Promising Alzheimer's Treatment Restores Memory Function in Preclinical Study
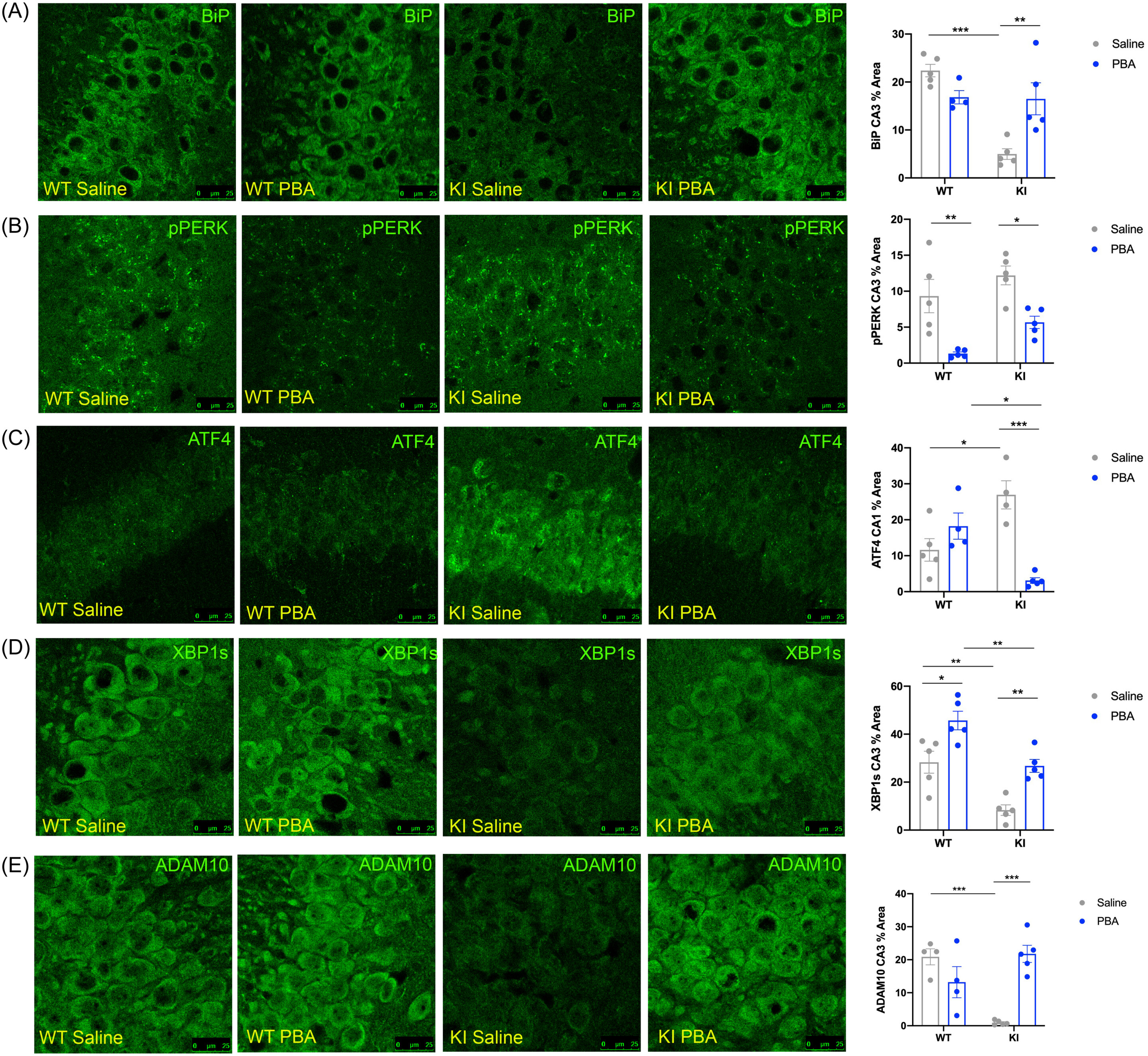
A compound called 4-phenylbutyrate (PBA) has shown promise in reversing signs of Alzheimer's disease and improving memory function in a preclinical study using mice. PBA, known as a "chemical chaperone," inhibits protein accumulation and helps restore normal proteostasis in the brain. The treatment was effective even when administered late in the disease course and showed potential in reducing amyloid beta plaques, a hallmark of Alzheimer's. PBA is already approved by the FDA for another metabolic disorder and can easily cross the blood-brain barrier.