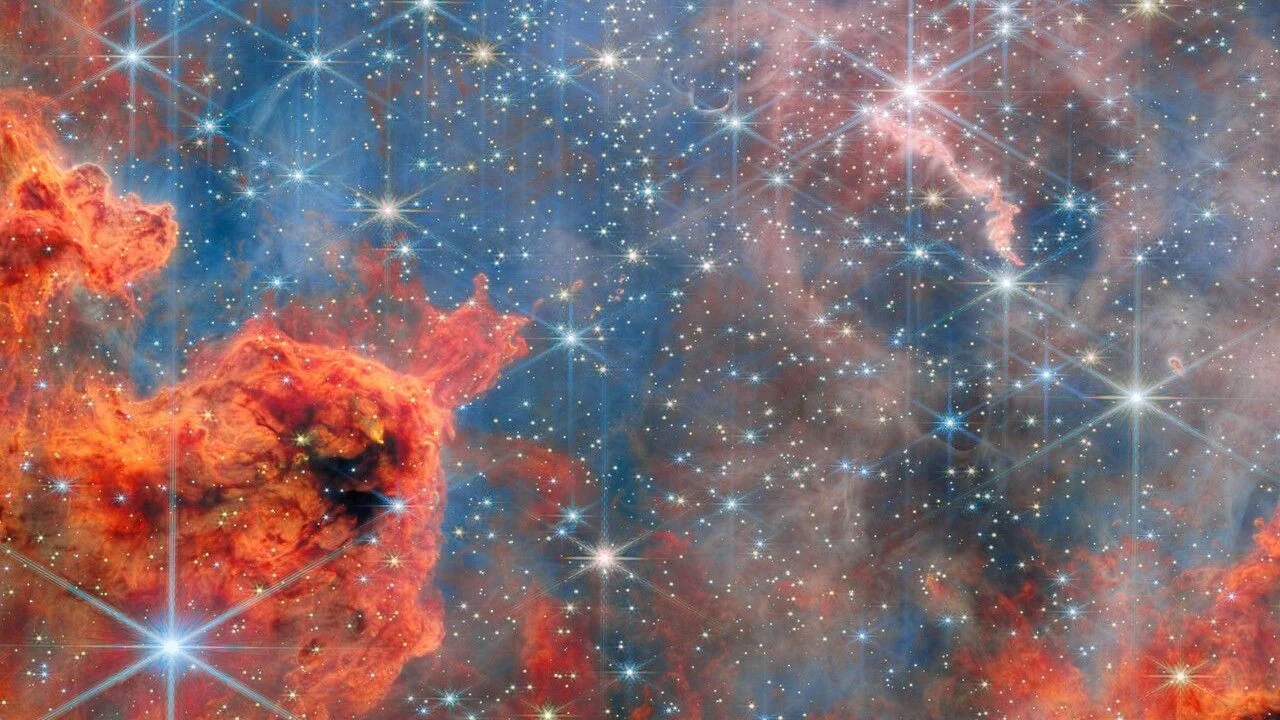
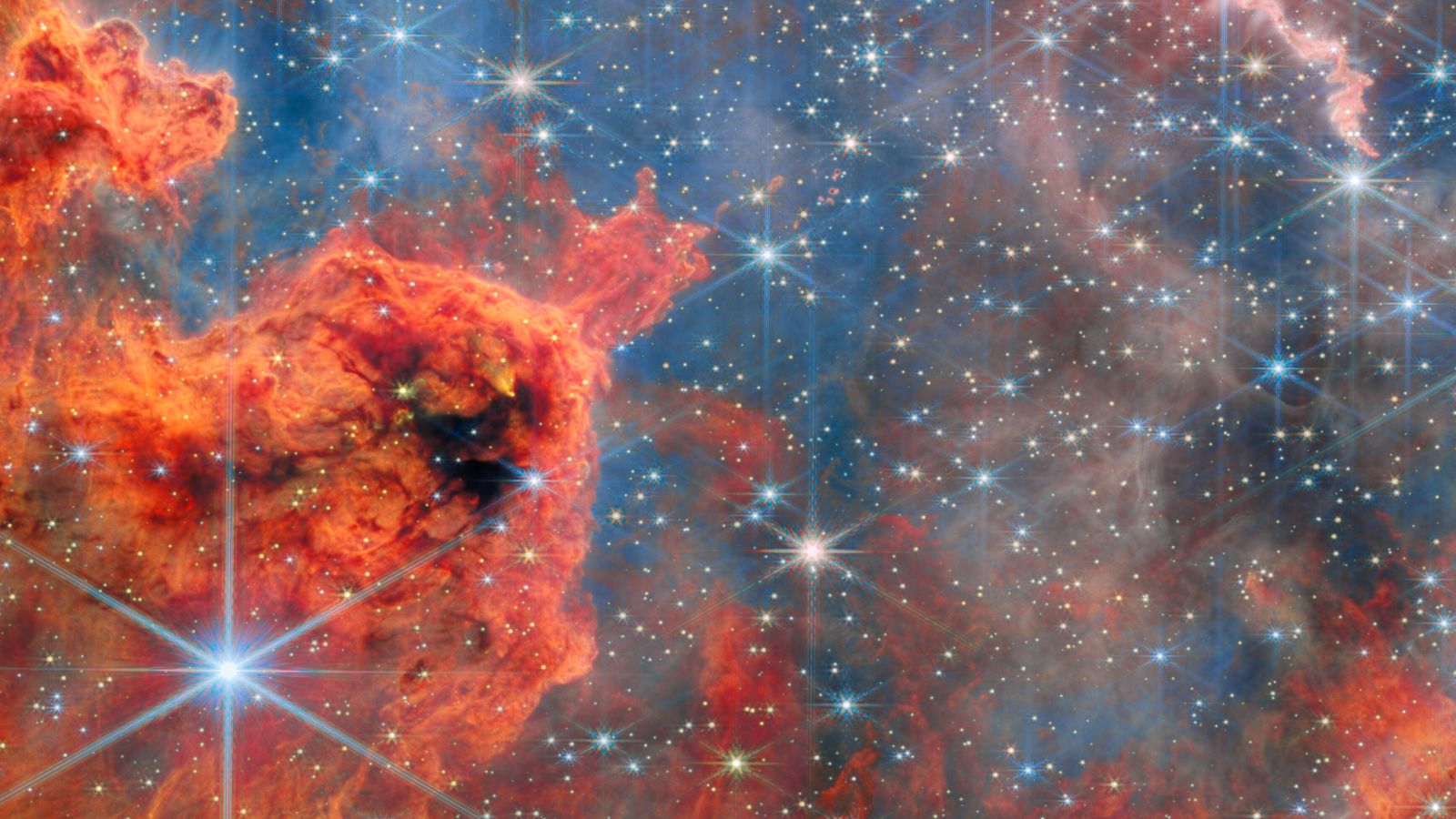
JWST reveals brown dwarfs in Westerlund 2: a stellar nursery’s hidden population
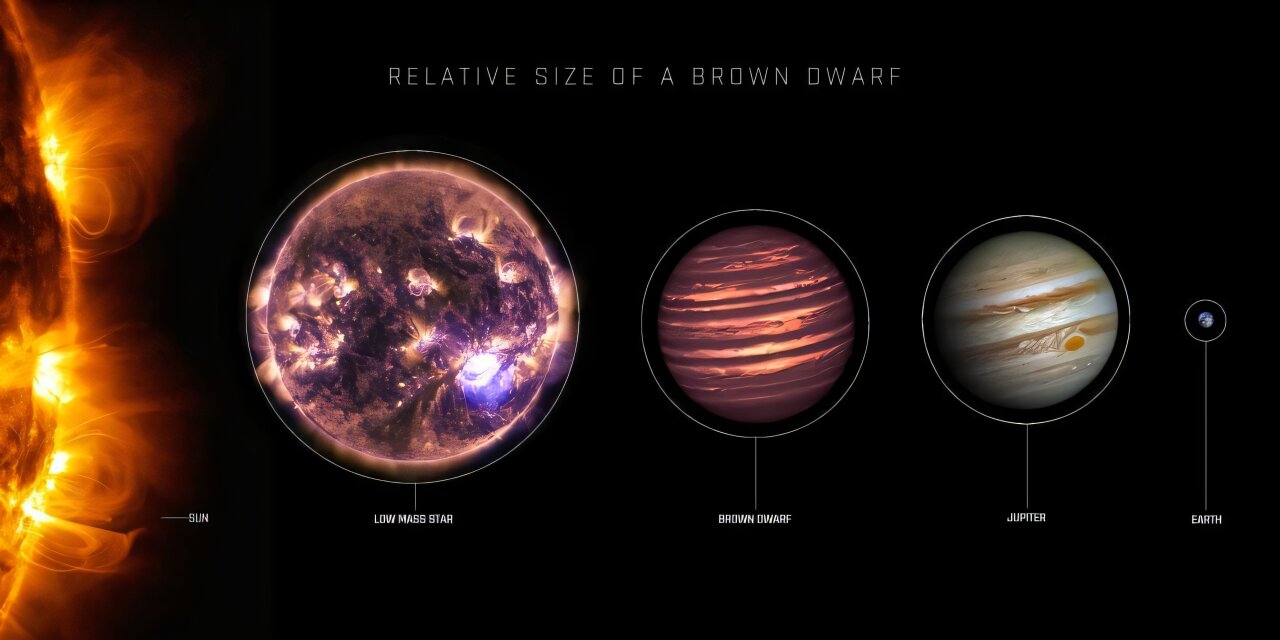
