
Innovative Drug Offers Hope for Postpartum Depression
A new drug offers promising advancements in the treatment of postpartum depression, potentially improving outcomes for new mothers suffering from this condition.
All articles tagged with #new drug

A new drug offers promising advancements in the treatment of postpartum depression, potentially improving outcomes for new mothers suffering from this condition.
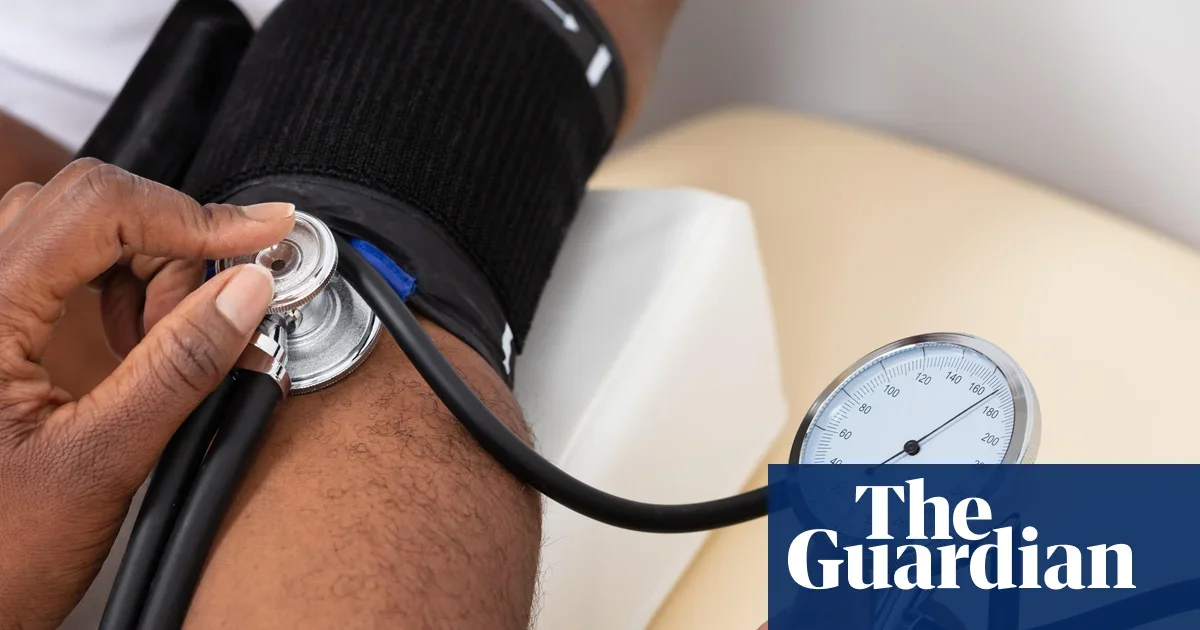
A new drug, baxdrostat, has shown promising results in significantly lowering blood pressure in patients with resistant hypertension, potentially reducing cardiovascular risks and representing a major scientific breakthrough in hypertension treatment.
