Dana-Farber Develops AI-Powered Tool for Rapid Leukemia Classification
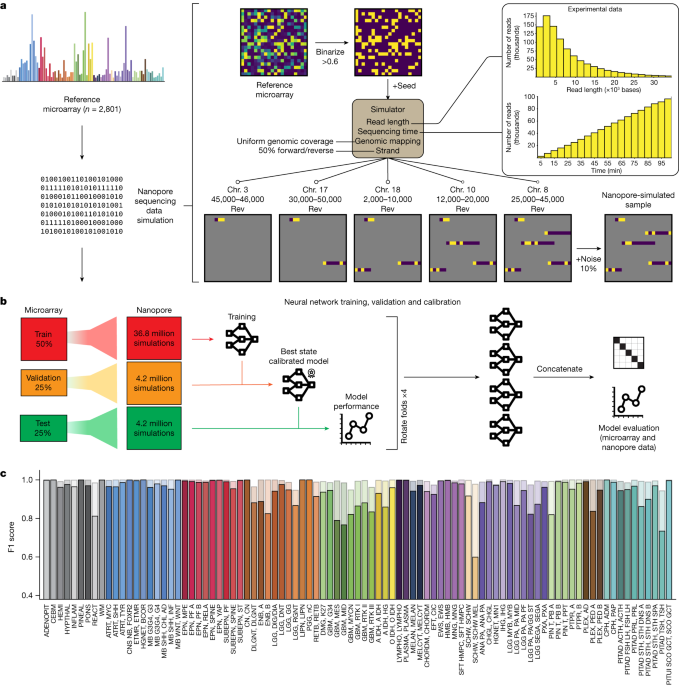
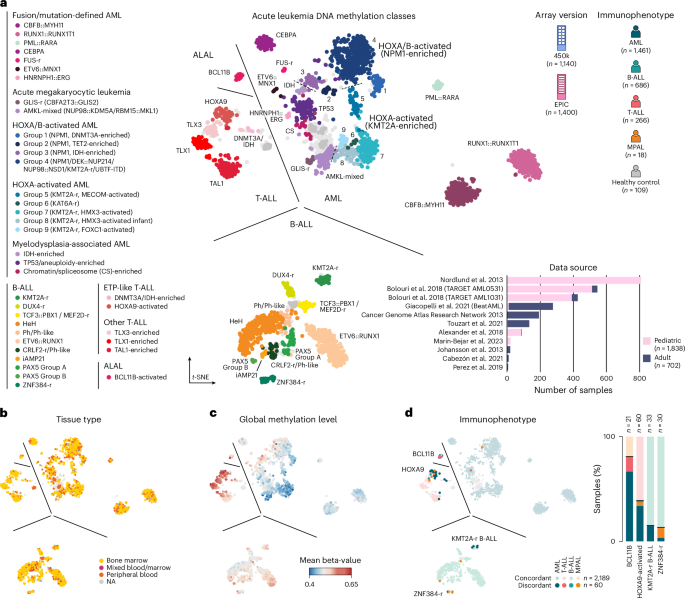
The article presents a rapid epigenomic classification method for acute leukemia using nanopore sequencing and machine learning, based on a comprehensive DNA methylation reference cohort, enabling faster and more precise diagnosis that can complement traditional diagnostic workflows.