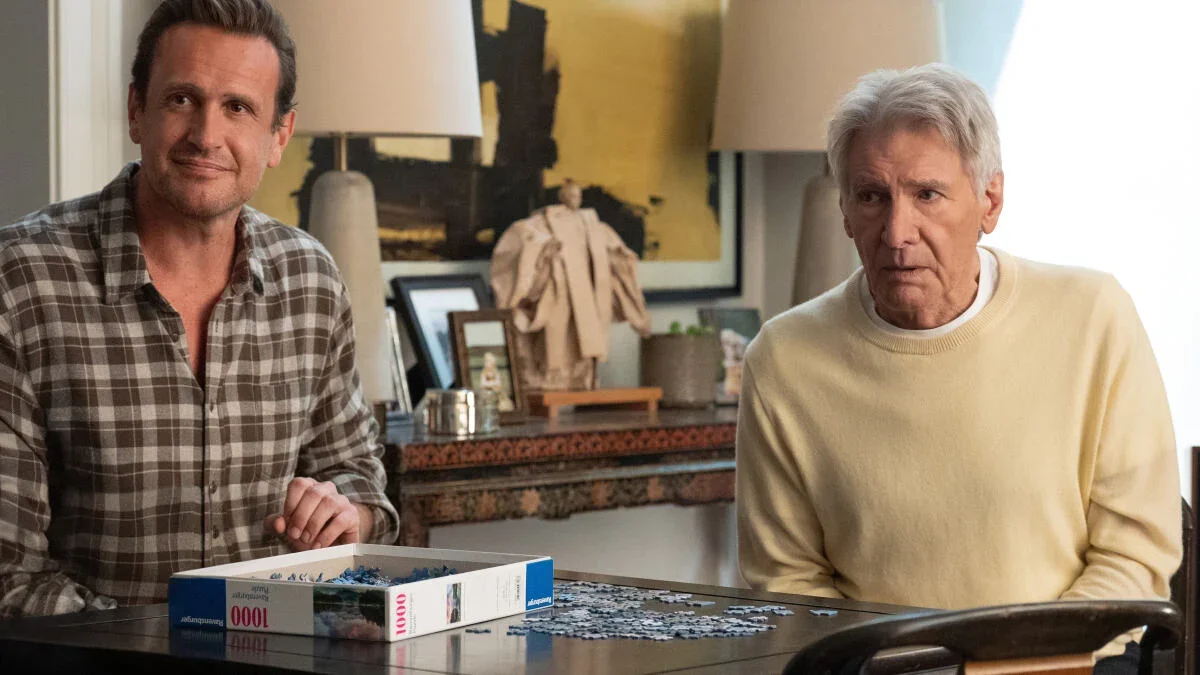
Shrinking Season 3 Opens With a Heart-Wrenching Parkinson's Hallucination
In Shrinking season 3 episode 1, Paul’s Parkinson’s progresses to the point where he hallucinates Gerry (Michael J. Fox) at the wedding cake, a scene that echoes an earlier clinic moment and signals the disease’s encroachment on more aspects of his life. The episode leaves viewers questioning whether Paul has been hallucinating all along, highlighting the painful, non-motor toll of Parkinson's as his world—and his marriage—are affected.