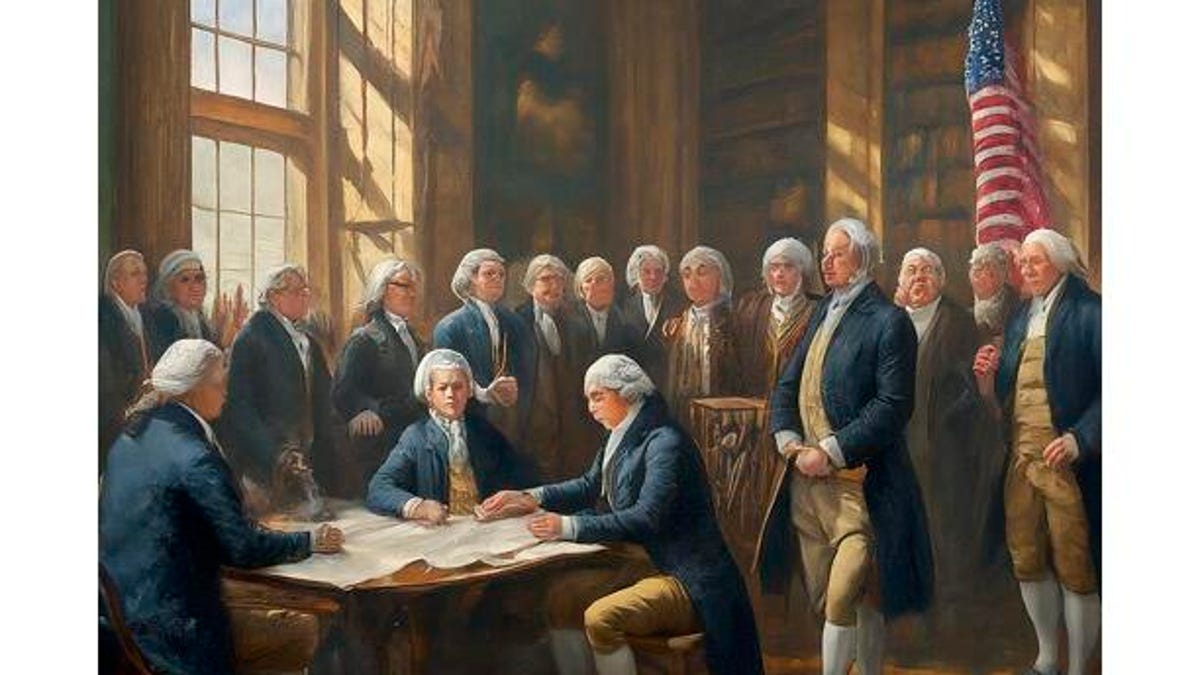
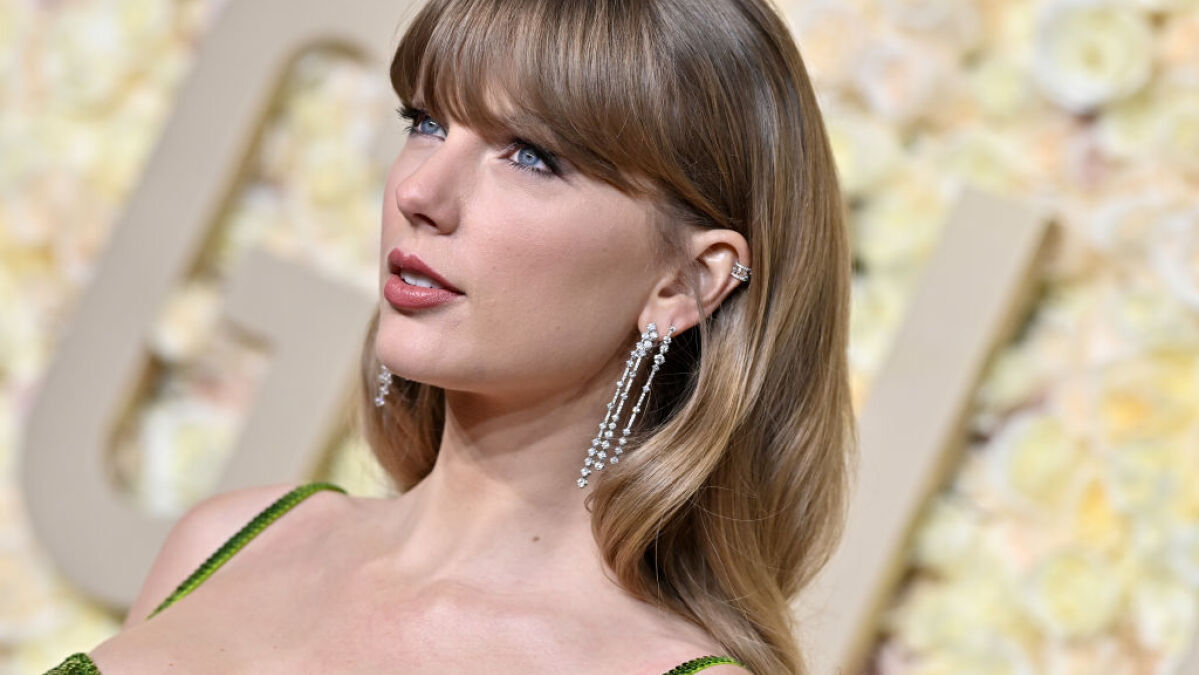
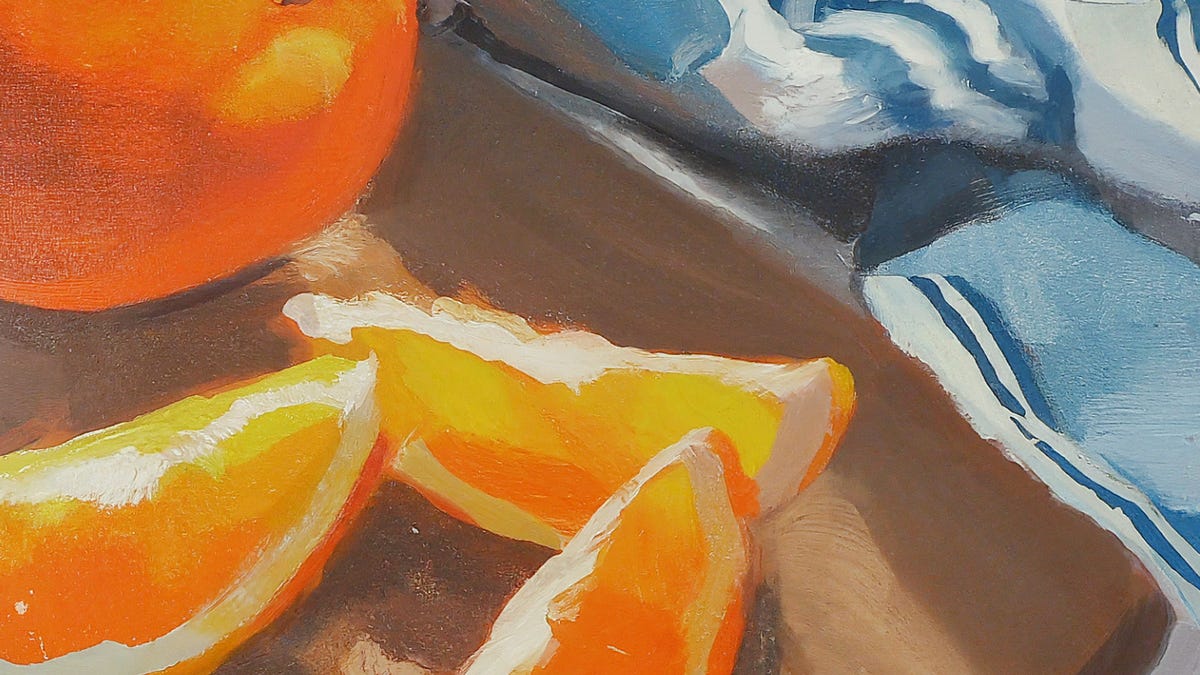
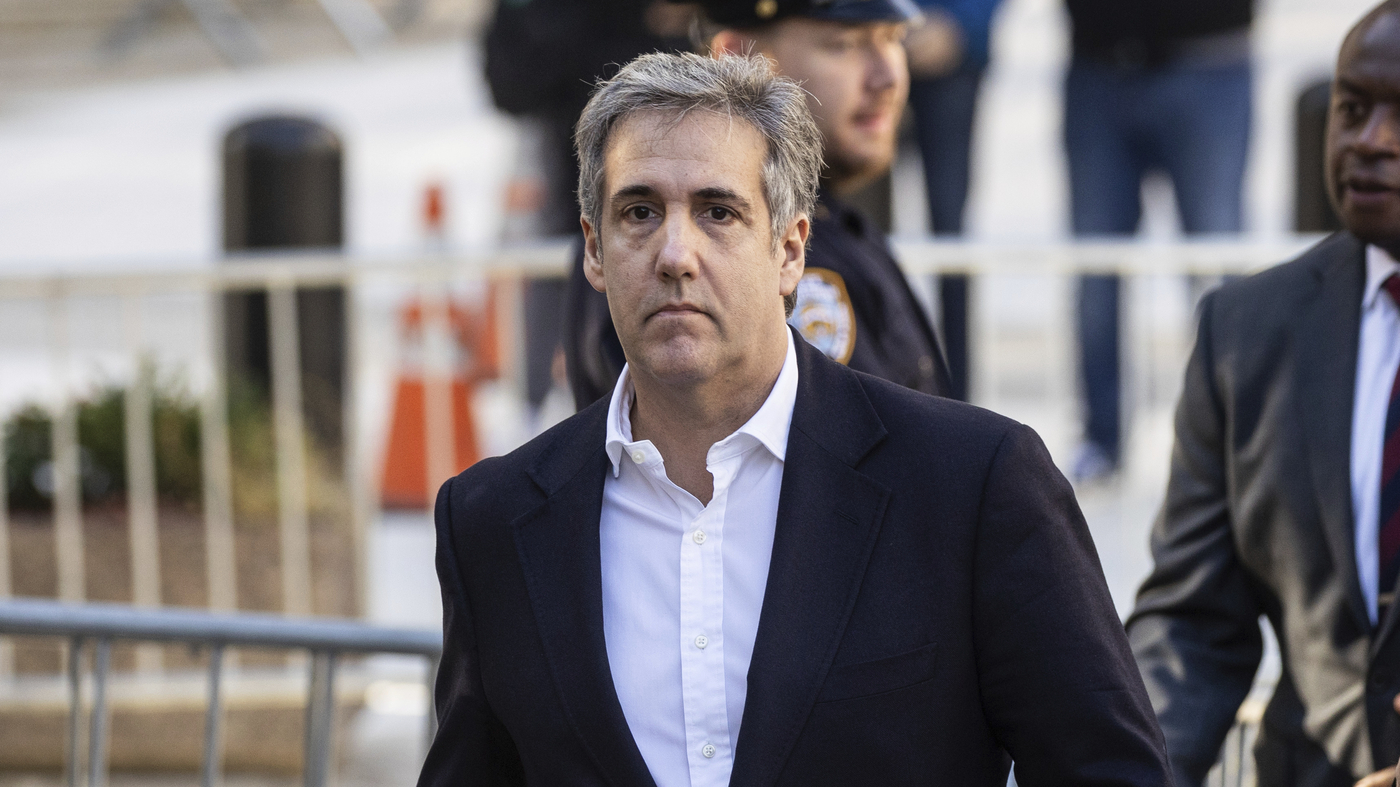
"Google's Gemini: The Ultimate Image Generation Tool?"
Google Bard, Google's AI chatbot, now allows users of its free version to create AI-generated images using the Gemini Pro and Imagen 2 model, promising "photorealistic outputs." Users can simply prompt the chatbot to create an image on the Bard website, and while the quality of the results may vary, the system typically offers different style options for each prompt. Notably, the images generated will bear a digital watermark from Google's SynthID, indicating their AI-generated nature.