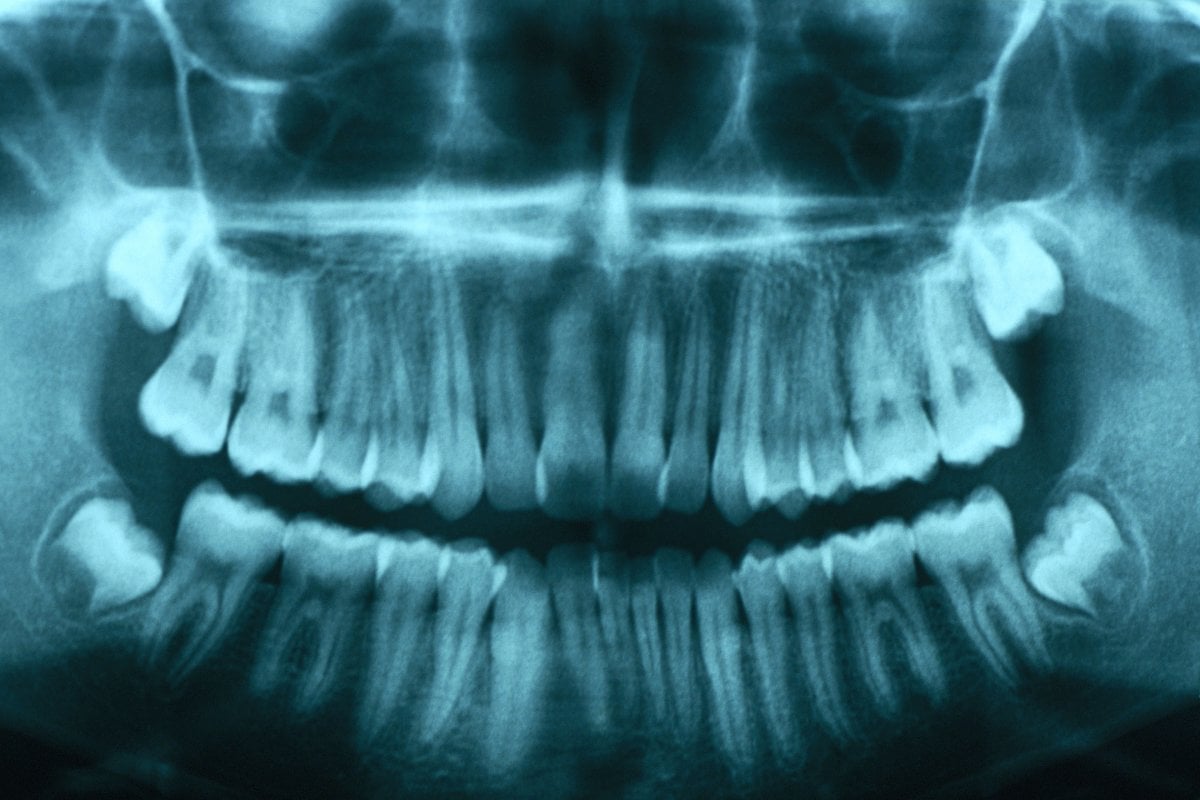
Scientists in Japan have developed a drug that can potentially regrow human teeth by suppressing the USAG-1 antibody, with successful trials on mice and plans for human trials, aiming for availability by 2030.
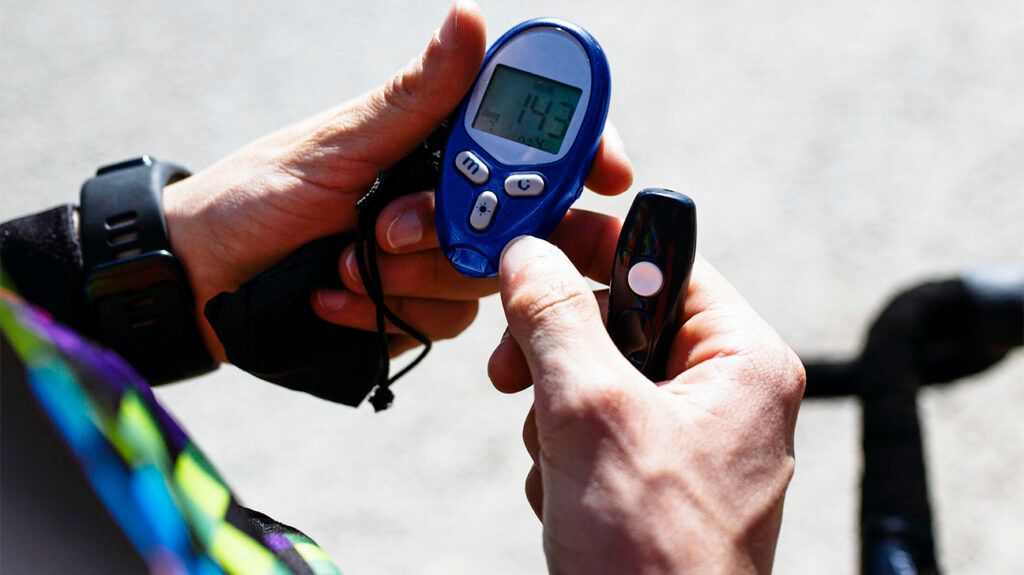
Swedish researchers have developed an oral drug that aids weight loss and treats type 2 diabetes by activating skeletal muscle metabolism, potentially preserving muscle mass unlike current GLP-1 drugs, with promising initial human trial results showing good tolerance and minimal side effects.
