Four Months in Isolation: Cameroon’s TB Ward Highlights Outdated Care
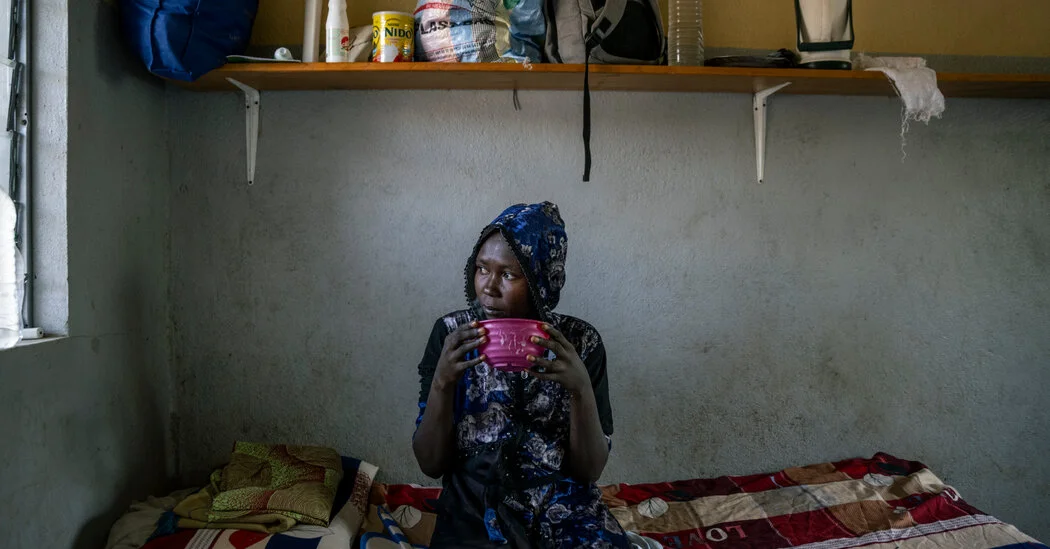
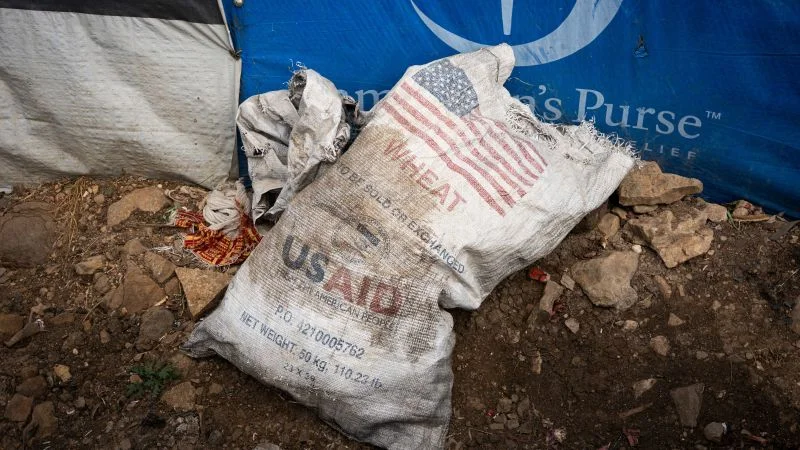
In northern Cameroon, patients with drug-resistant TB are kept in an isolation ward for months under a policy deemed obsolete in wealthier nations, reflecting resource gaps that prevent updating practice and separating families from care.