Unveiling the Age of Enigmatic Stars in the Milky Way's Core
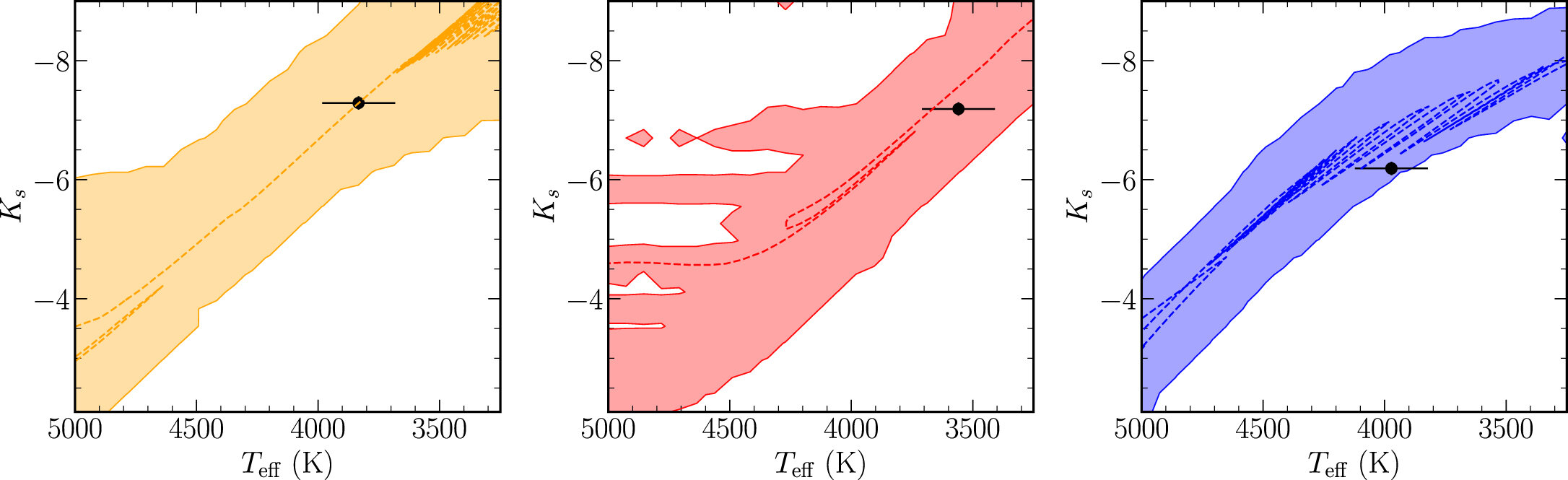
Astronomers from Lund University have used high-resolution data from the Keck II telescope in Hawaii to determine the age of three stars located in the nuclear star cluster at the heart of the Milky Way. The stars were found to be unusually young, with ages ranging from 100 million to 1 billion years. This discovery challenges the previous belief that the nuclear star cluster is an ancient part of the galaxy and suggests that active star formation is occurring in this region. The researchers also observed significant variations in the iron levels of the stars, indicating an inhomogeneous inner region of the galaxy and providing insights into the early universe.