
Health Medicine News
The latest health medicine stories, summarized by AI
Featured Health Medicine Stories

"Zepbound: A Promising Solution for Sleep Apnea and Obesity"
Eli Lilly's new weight loss drug tirzepatide, already approved for obesity, has shown promising results in reducing episodes of obstructive sleep apnea in people with obesity. In addition to significant weight loss, participants experienced easier breathing at night and fewer sleep apnea episodes. Tirzepatide belongs to a class of drugs known as incretins, which mimic gut and brain hormones important for regulating hunger and metabolism. The drug's potential to address both obesity and sleep apnea simultaneously could lead to a new treatment option for the underlying disease of sleep apnea.
More Health Medicine Stories

"Early PCI Shows Promise in Reducing Risks of Vulnerable Coronary Plaques"
The PREVENT trial of preventive coronary stents targeting vulnerable plaques showed promising results at the American College of Cardiology meeting, with an 89% reduction in major cardiac events at 2 years. However, concerns about the small number of events, overestimation of outcome rates, open-label design, and limited clinical translation suggest caution in interpreting the results. While the study provides hope in understanding vulnerable plaques, it's too early to change current PCI practice, and further studies are needed to validate these findings.

"Synergistic Benefits: Probiotics and Vitamin D Alleviate Schizophrenia Symptoms"
A study suggests that probiotics with vitamin D may improve cognitive function in individuals with schizophrenia. The research involved 70 adults with schizophrenia who took either a placebo or the supplements daily for 12 weeks. Those on the supplements showed improvement in a cognitive function test, but not in overall disease severity. The study indicates that co-administration of probiotics and vitamin D has beneficial effects on the improvement of cognitive function in schizophrenic patients.
"Pfizer's RSV Vaccine Shows Promise for High-Risk Adults Under 60"
Pfizer's RSV vaccine, Abrysvo, has shown potential to protect high-risk adults aged 18 to 59 from respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in a late-stage clinical trial, widening its possible use beyond older adults and expectant mothers. The initial data suggests that the vaccine could help protect a wider population from RSV, which causes thousands of hospitalizations and deaths among older Americans and hundreds among infants each year. Pfizer plans to submit the data to regulatory agencies and file for expanded approval of Abrysvo for ages 18 and up, aiming to gain more share of the RSV market. The vaccine elicited an immune response against RSV A and RSV B, and the safety data in high-risk adults ages 18 to 59 was consistent with the results in adults 60 and above.

"Reconsidering Beta-Blockers After Heart Attack: Insights from REDUCE-AMI Trial"
The REDUCE-AMI trial investigated the use of beta-blockers post-myocardial infarction (MI) in patients with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction and found no significant difference in the primary endpoint of death or MI between the beta-blocker and control groups. The trial's pragmatic nature and the changing landscape of MI care, with the widespread use of revascularization and modern therapies, raise questions about the relevance of beta-blockers in current post-MI care. The results challenge the long-standing dogma of beta-blocker use after MI and emphasize the importance of retesting old treatment paradigms, while ongoing trials may provide further insights into the role of beta-blockade in post-MI care.
"Advancements in Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer"
Pancreatic cancer, the third leading cause of cancer deaths in the US, lacks a standard early detection test, but researchers are exploring blood-based liquid biopsy tests to spot early cases. A study presented at the American Association for Cancer Research detailed a liquid biopsy test that detected 97% of stage I and II pancreatic cancers in volunteers. While there's excitement about the potential of these tests, more research is needed before they can be used clinically. Early detection could significantly improve survival rates for pancreatic cancer, which is often diagnosed at advanced stages, and developing a reliable early detection test could dramatically change the landscape for patients.

"Potential Link Between Ozempic and Fertility Concerns"
Reports of unexpected pregnancies in women using weight loss injections like Ozempic and Wegovy have sparked speculation about a potential link to fertility, but experts caution that the pregnancies are likely due to the significant weight loss caused by the injections rather than a direct fertility-boosting effect. The weight loss from these injections may indirectly address fertility issues related to obesity, insulin resistance, and hormone imbalances. However, these medications are not recommended for women who are not overweight and struggling to conceive, as they could lead to malnutrition and are not considered safe during pregnancy. Women who become pregnant while using these injections should stop immediately and seek medical advice for evaluating the impact on the pregnancy and fetus.

