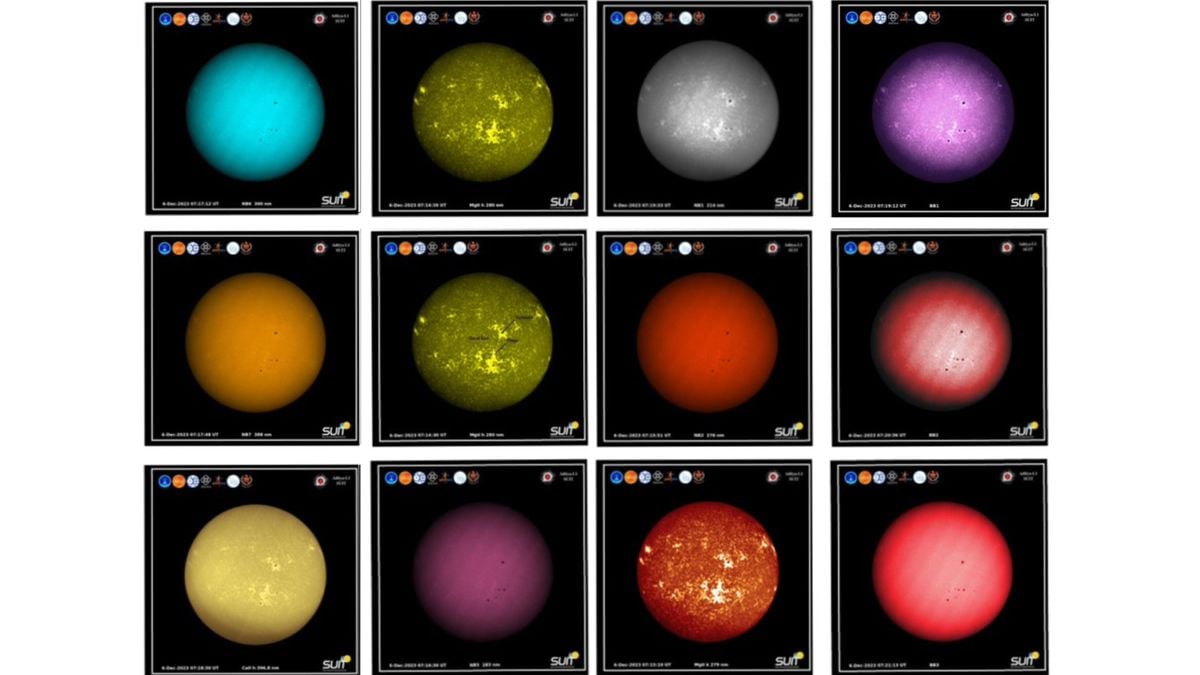
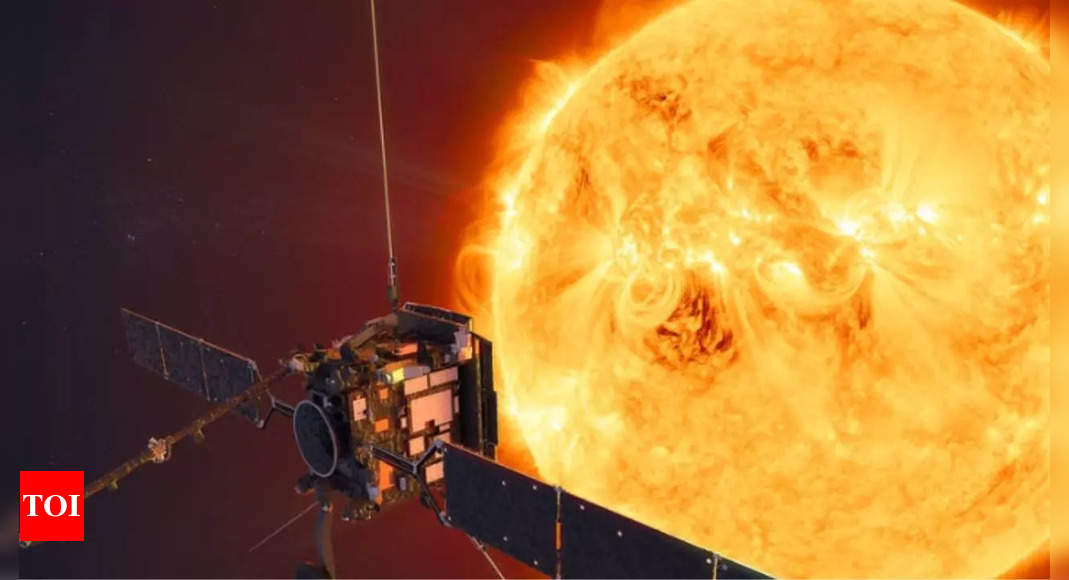
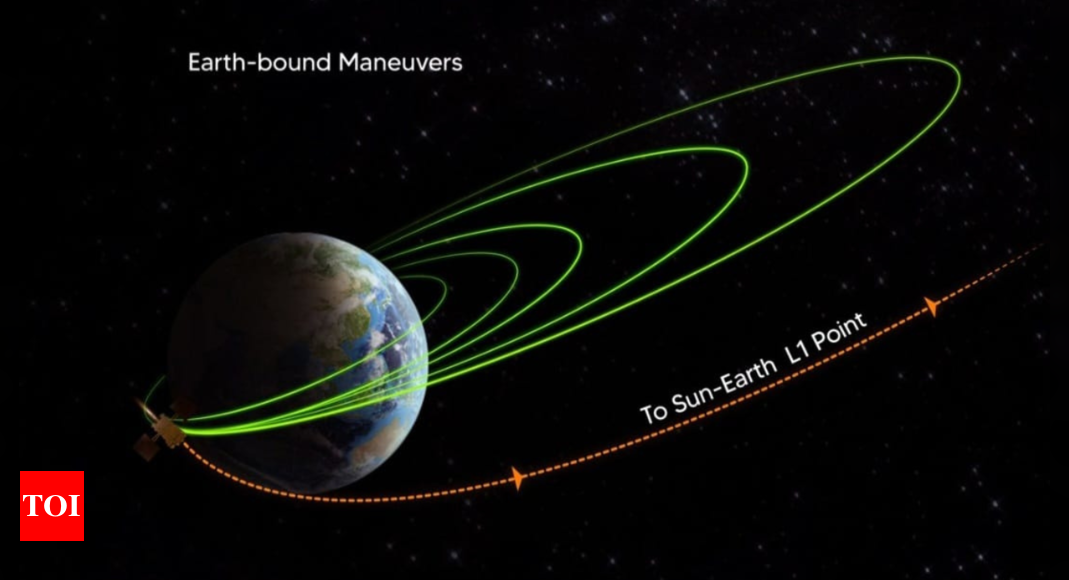
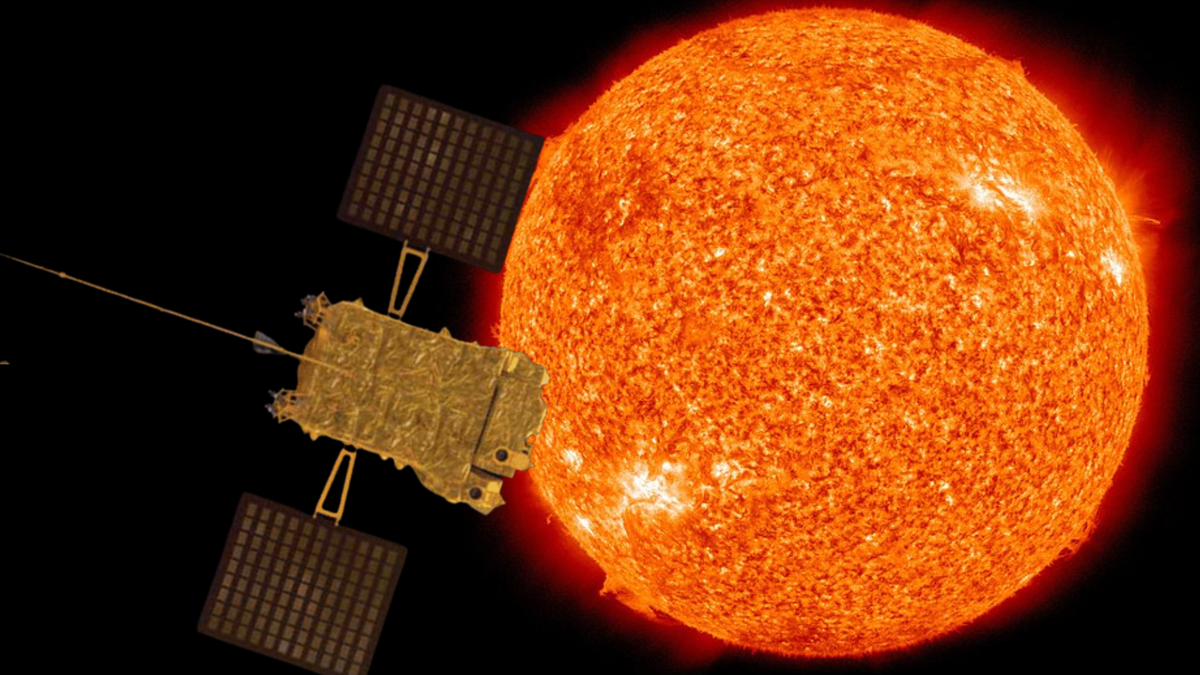
