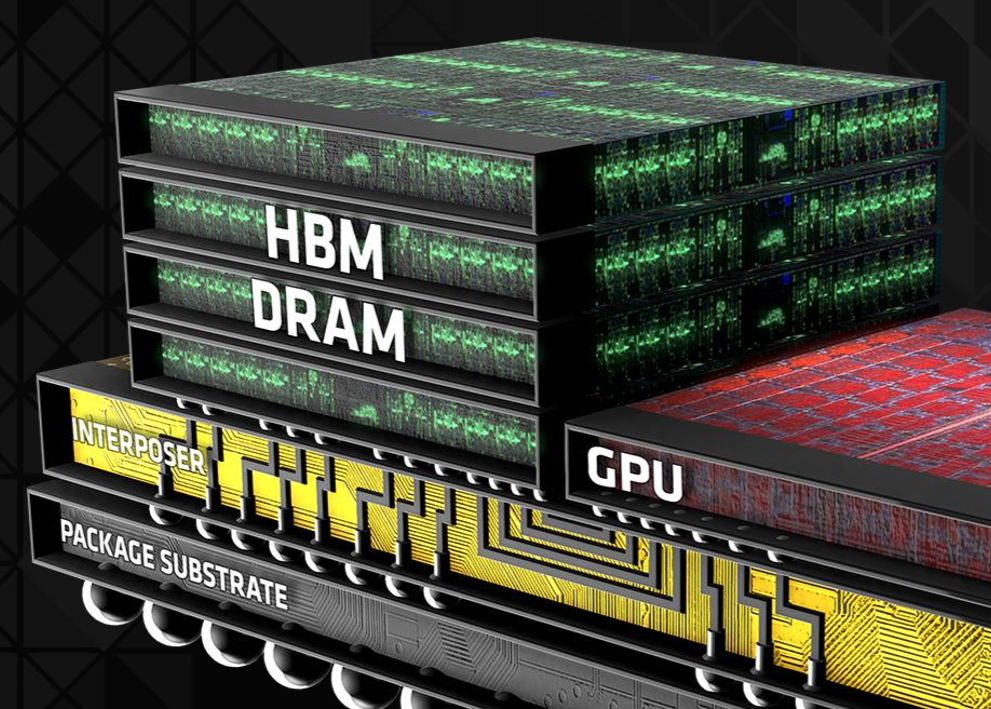
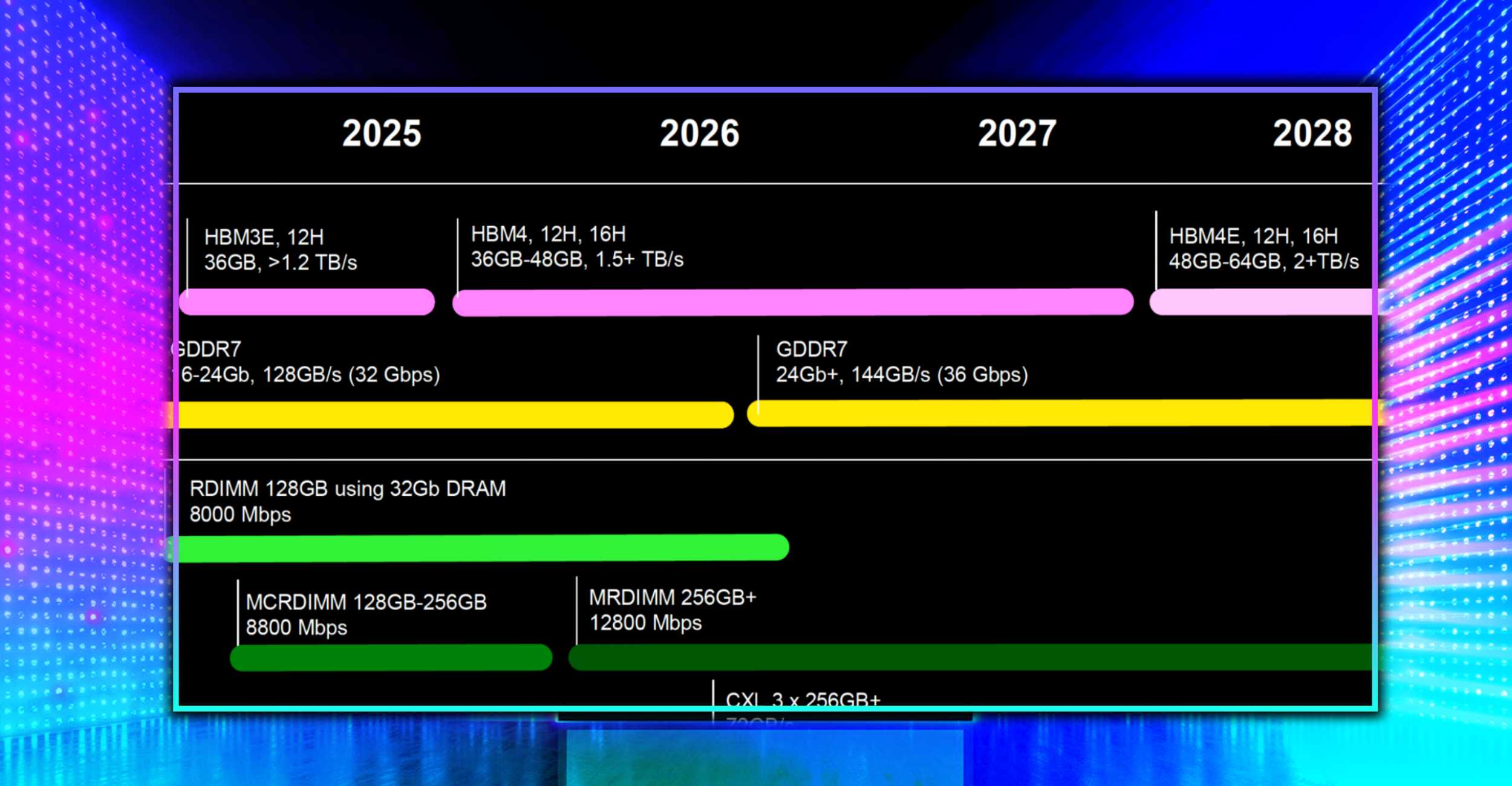
Samsung Poised to Lead NVIDIA’s Vera Rubin AI Push with HBM4 Memory
Samsung is set to supply HBM4 memory for NVIDIA’s Vera Rubin AI servers, with shipments expected as early as June and customer deliveries starting in August. Samsung’s HBM4 delivers 11 Gbps+ pin speeds using a 4nm logic base die from its own foundry, giving it a supply advantage over rivals and signaling a strong comeback in high-end memory for Vera Rubin, which will be showcased at GTC 2026.