"Promising Results: Geneos Cancer Vaccine Shrinks Liver Tumors in Small Trial"
In a small trial, nearly a third of patients with advanced liver cancer who received a personalized vaccine developed by Geneos Therapeutics along with an immunotherapy drug saw their tumors shrink, suggesting that vaccines based on mutations only present in a patient's tumor may boost the immune system's ability to recognize and attack hard-to-treat cancers. The study involved 36 patients with hepatocellular carcinoma, and the combination therapy resulted in a 30.1% tumor shrinkage rate, compared to the typical 12-18% response with immunotherapy alone. Larger trials are being planned to confirm these findings.

"Study Reveals Lack of Evidence for Many Accelerated Approval Cancer Drugs"
A study found that most cancer drugs granted accelerated approval by the FDA do not demonstrate clinical benefits within five years, despite the program being intended to give patients early access to promising drugs. Between 2013 and 2017, 63% of cancer drugs granted accelerated approval were converted to regular approval, even though only 43% demonstrated a clinical benefit in confirmatory trials. The study raises concerns about whether patients understand the uncertainty surrounding drugs with accelerated approval and emphasizes the importance of doctors carefully explaining the evidence to patients. Congress recently updated the program, giving the FDA more authority and streamlining the process for withdrawing drugs when companies don’t meet their commitments.

"Wegovy Shows Promise for Heart Failure and Diabetes in New Study"
A new study published in the New England Journal of Medicine found that the weight-loss drug Wegovy offers health benefits for people with Type 2 diabetes and obesity-related heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, a common form of heart failure. The research showed that participants who took Wegovy experienced significant weight loss, reduction in heart failure-related symptoms, and improvements in physical limitations compared to those who took a placebo. The study suggests that Wegovy may be an effective and safe treatment for a broad population, including those with diabetes, and could potentially open up a new way of treating heart failure by addressing obesity as a systemic cardiometabolic condition.
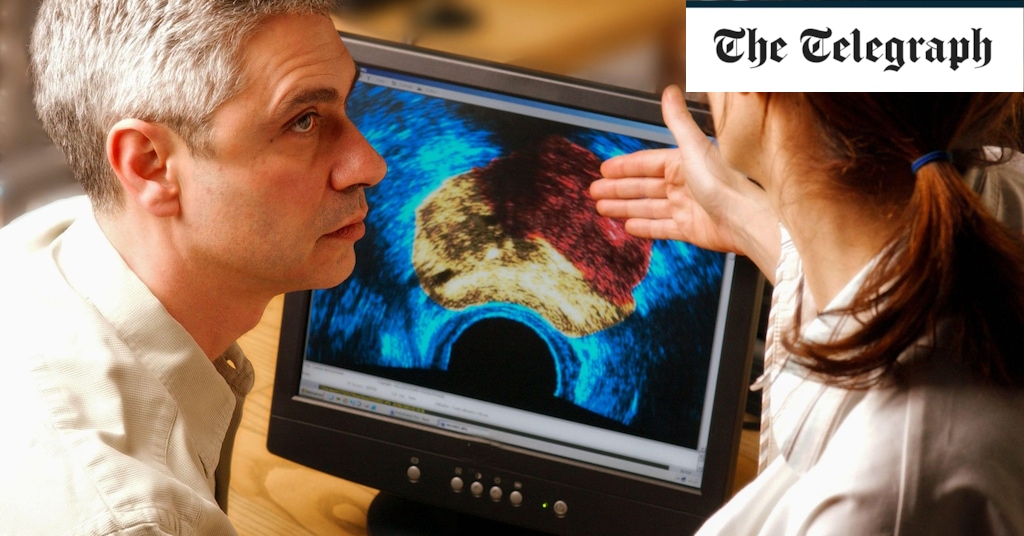
"Study Suggests Prostate Cancer Screening Does More Harm Than Good"
A 15-year trial on prostate cancer screening using the PSA blood test found that while it had a small impact on reducing deaths, it also led to a worrying level of overdiagnosis, with one in six flagged cases being wrong. The study showed that the potential harms of the test, including unnecessary treatment and physical side effects, outweigh the benefits. Experts emphasize the need to find better ways to detect aggressive prostate cancers and are exploring alternatives such as MRI scans. The UK National Screening Committee does not currently recommend screening for prostate cancer due to the unclear balance between benefits and harms.
