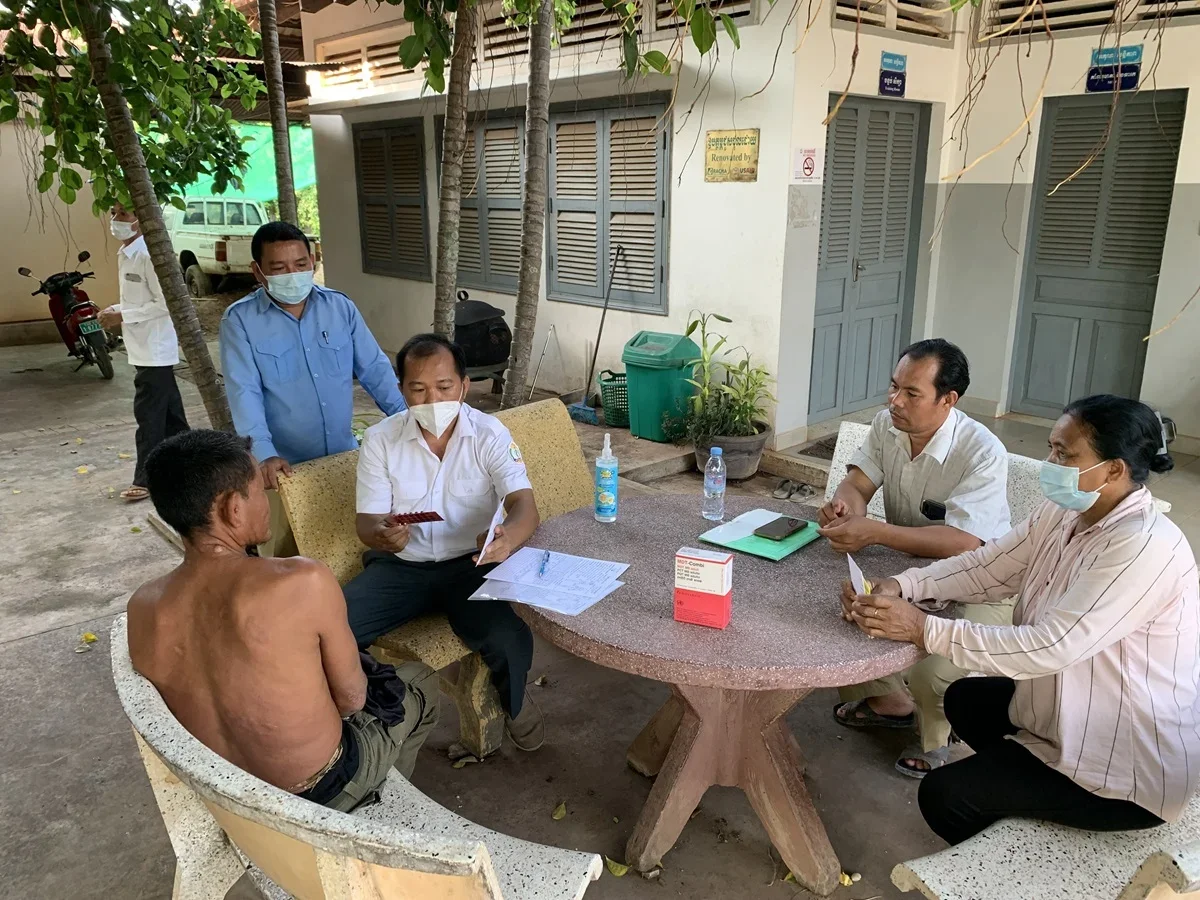
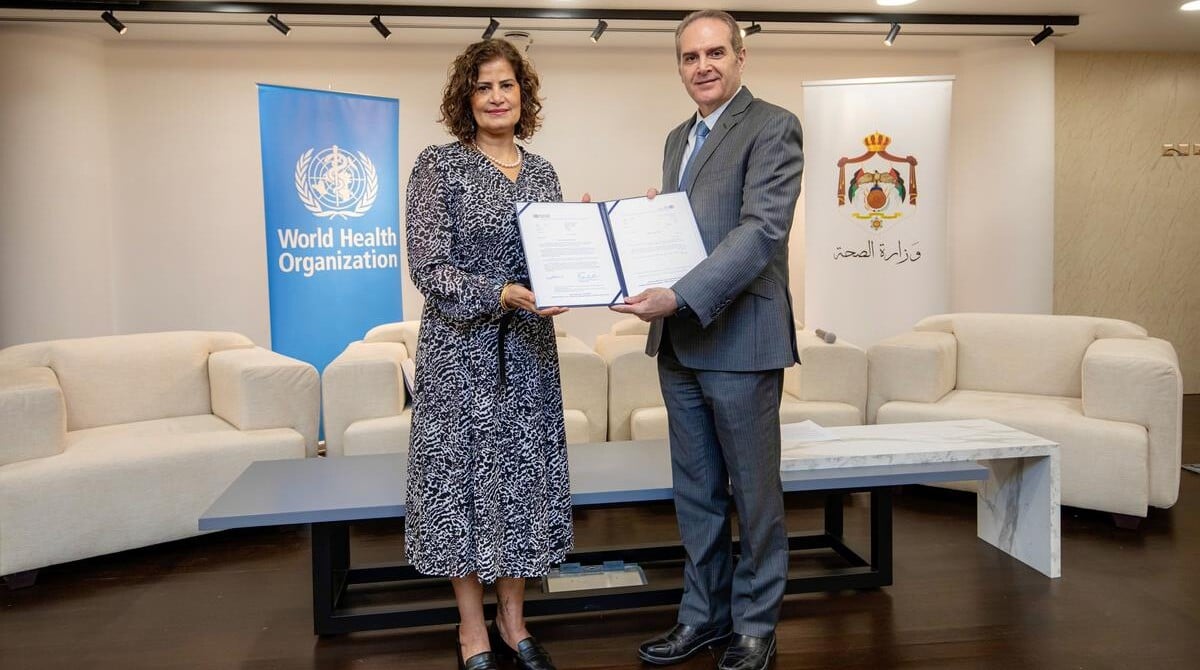
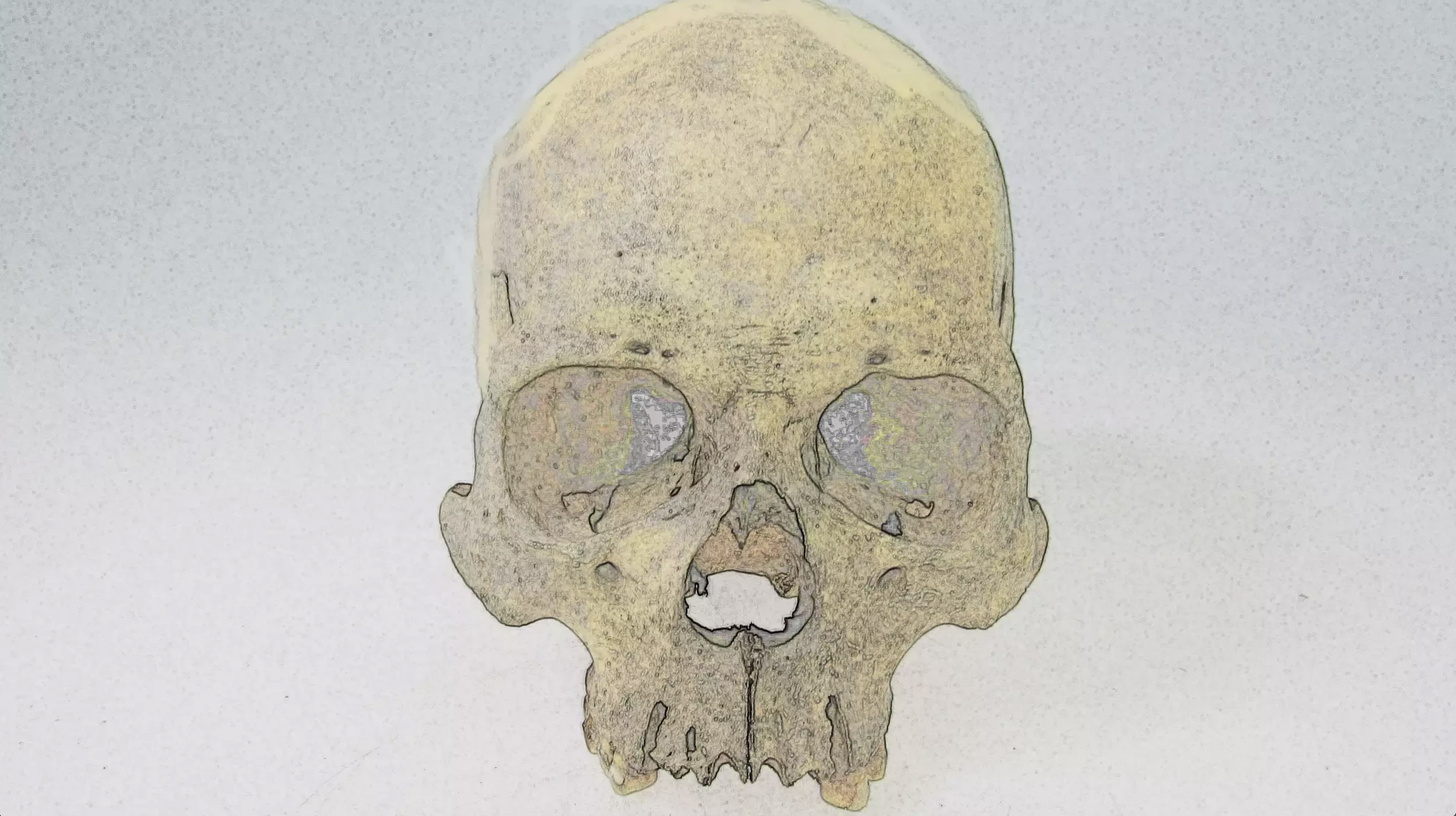
