Research Warns Against Extreme Temperatures for Kidney Disease Patients
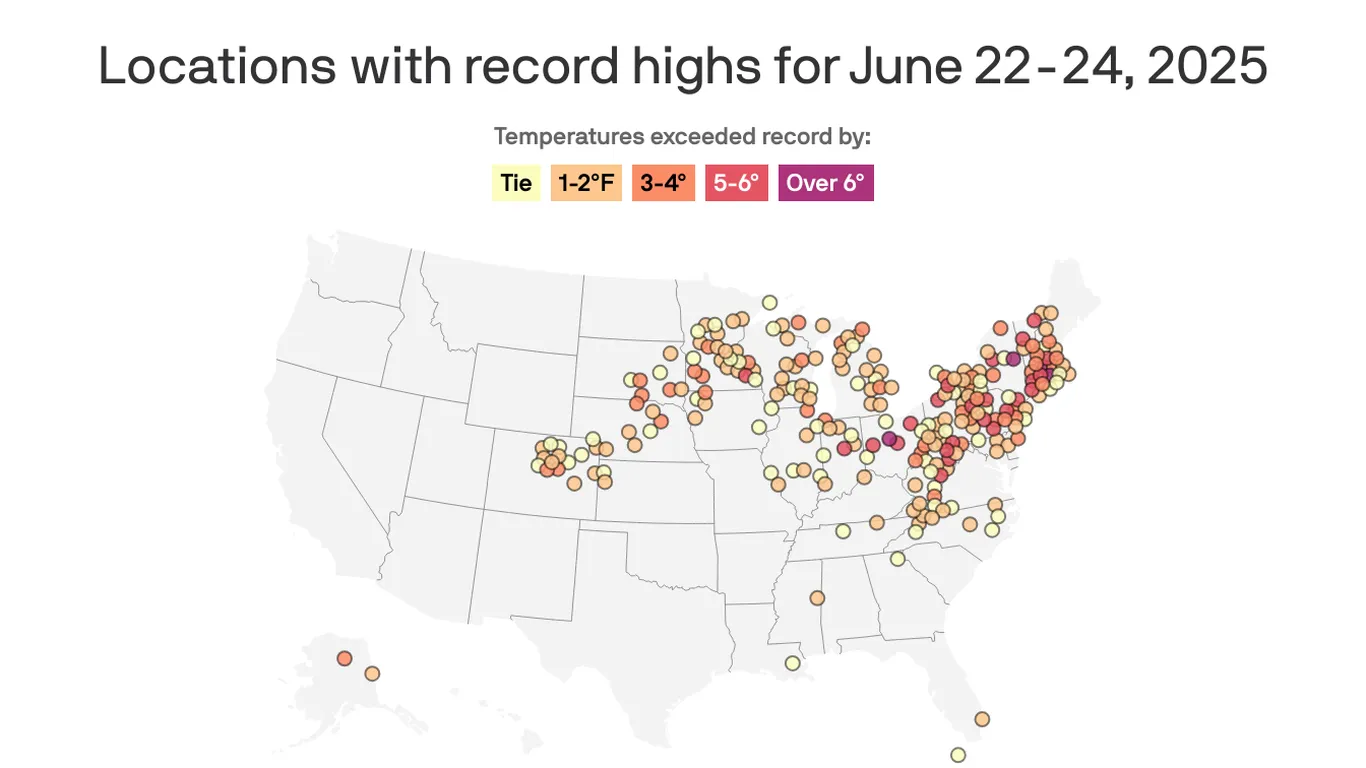
Research shows that climate change-induced extreme heat and cold contribute to the rise in chronic kidney disease (CKD) globally, with dehydration from temperature extremes damaging kidneys. CKD affects over 788 million people worldwide, with key risk factors including high salt diets, high blood pressure, obesity, and non-optimal temperatures. Greater prevention, screening, and accessible treatments are needed to address this growing health issue.