"Revolutionizing Plasmonic Catalysis with Black Gold and Solar Light"
Originally Published 1 year ago — by Phys.org
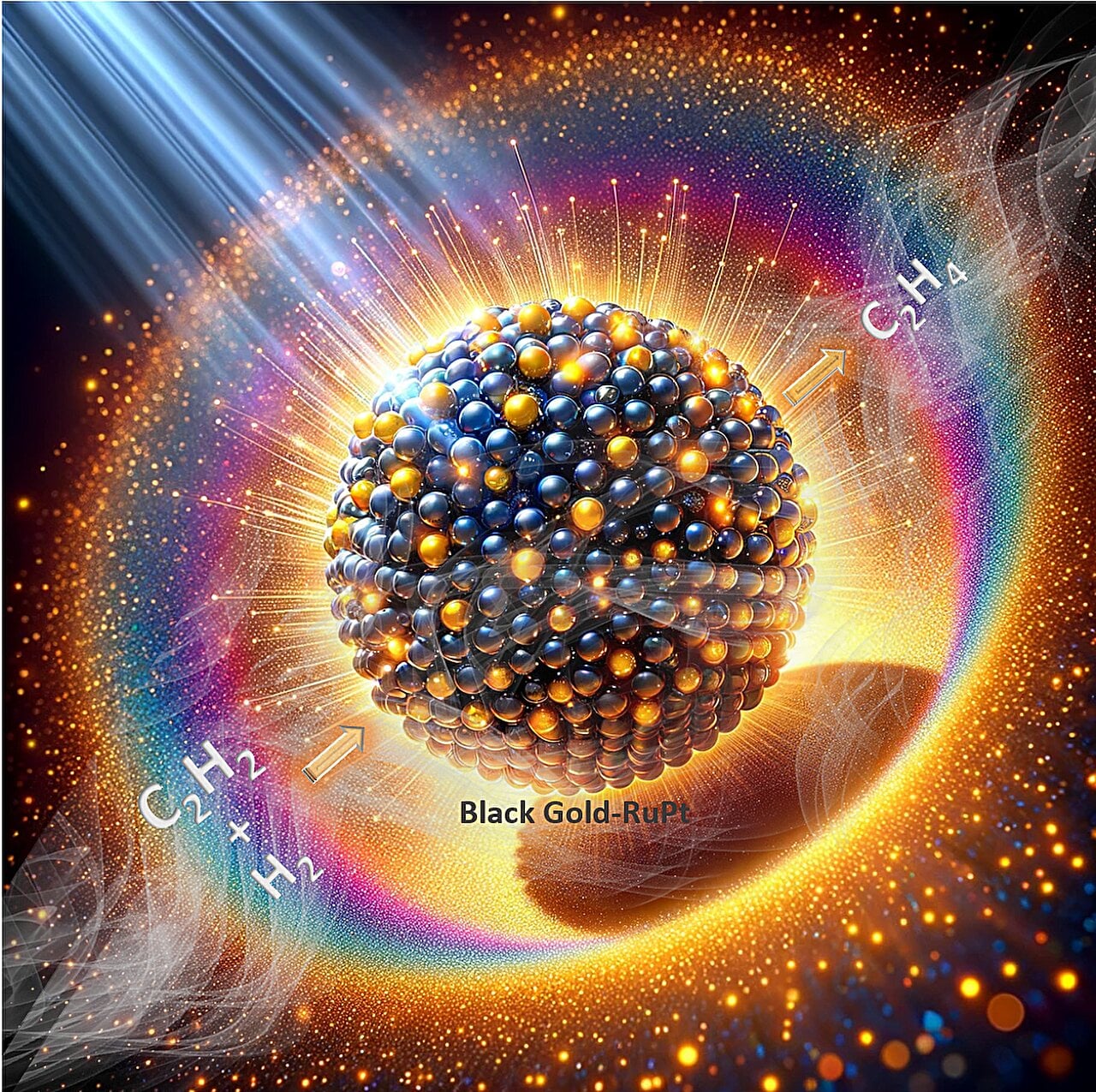
Researchers at Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR) in Mumbai have developed an innovative plasmonic reduction catalyst stable in air, merging platinum-doped ruthenium clusters with "plasmonic black gold" to efficiently harvest visible light and achieve remarkable performance in the semi-hydrogenation of acetylene. This catalyst exhibits unprecedented stability for at least 100 hours and offers significant contributions to the understanding of plasmonic catalysis, paving the way for developing sustainable and energy-efficient catalytic systems with potential applications in various reduction reactions.
