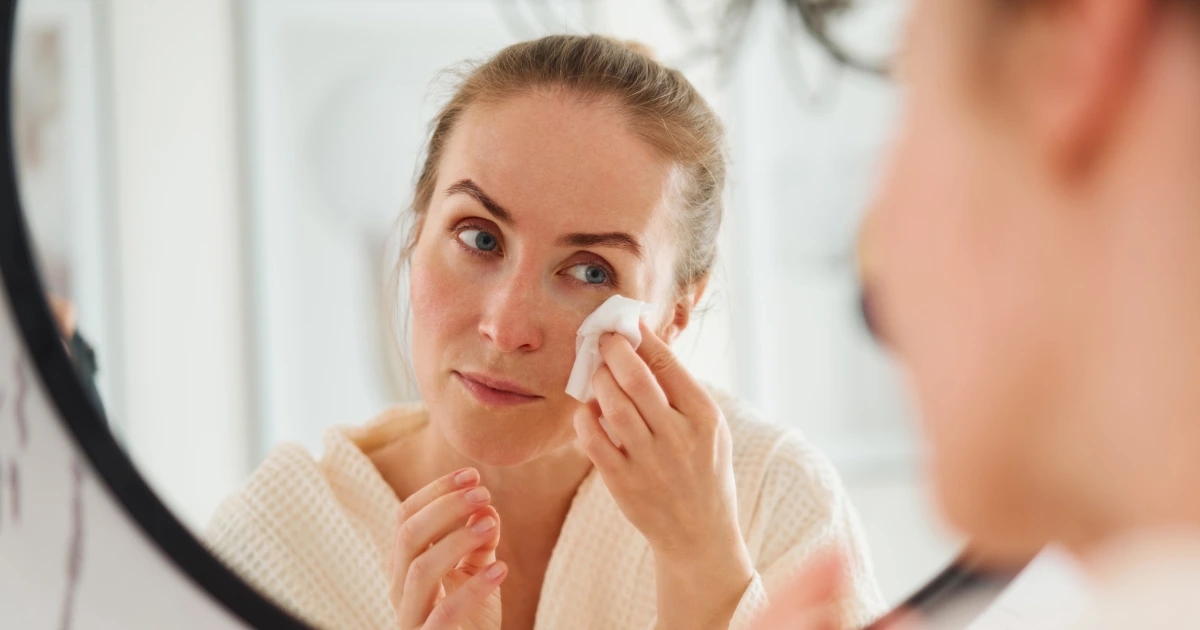
Neutrogena Recalls Over 15,000 Makeup Wipes Due to Bacterial Contamination
Neutrogena has recalled its Makeup Remover Ultra-Soft Cleansing Towelettes due to bacterial contamination with P. gergoviae, which can cause severe infections in vulnerable individuals. The recall affects products sold in several states and was classified as a Class II risk by the FDA, indicating potential for temporary health effects. The company stated the recall was out of caution and no other products are affected.