India’s Aditya-L1 to Observe Sun’s Peak Activity in 2026
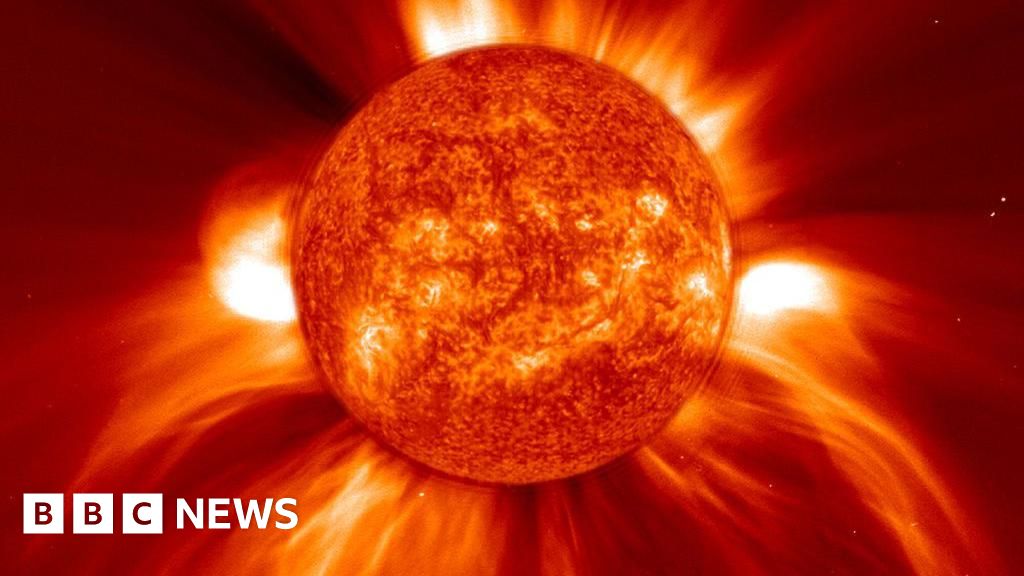
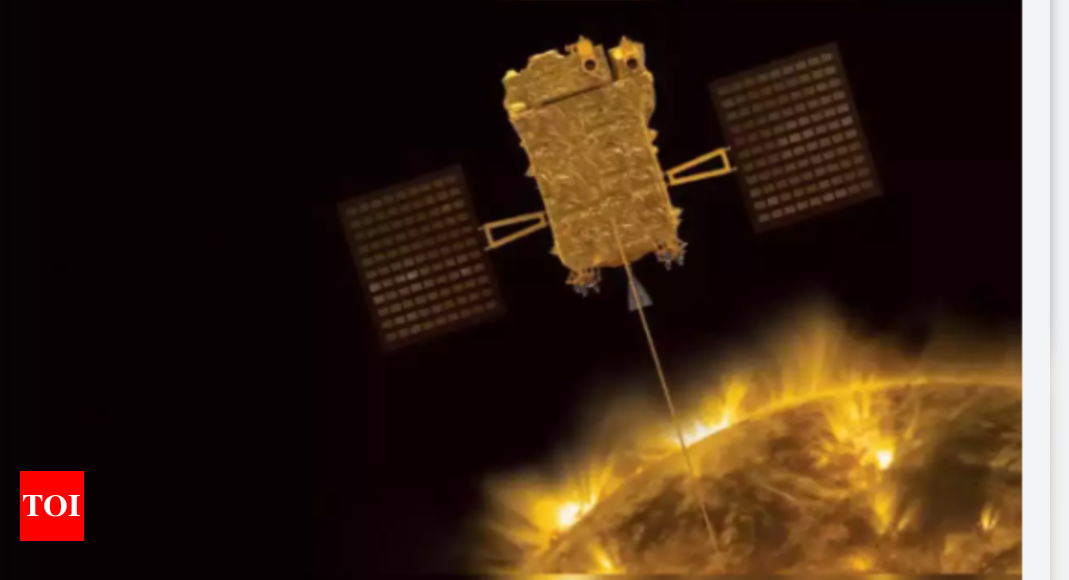
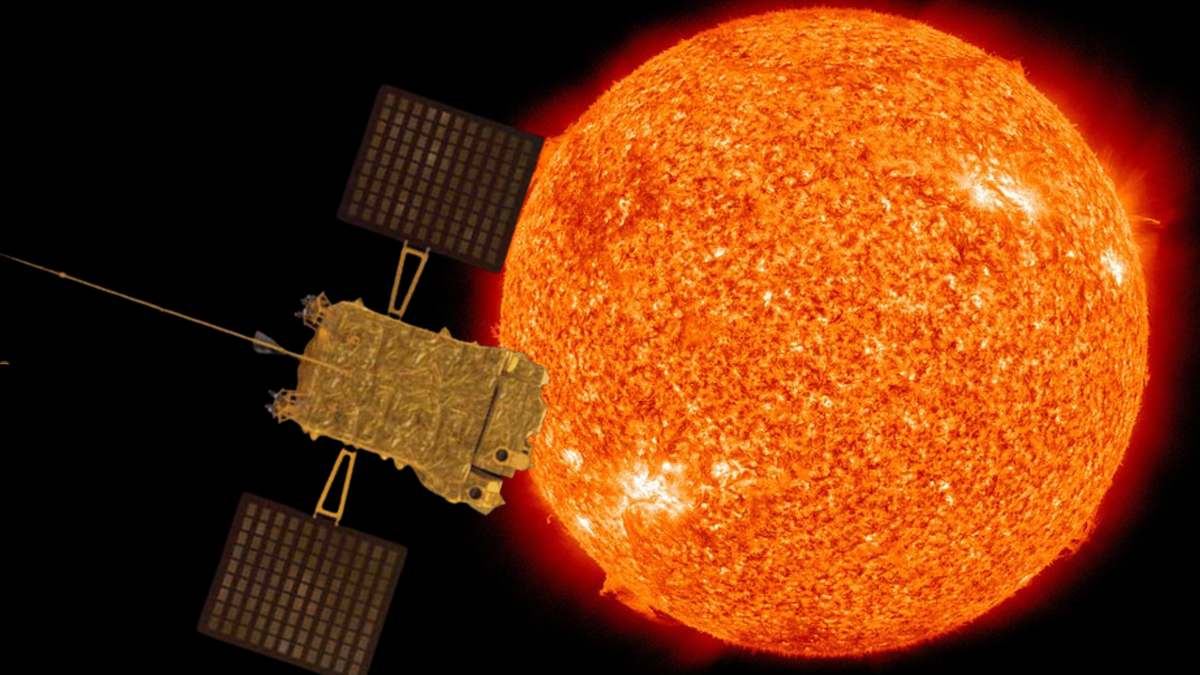
