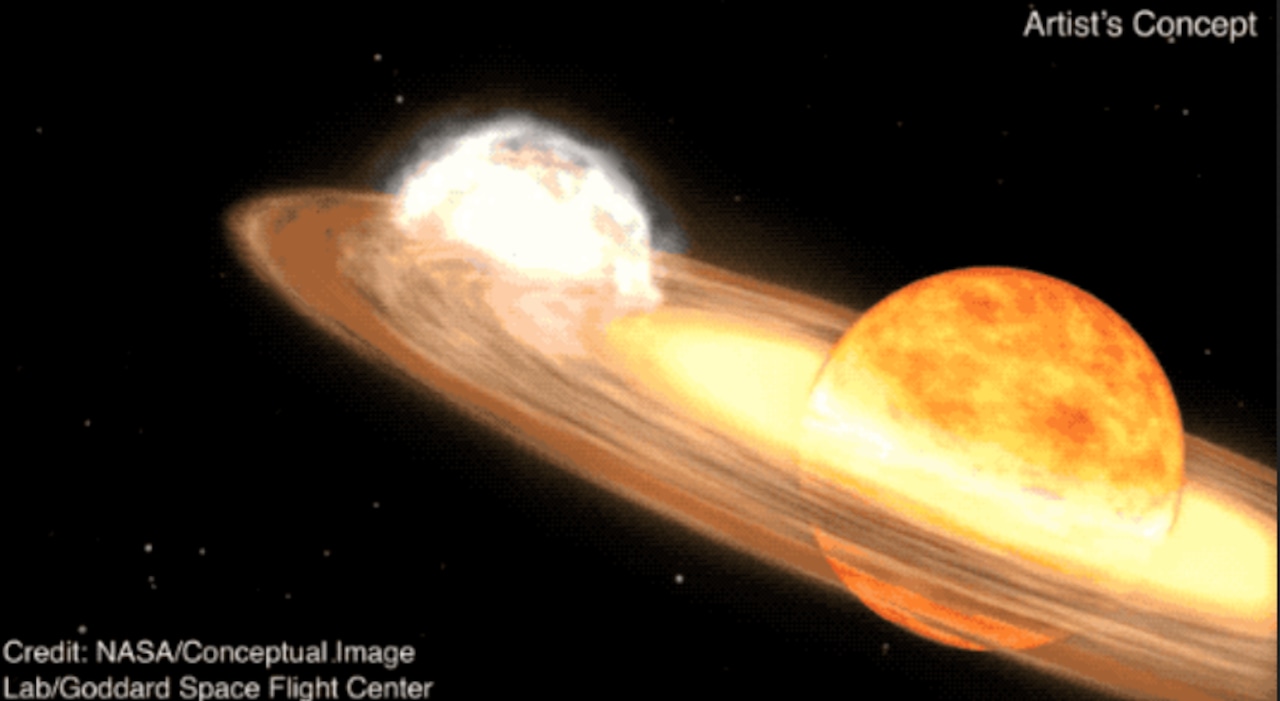
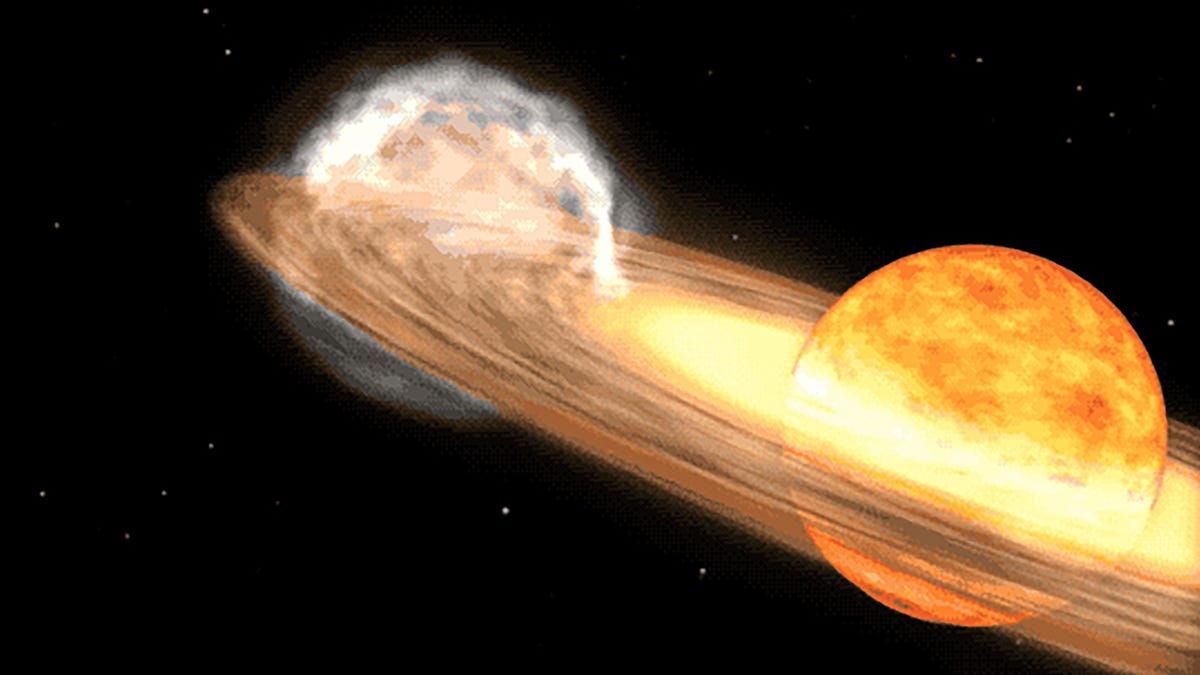
"Get Ready to Witness a Rare Nova Explosion: A Once-in-a-Lifetime Opportunity"
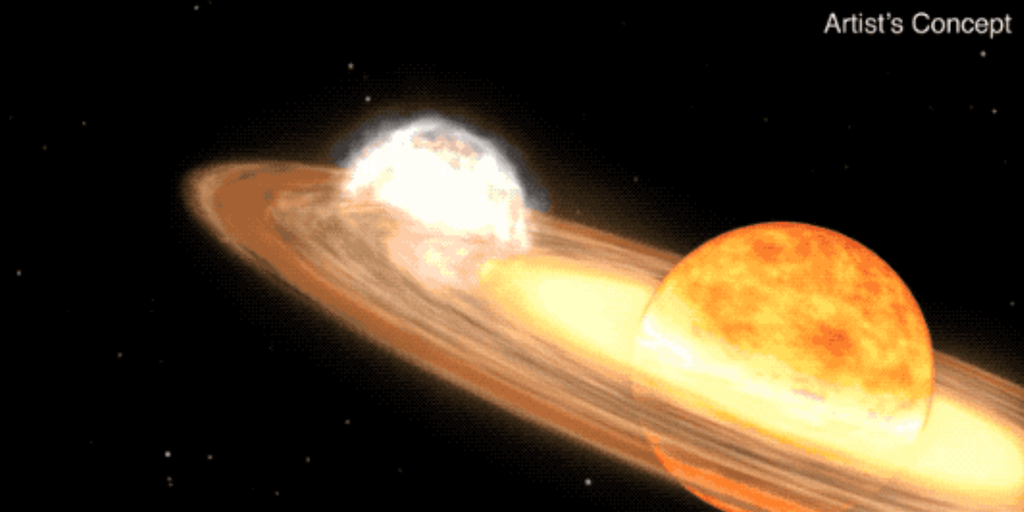
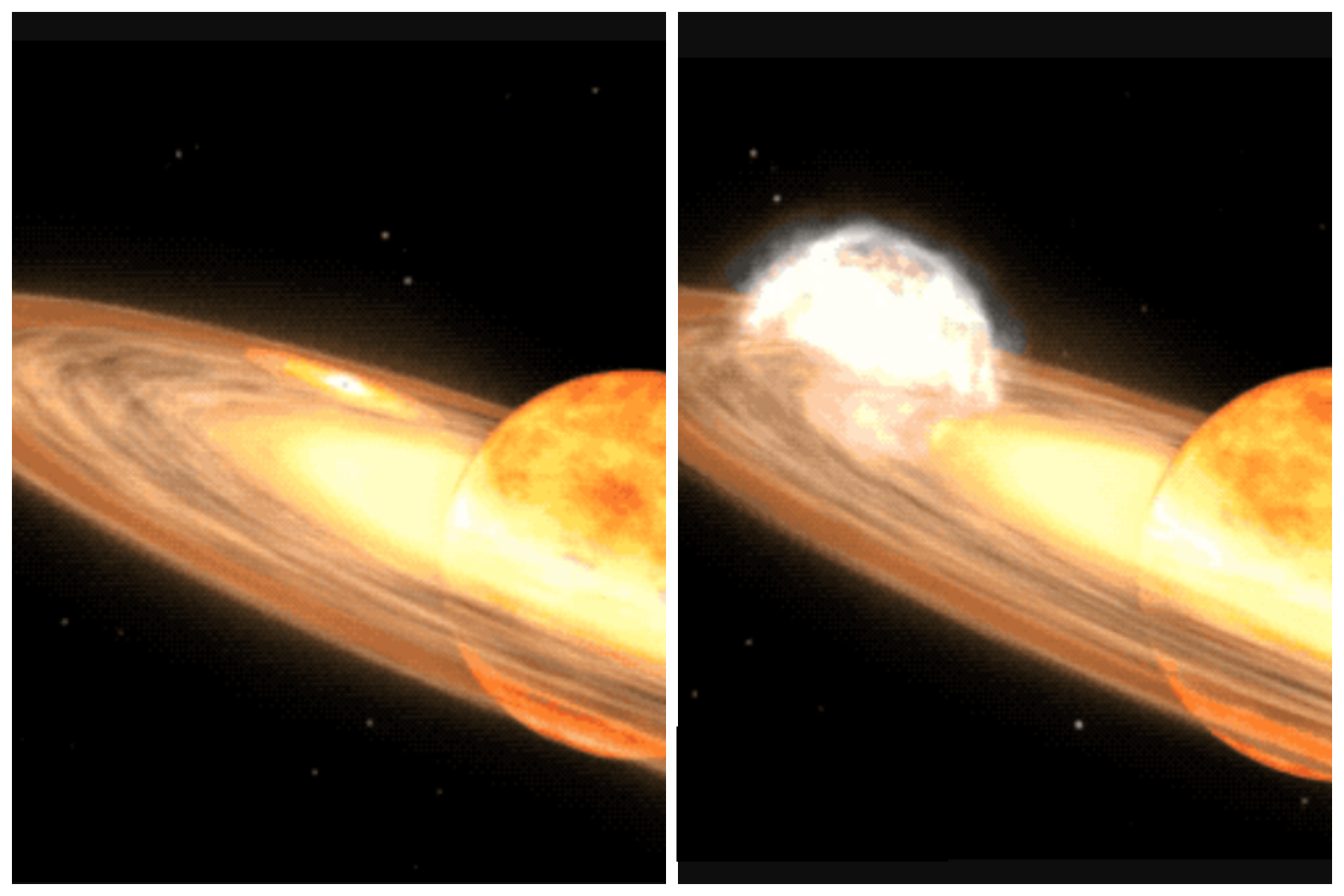