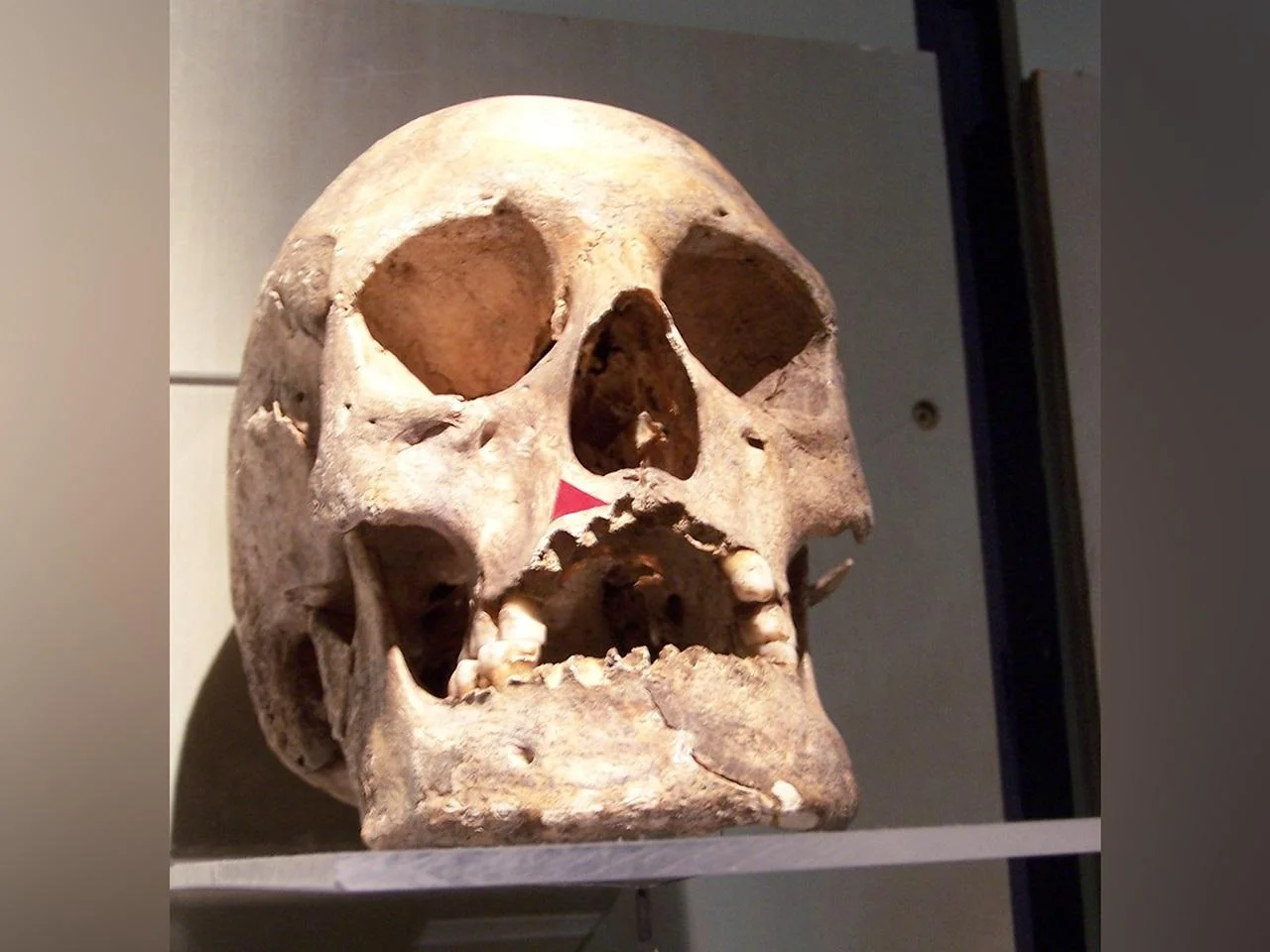
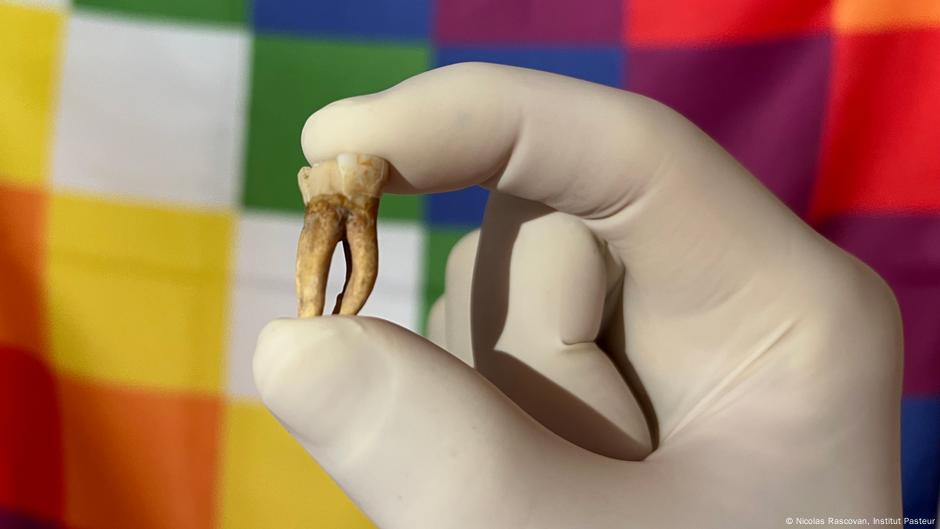
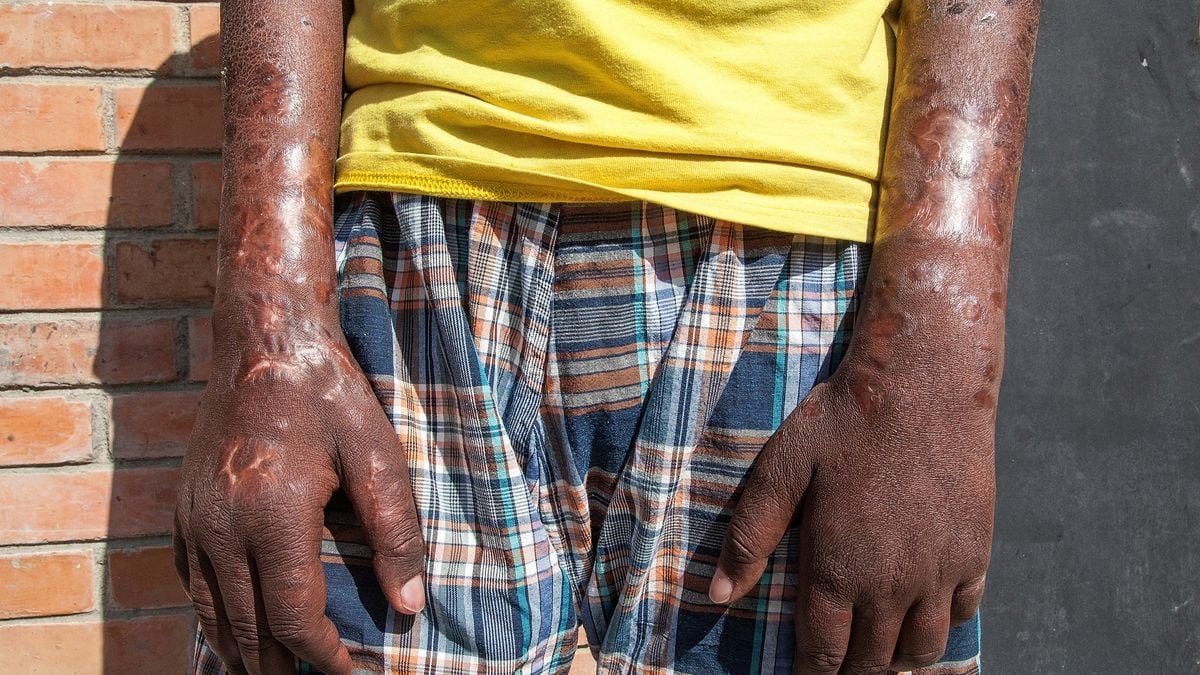
WHO renews its commitment to a leprosy-free world ahead of World Leprosy Day, highlighting free multidrug therapy and post-exposure prophylaxis, a 25-year partnership with novartis, and ongoing anti-stigma efforts, while noting 172,717 new cases in 2024 across 188 reporting areas.