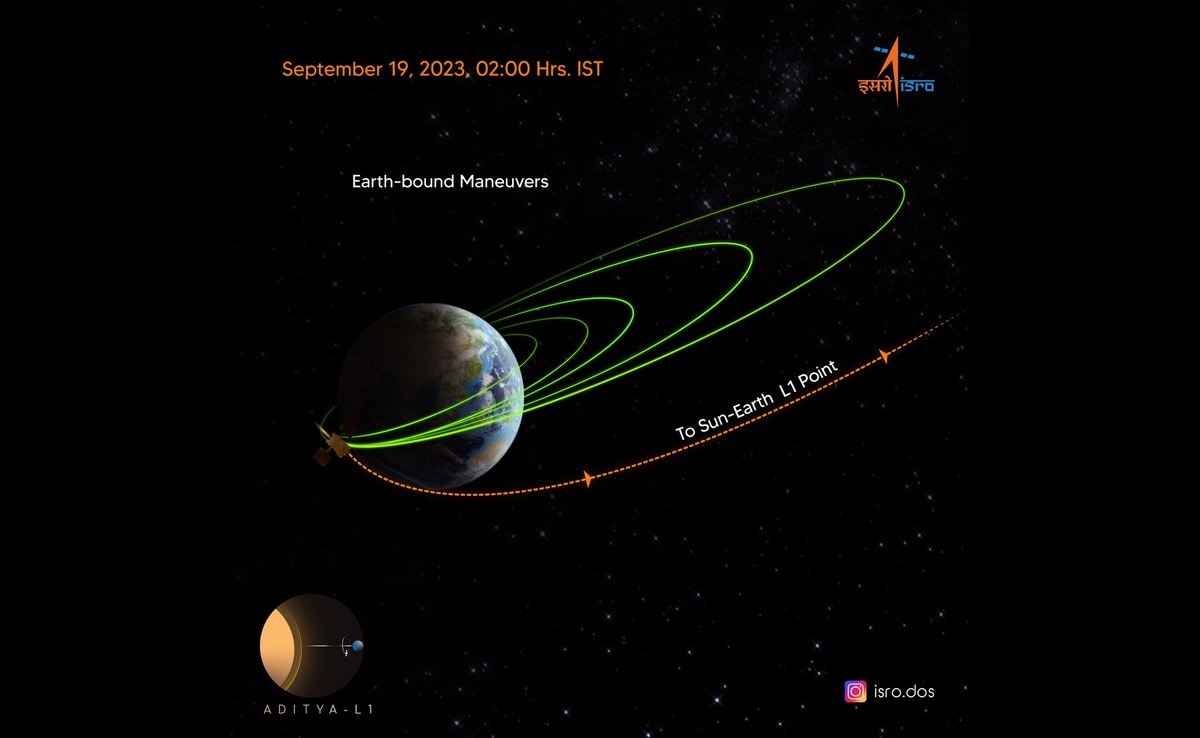
India's Aditya-L1 solar mission is poised to observe the Sun during its maximum activity cycle in 2026, a period marked by increased solar storms and coronal mass ejections (CMEs). The mission aims to study these phenomena to better understand solar behavior and improve space weather forecasting, which is crucial for protecting Earth's infrastructure and satellites. Aditya-L1's unique instrumentation allows continuous observation of the Sun's corona, providing valuable data during this intense solar period.