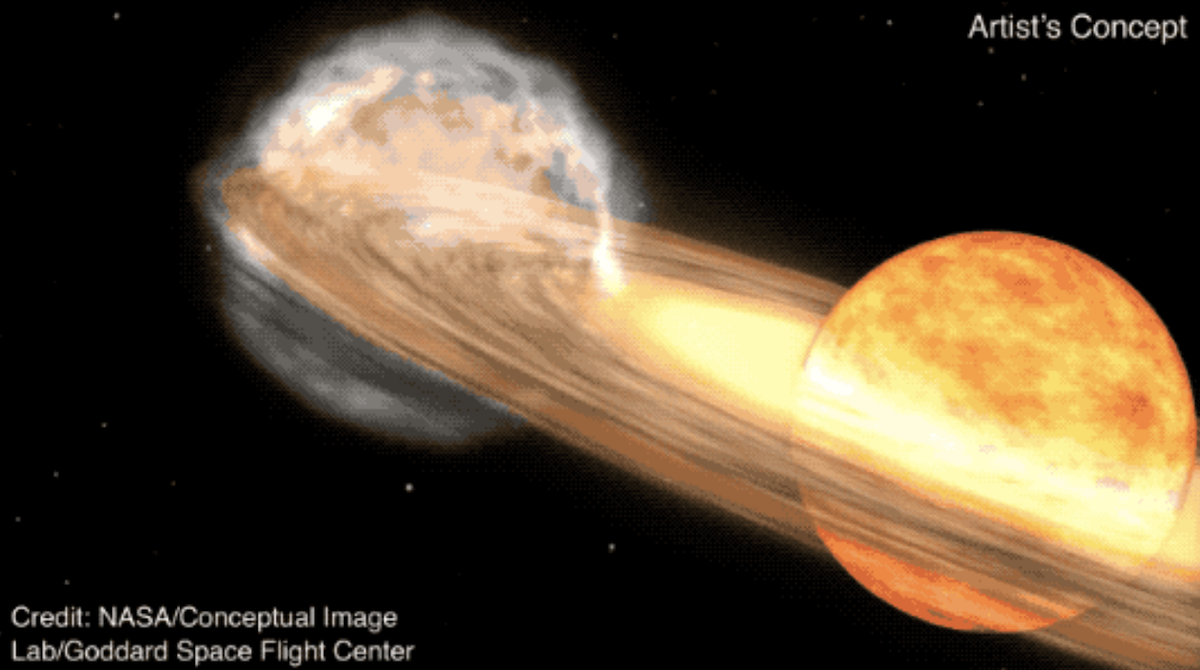
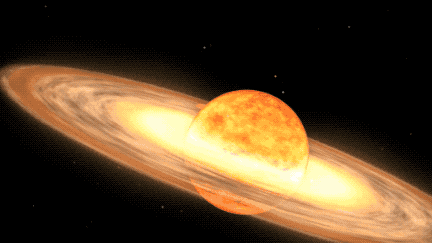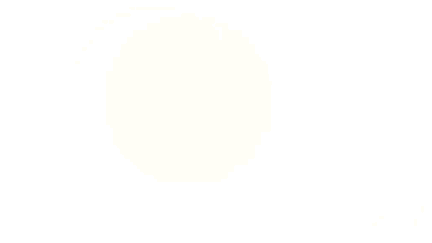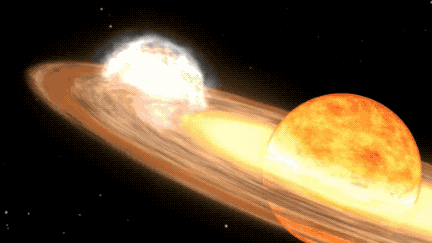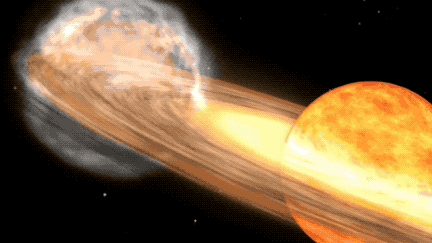
A star system located 3,000 light-years away is expected to become visible to the naked eye due to a nova outburst, a rare event that occurs approximately every 80 years. Known as T Coronae Borealis, or T CrB, the star last exploded in 1946 and is predicted to do so again between February and September 2024. NASA experts describe this as a "once-in-a-lifetime" event, with the star system becoming as bright as the North Star during the outburst, visible for several days and longer with binoculars.