Ancient Bedrock Unveils Earth's Violent Origins and Early Life
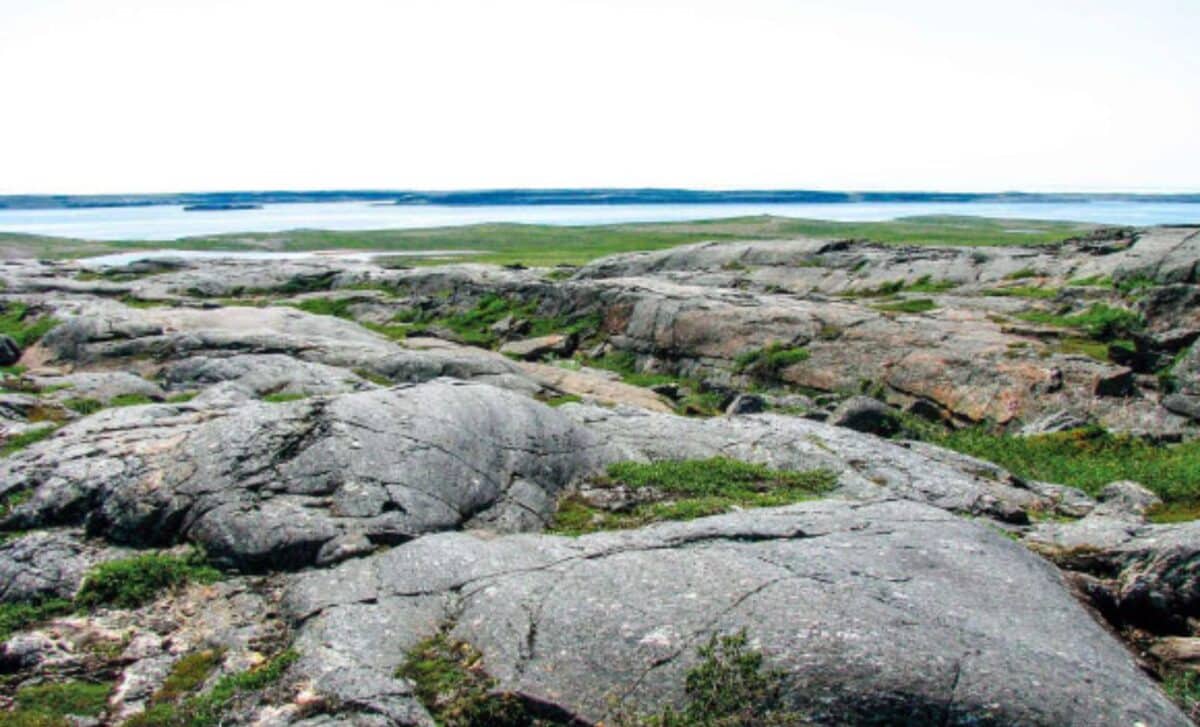
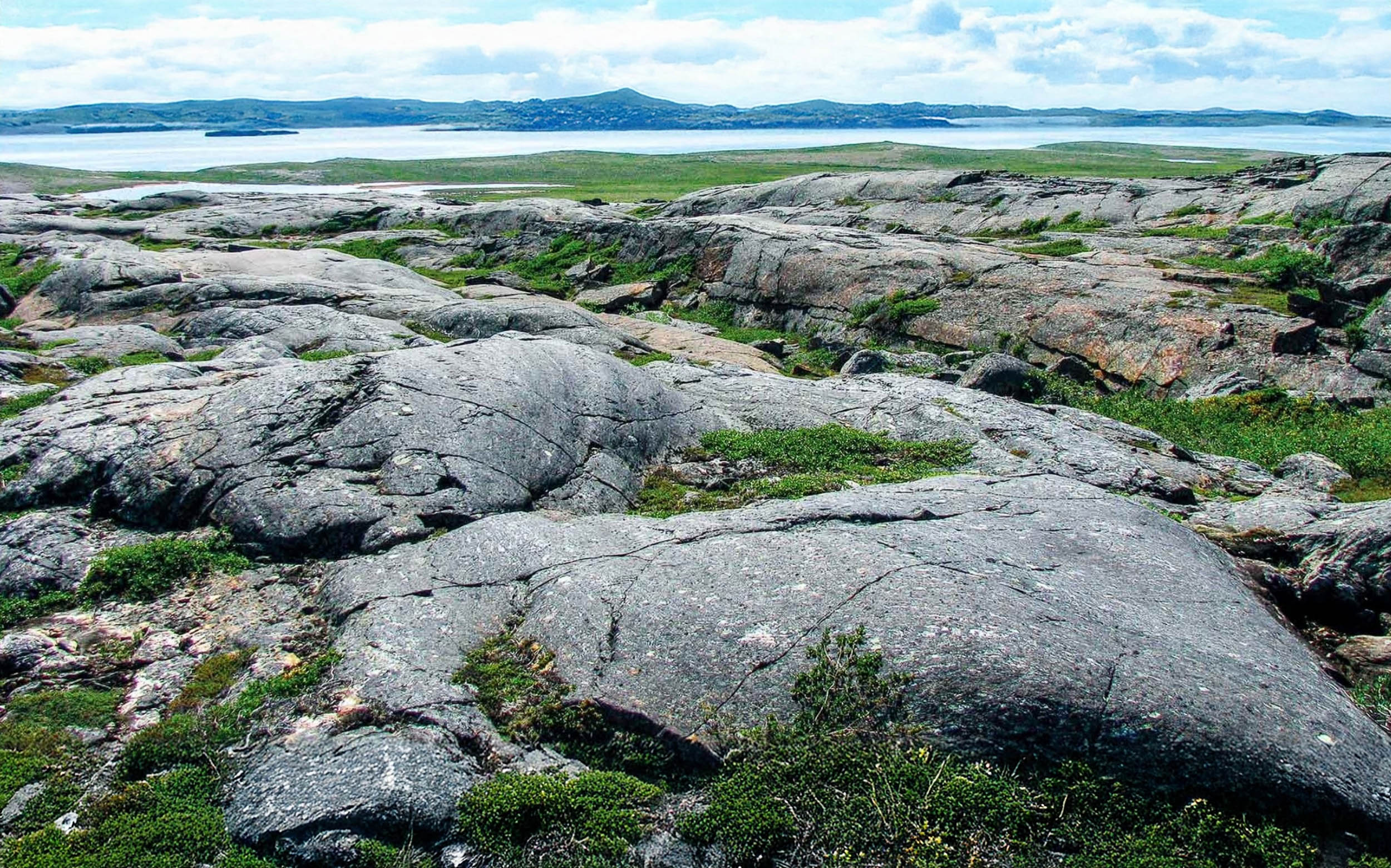
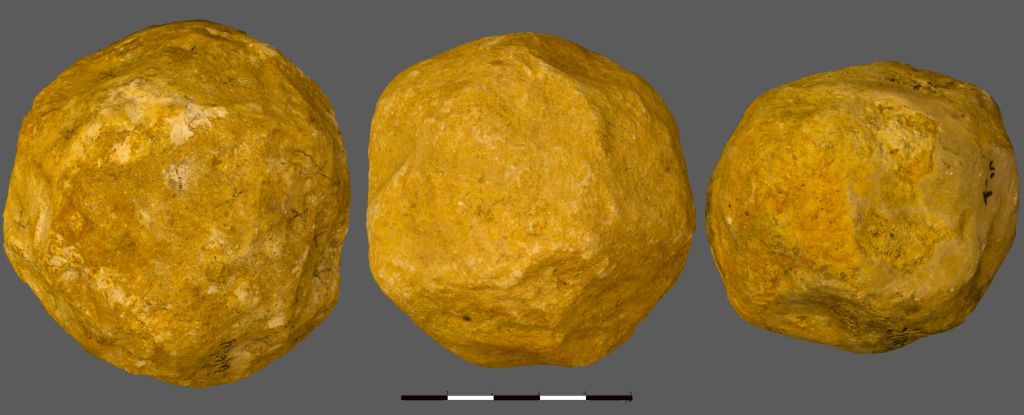
Scientists have found evidence suggesting that rocks in Canada's Nuvvuagittuq Greenstone Belt could be over 4.3 billion years old, potentially making them the oldest known rocks on Earth and offering insights into Earth's early crust and conditions, though the dating results are still debated among geologists.