NASA’s Athena hits 20 petaflops, boosting rockets, aircraft, and AI
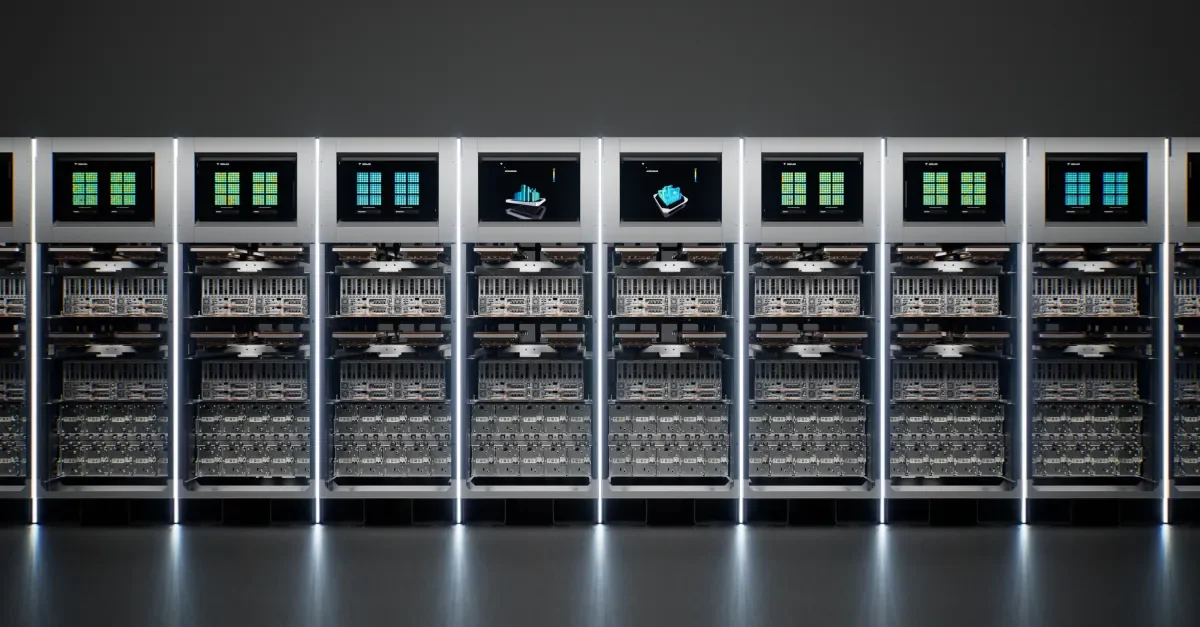
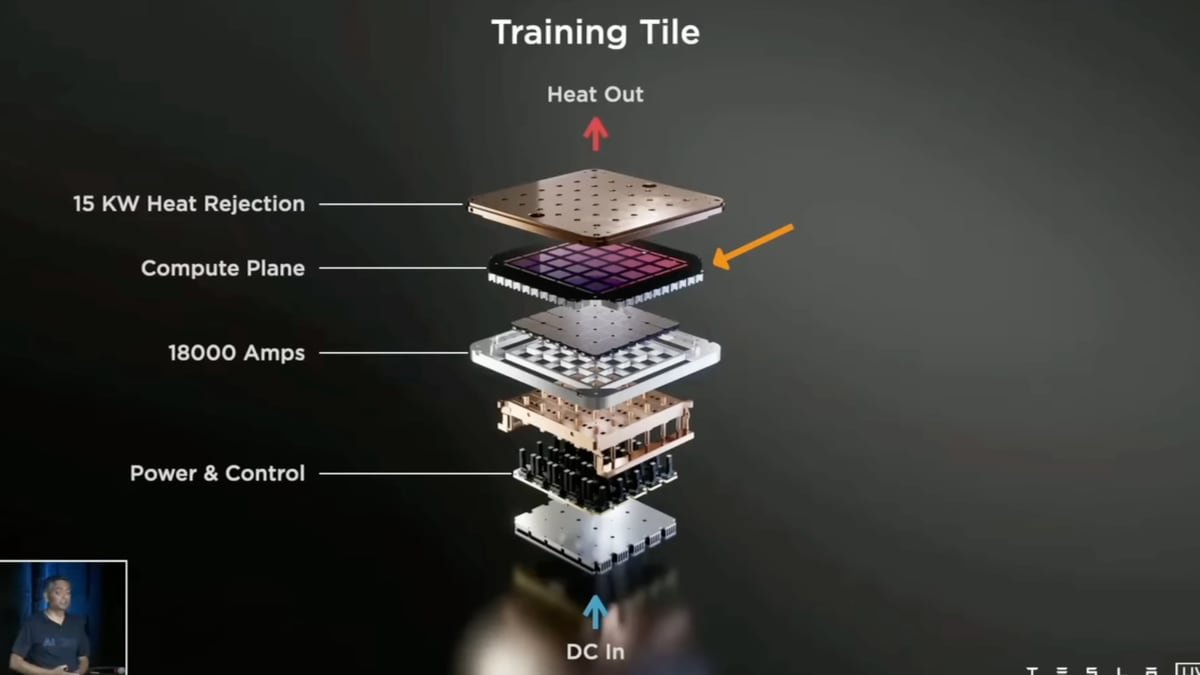
NASA has unveiled Athena, its most powerful supercomputer to date, delivering over 20 petaflops at the Ames Research Center to run complex rocket and aircraft simulations, train large AI models, and analyze vast mission data with a hybrid on-site and cloud approach; the system is available to NASA researchers and external scientists, as Artemis II preparations continue.