Macron rejects free-speech defenses, calls for transparent social-media algorithms
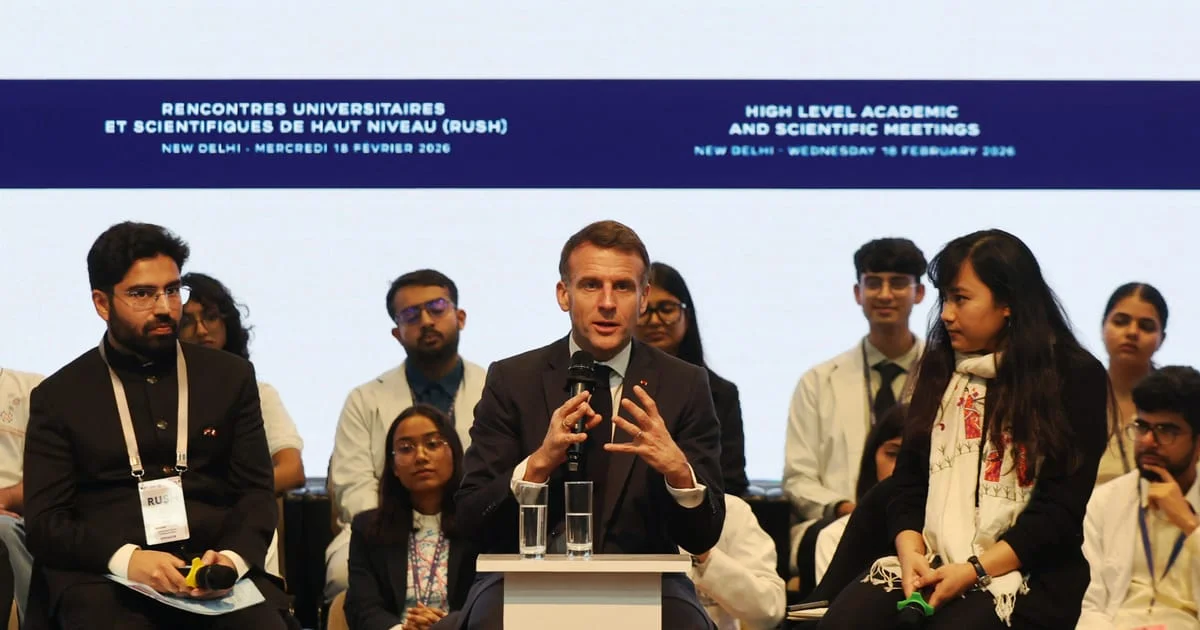
French President Emmanuel Macron denounced tech giants' claims to defend free speech, insisting platforms must be transparent about how their algorithms work and acknowledging inherent biases; he made the remarks during a New Delhi event on India-France university partnerships, framing the debate within broader EU tech rules and his push to curb youth access to social media.