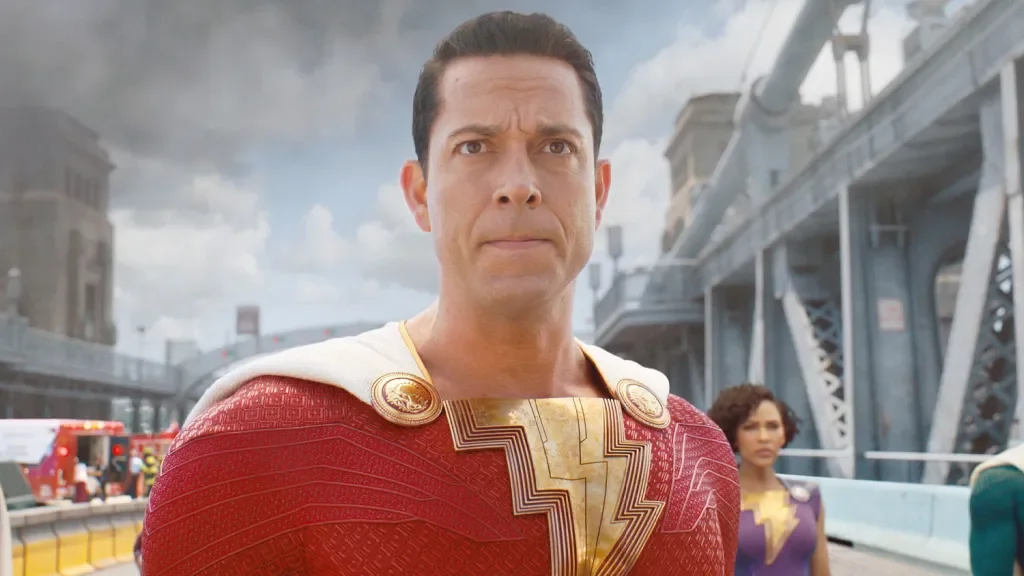
Shazam! Star Zachary Levi Gobsmacked by Seedance 2.0's AI Pace
Shazam! star Zachary Levi says he’s gobsmacked by Seedance 2.0’s rapid AI progress, posting clips and noting how quickly generative AI can produce content; the piece highlights Hollywood IP concerns and ByteDance’s pledge to strengthen safeguards after studios’ legal pressure.