Gamma Radiation Sparks Life's Building Blocks from Simple Gases
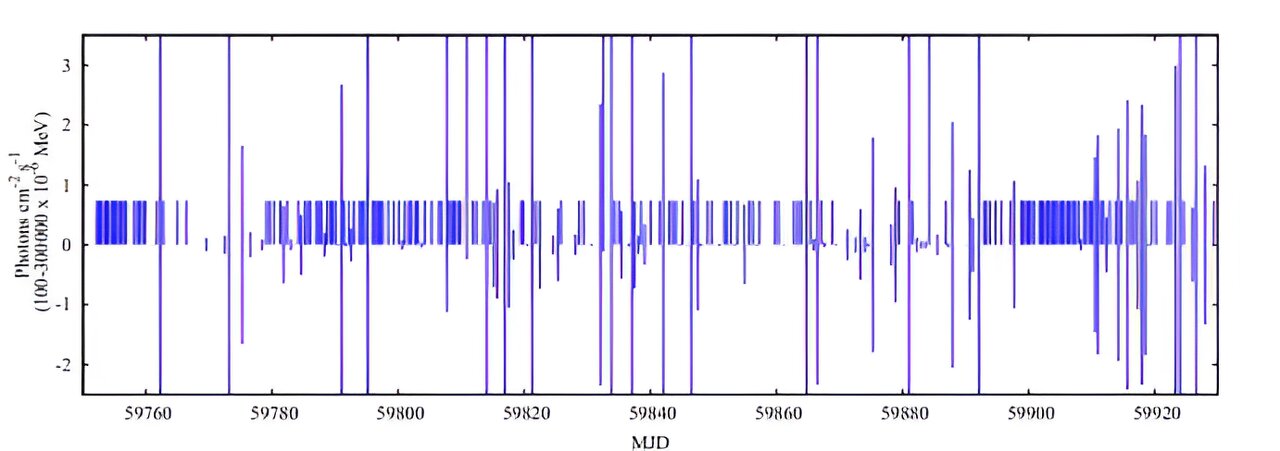
New research from the University of Science and Technology of China reveals that gamma radiation can transform methane into complex molecules, including amino acids like glycine, under mild conditions. This process, which occurs at room temperature, could provide insights into the formation of organic molecules in space and the origins of life. The study also suggests potential industrial applications for converting methane into valuable products using gamma radiation, a sustainable energy source. The findings highlight the role of interstellar dust and radicals in these chemical reactions.