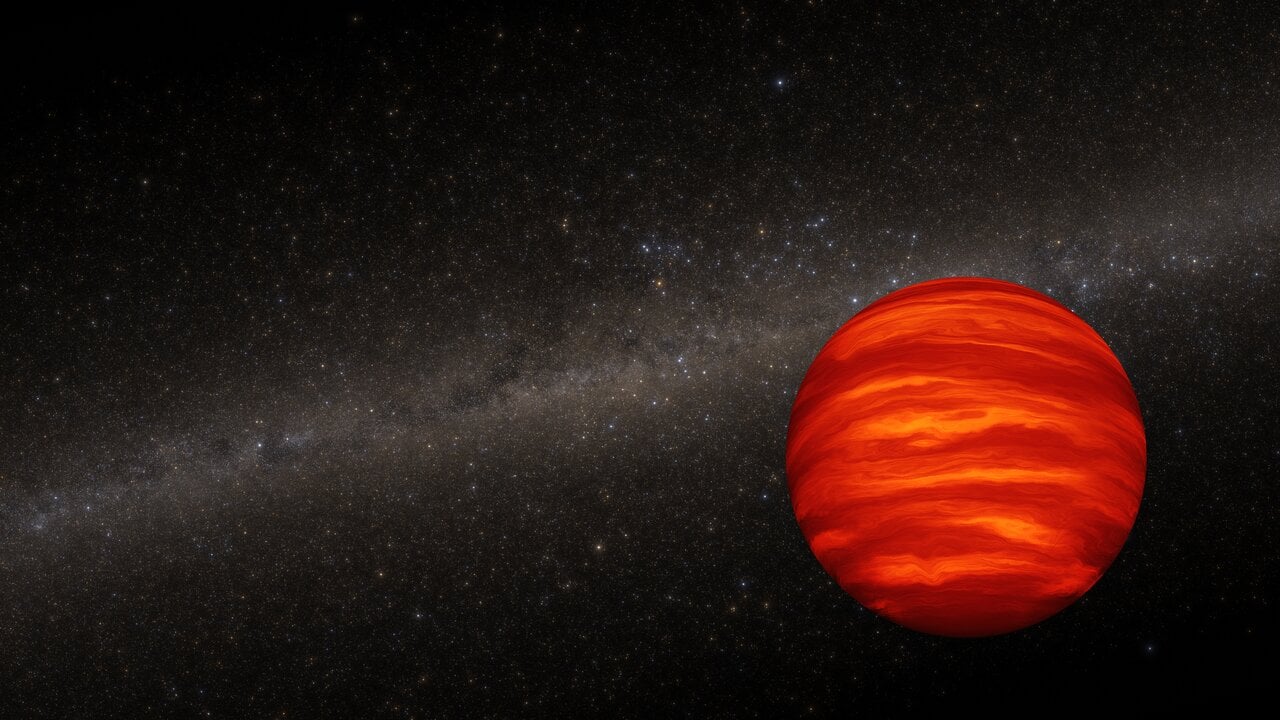
JWST’s infrared portrait of Westerlund 2, a young, massive star cluster about 20,000 light-years away in Gum 29, shows thousands of stars and brown dwarfs—“failed stars” too light to fuse—identified via methane and PAH emission. The discovery sheds light on ongoing star formation and how planet-forming disks around massive stars evolve, offering a new window into the life cycles of stars in our galaxy.