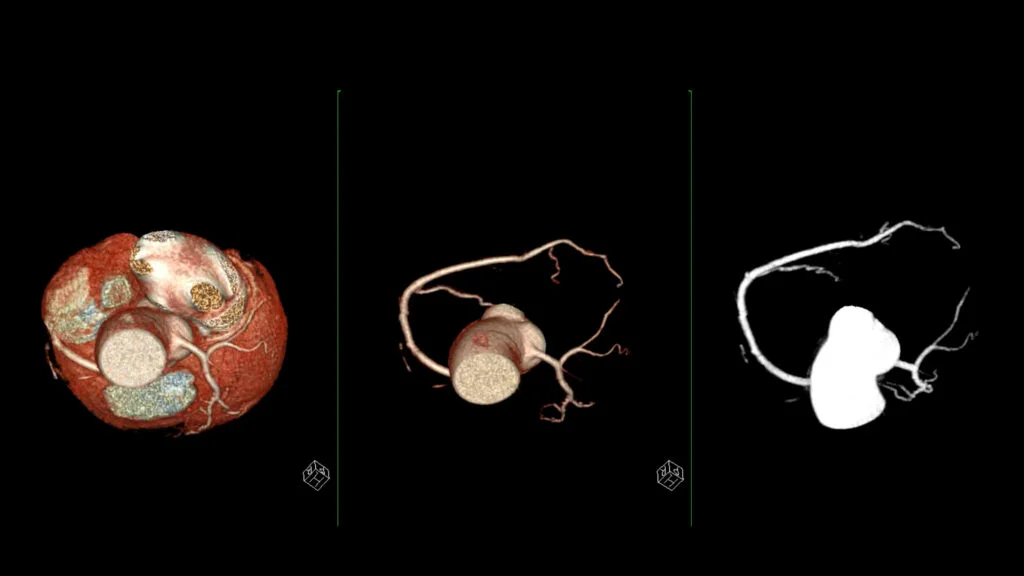
Women’s heart risk rises at lower plaque levels, study shows
A Circulation study of ~4,200 adults undergoing coronary CT angiography finds that women have lower total plaque but a higher risk at lower plaque burdens than men, with risk beginning around 20% plaque in women versus 28% in men and rising more steeply as plaque increases. The findings highlight non-obstructive disease and the need for sex-specific risk assessment and broader use of quantitative plaque analysis for early, personalized prevention in women.