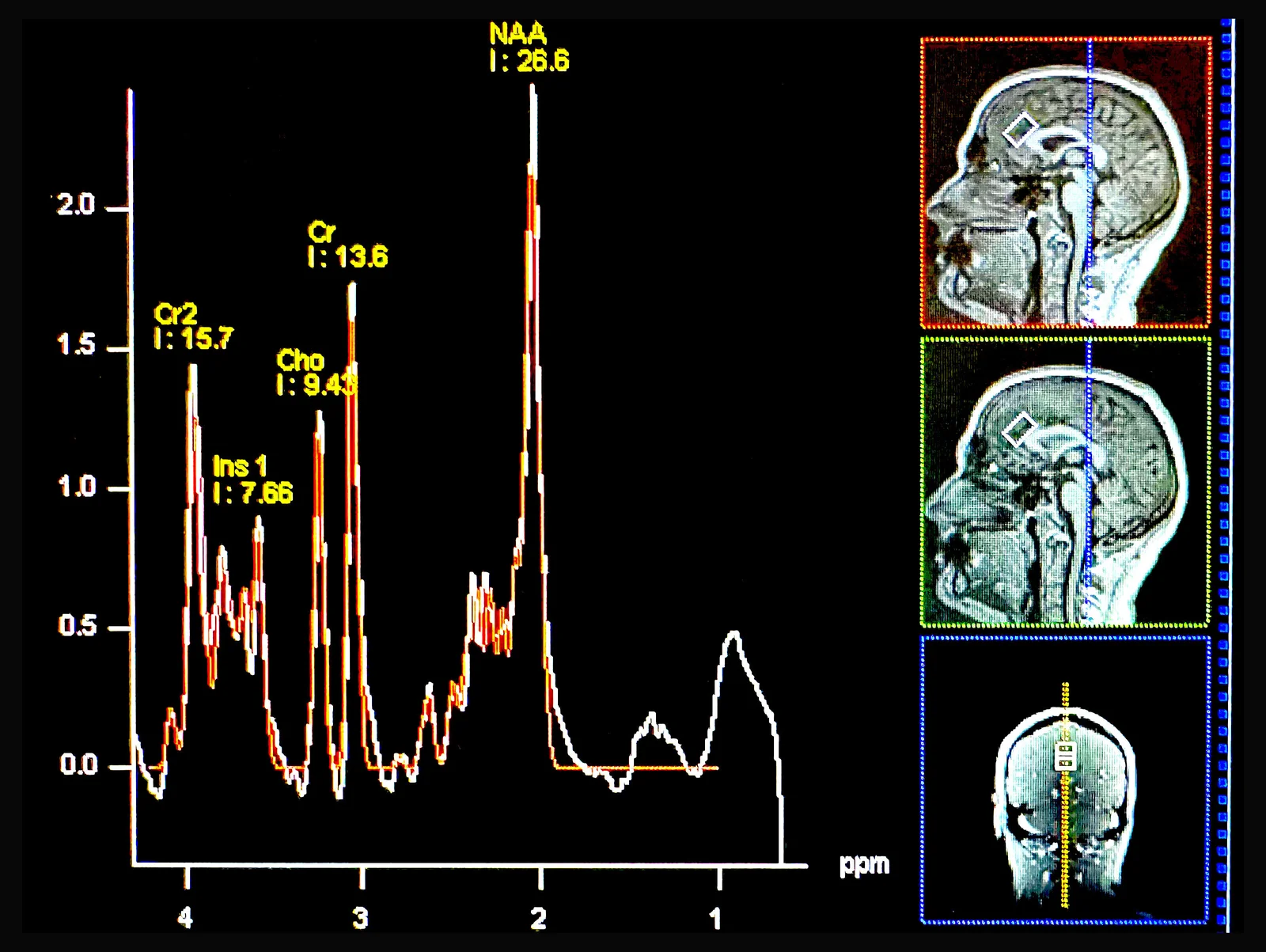
Low Brain Nutrient Levels Linked to Anxiety Disorders
Research shows that individuals with anxiety disorders have about 8% lower levels of choline in their brains, particularly in the prefrontal cortex, which may be linked to the condition. The study suggests that dietary intake of choline, found in foods like eggs, fish, and meat, could potentially influence brain chemistry and anxiety symptoms, although more research is needed. The findings highlight the importance of nutrition in mental health and the potential for nutritional approaches to aid in managing anxiety.



