UK Introduces Innovative Tongue Implant for Sleep Apnea Relief
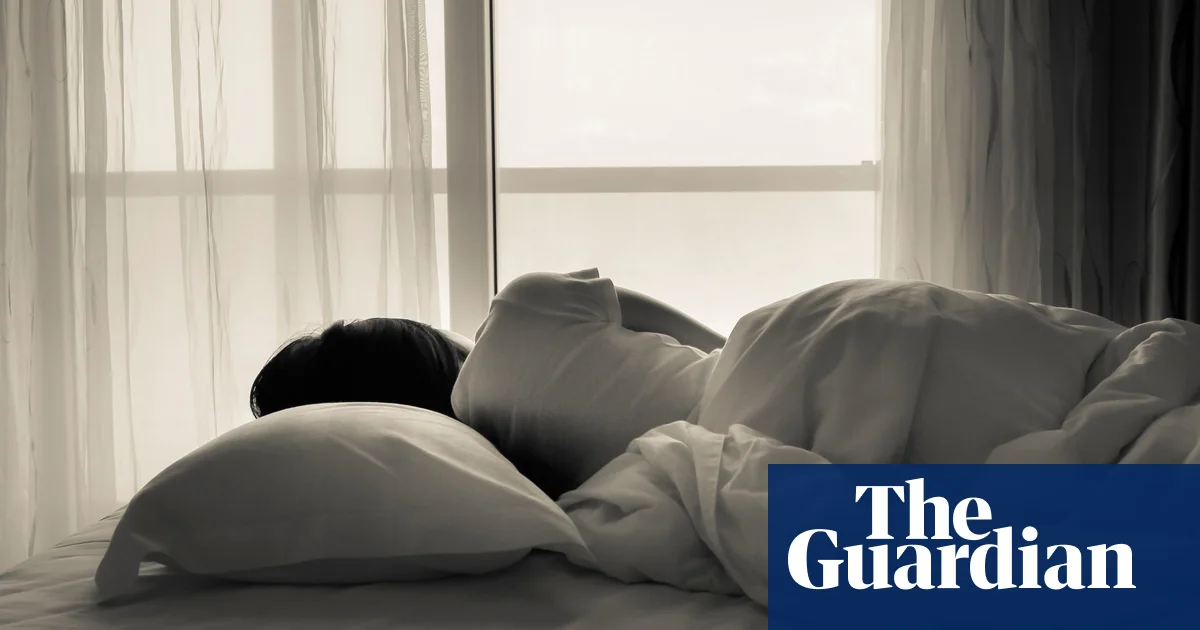
In a UK first, patients with sleep apnoea have been fitted with a new app-controlled implant that stimulates tongue nerves to aid breathing during sleep. The Genio implant, developed by Nyxoah, was successfully implanted in two patients at University College London Hospitals. This device offers an alternative to CPAP machines, which can be uncomfortable for some users. The implant is controlled by an external chip and can be adjusted via a smartphone app. This development marks a significant advancement in treatment options for sleep apnoea patients in the UK.