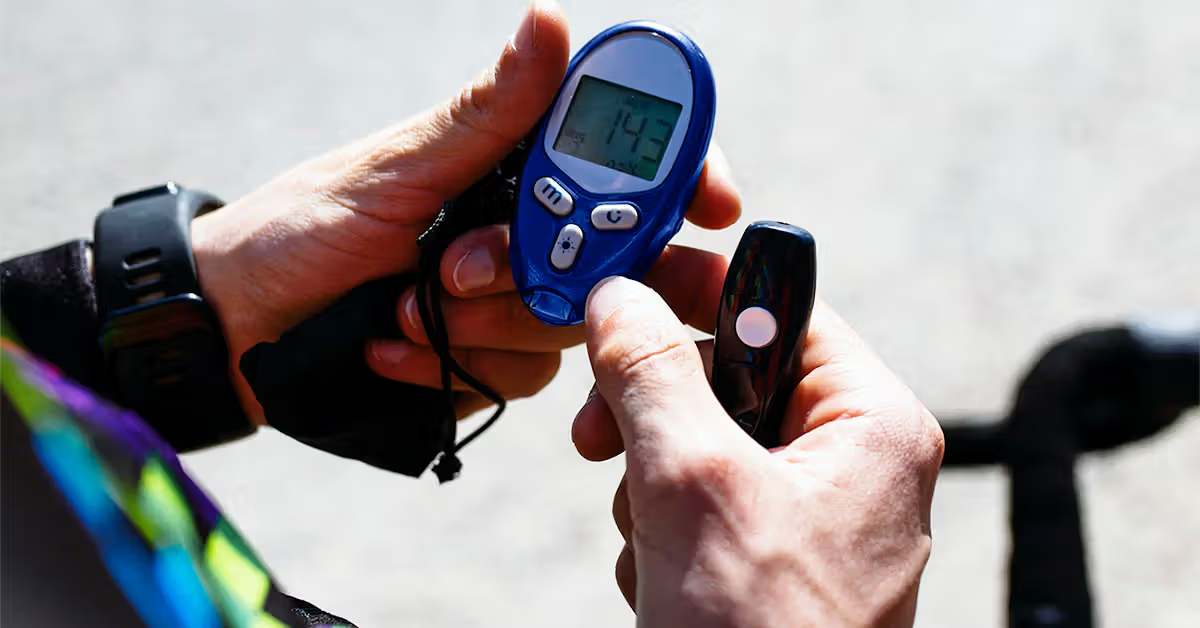
Swedish researchers have developed an oral drug that aids weight loss and manages type 2 diabetes by enhancing skeletal muscle metabolism, potentially avoiding muscle loss associated with current GLP-1 drugs like Ozempic. Initial phase 1 trials show good tolerance and minimal side effects, paving the way for further studies to confirm its efficacy and safety.

The announcement of a new drug, donanemab, that can slow the pace of Alzheimer’s by about a third is a cause for celebration. However, the drug will not help everyone as Alzheimer’s only contributes to between 60% and 70% of cases. Patients need to be at an early stage for the highly expensive treatment to be most effective, and diagnosis takes an average of three years in the UK. Three people with first-hand experience of Alzheimer’s tell what a cruel and pitiless disease it is and how many human tragedies would be prevented if it eventually became a manageable, even a curable, condition.