"Physicists Achieve Ultracold Quantum State with Dipolar Molecules"
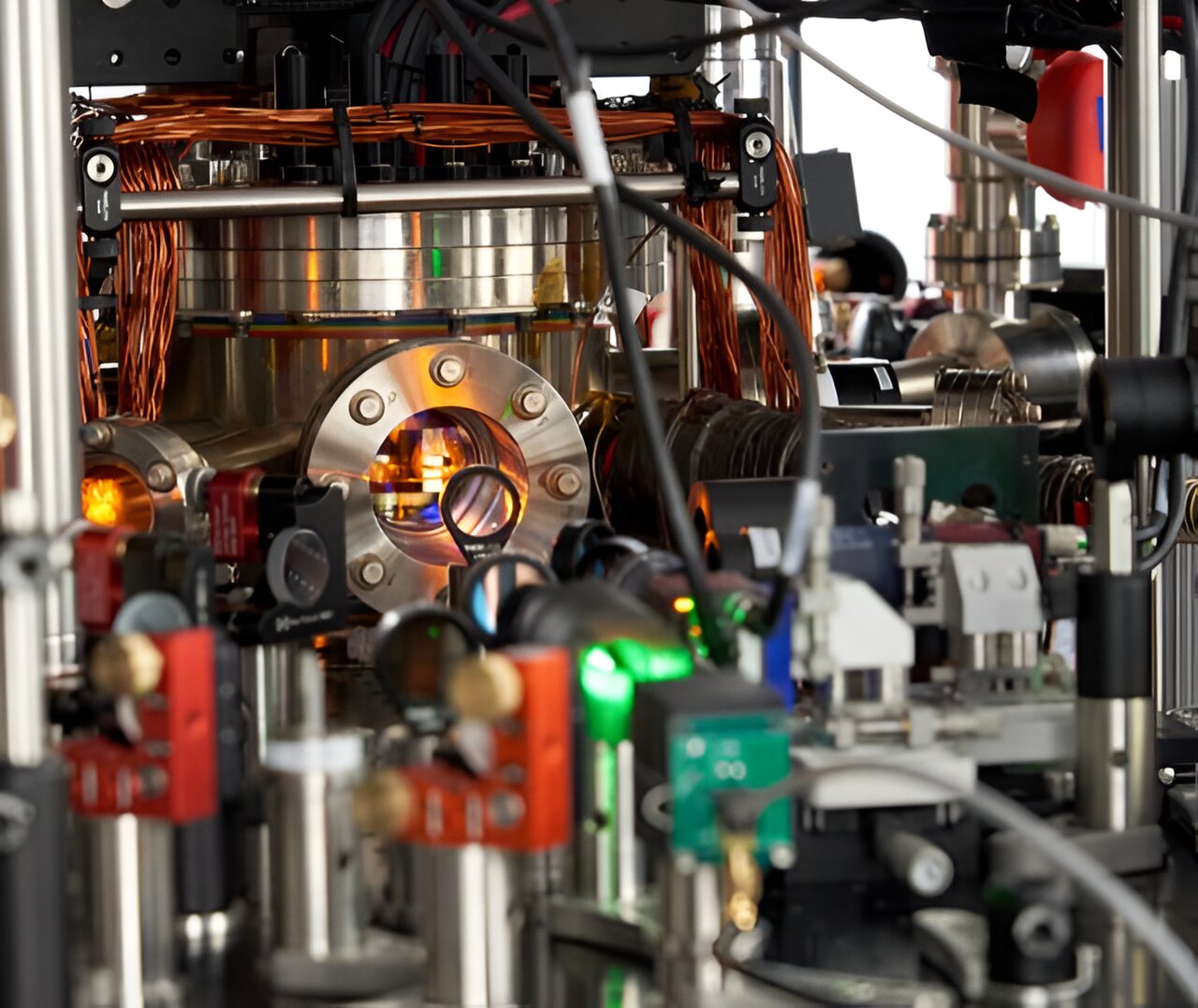
Physicists at Columbia University have created a Bose-Einstein Condensate (BEC) from sodium-cesium molecules at just five nanoKelvin, utilizing microwaves to prevent molecular collisions and achieve ultracold temperatures. This breakthrough opens new avenues for exploring quantum phenomena and developing quantum simulations, marking a significant advancement in the field of ultracold physics.