Radiologists trump AI in detecting lung diseases on chest X-rays
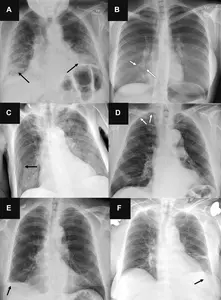
Radiologists outperformed commercially available AI tools in accurately identifying the presence and absence of three common lung diseases on chest X-rays, according to a study published in Radiology. While AI tools showed moderate to high sensitivity rates, they produced more false-positive results than radiologists, especially when multiple findings were present or for smaller targets. The study highlights the need for further testing of AI tools in real-life clinical scenarios and emphasizes the importance of radiologists' expertise in interpreting complex chest X-rays. AI systems could serve as a valuable second opinion for radiologists but should not be autonomous in making diagnoses.