Quebec’s seniors face rising fatal falls, triggering a stronger prevention push
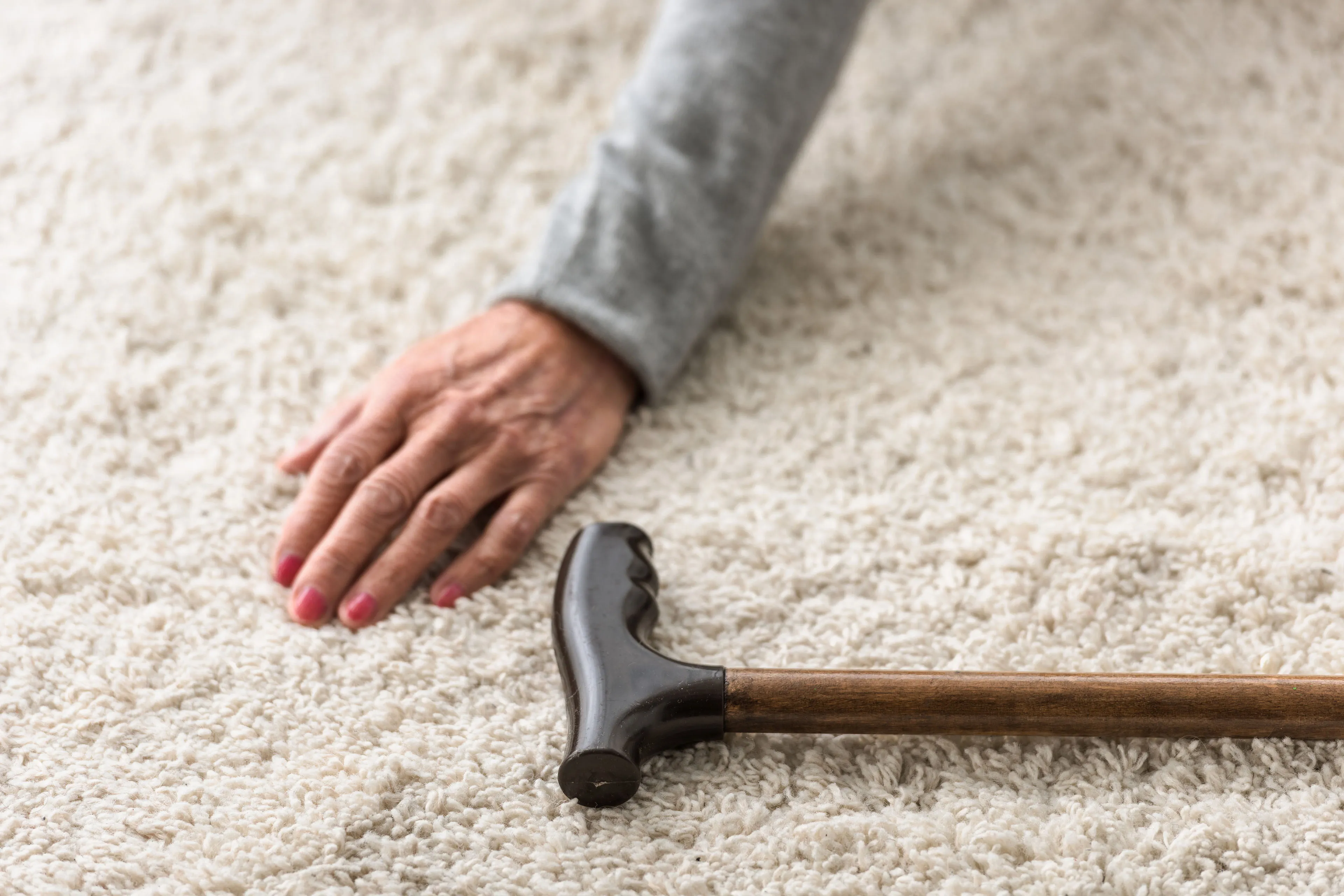
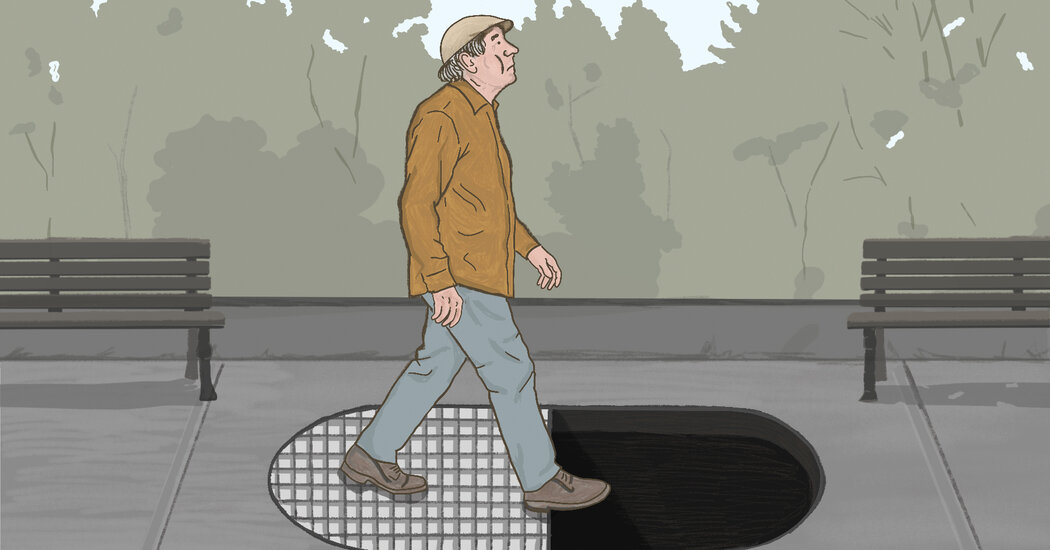
A 2025 INSPQ study shows falls are the leading cause of death and hospitalization from unintentional injuries among Quebecers 65+, with fall-related deaths quadrupling since 2000 (about 2,355 deaths in 65+ by 2021). About one in three older adults fall each year, rising to about half of those 85+, and traumatic brain injuries from falls are increasing. In response, Quebec unveiled multidisciplinary prevention efforts: a McGill-led falls-and-fractures clinic, Vivifrail home-exercise program, the DURAgym supervised program, Stand Up! fall-prevention initiatives, and community programs, plus medication reviews and home-safety assessments to keep seniors out of hospital and long-term care. The overarching message is clear: falling is not normal, and proactive prevention helps maintain autonomy and reduce suffering for older adults.