Effective Diet Strategies for Managing Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity
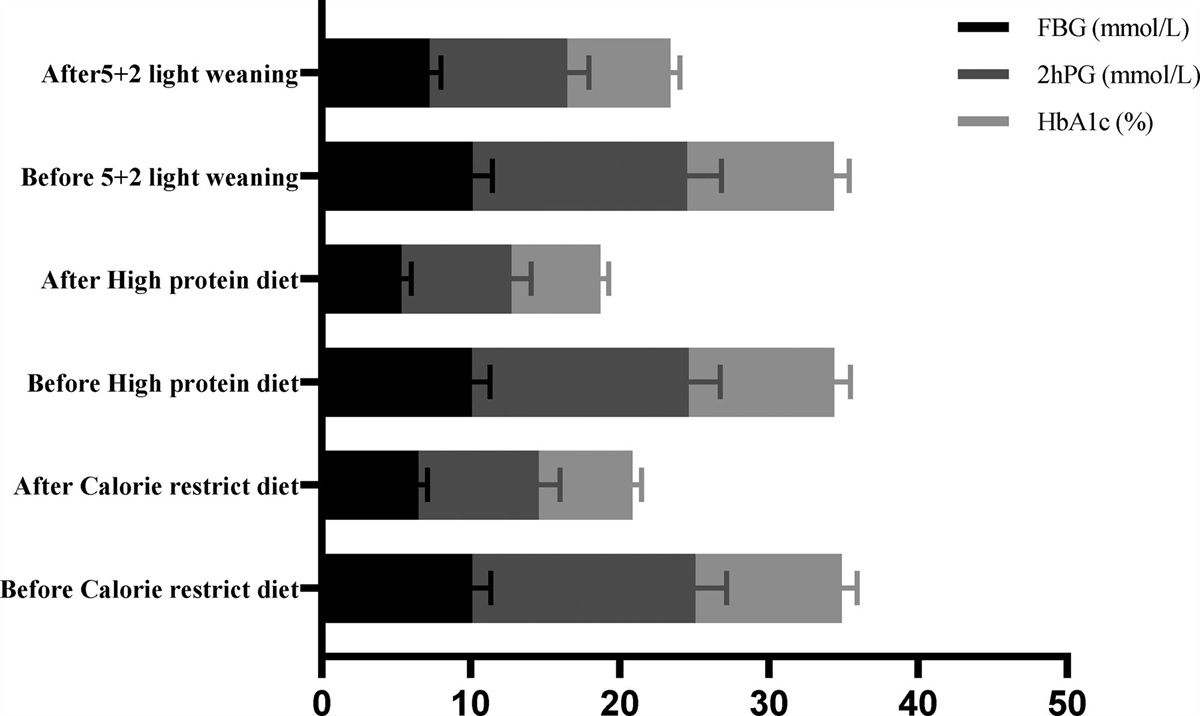
A study presented at ENDO 2025 found that intermittent energy restriction (fasting twice a week) may be more effective in managing type 2 diabetes and obesity compared to time-restricted or continuous calorie restriction, showing benefits in blood glucose, insulin sensitivity, and adherence.