"Breakthrough Antibiotic Offers New Hope Against Superbugs"
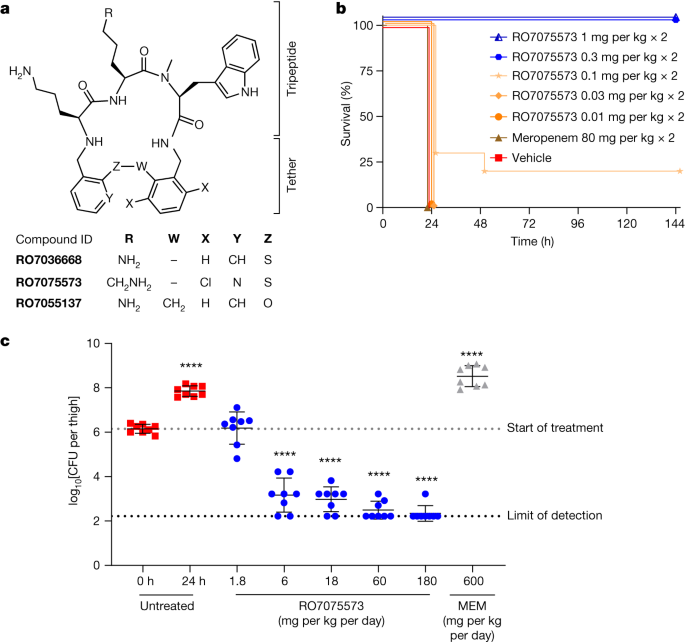
A potential new antibiotic, zosurabalpin, has shown promise in treating lethal hospital infections caused by the drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, a priority-one critical pathogen. Prof Laura Piddock from the Global Antibiotic Research and Development Partnership reported that the compound disrupts the bacterium's protective membrane, proving effective in lab and mouse studies. Although "first-in-man" studies have been conducted, extensive clinical trials and economic considerations remain before the drug can be widely used in hospitals. Despite the challenges, the discovery offers hope for treating various hard-to-treat infections.