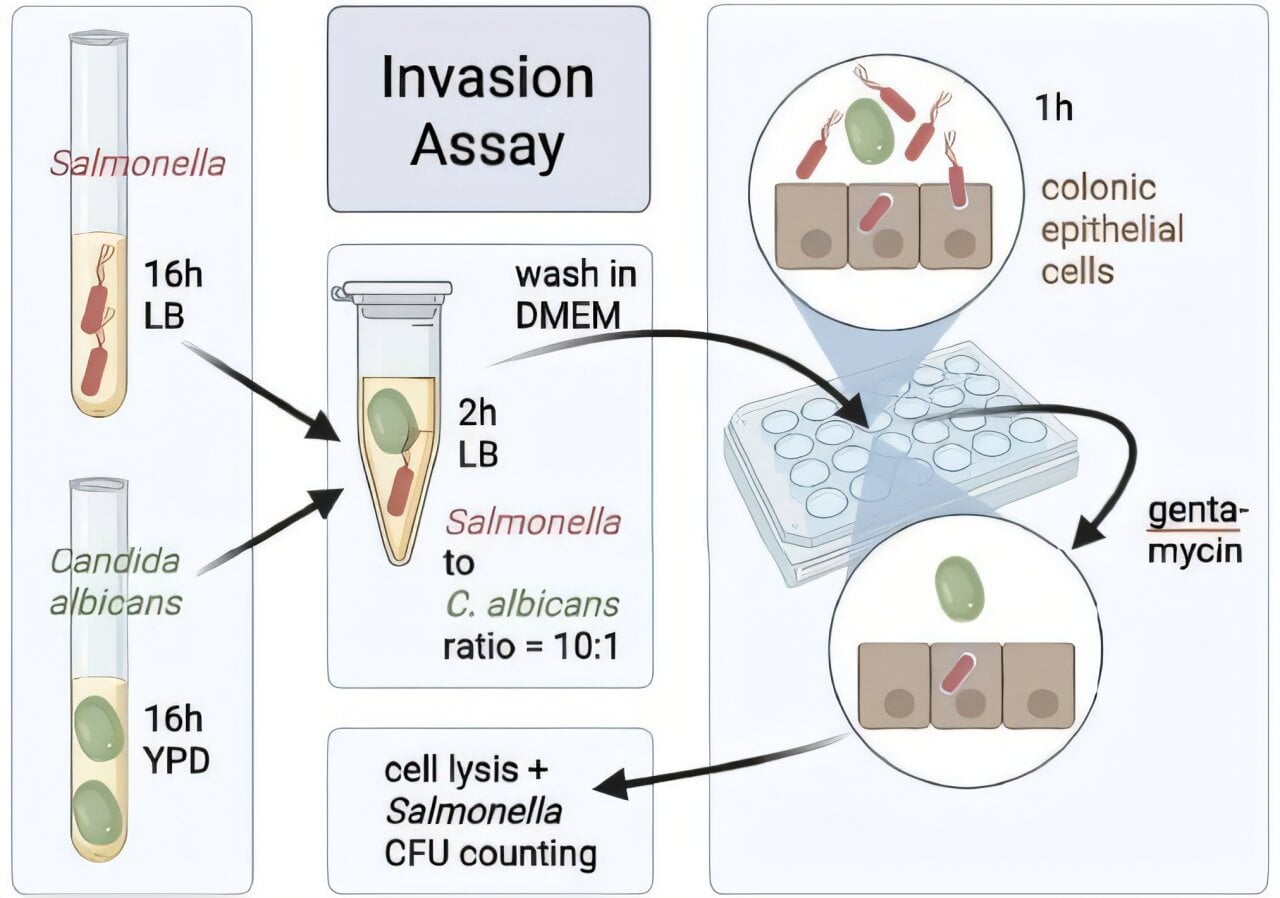
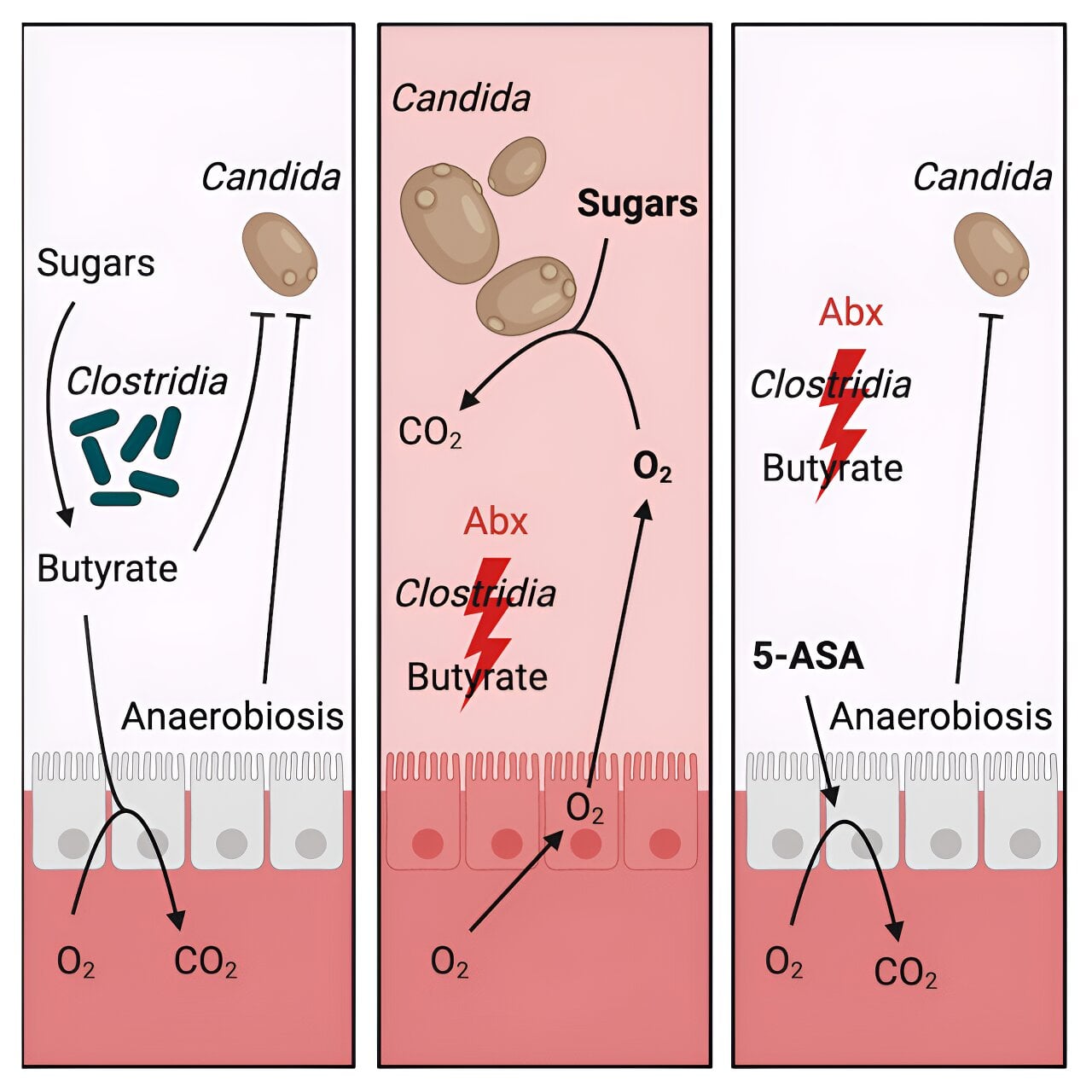
Gut Microbiome and Fungus Influence Alcohol Consumption and Brain Reward
A study found that overgrowth of the gut fungus Candida albicans increases PGE2 levels, which cross into the brain and alter dopamine signaling, leading to decreased alcohol preference in mice; blocking PGE2 restores drinking behavior, highlighting a potential new target for treating alcohol use disorder.