Dietary Fat Shifts in Cooking Oils May Slow Prostate Cancer Growth, Small Study Suggests
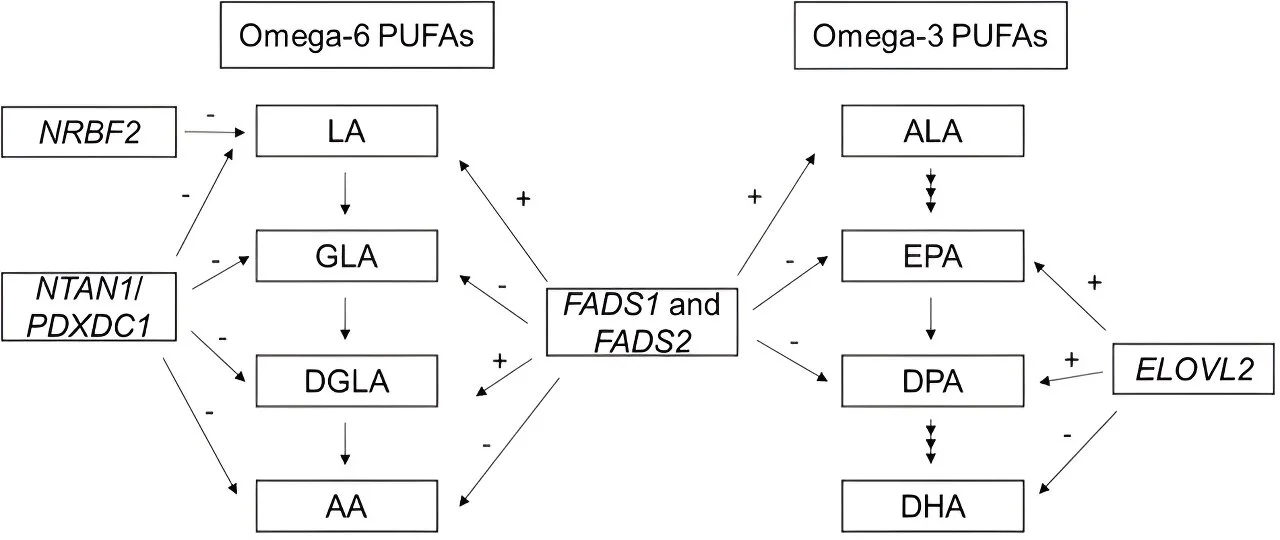
A small UCLA-led trial in men with early prostate cancer on active surveillance found that reducing omega-6 fats and increasing omega-3 fats (via diet and fish oil) correlated with slower cancer cell growth, evidenced by lower Ki-67 after one year; PSA and tumor grade didn’t change. The study isn’t proof and larger, longer research is needed, but practical steps include cutting fried/ultra-processed foods and eating fatty fish regularly.