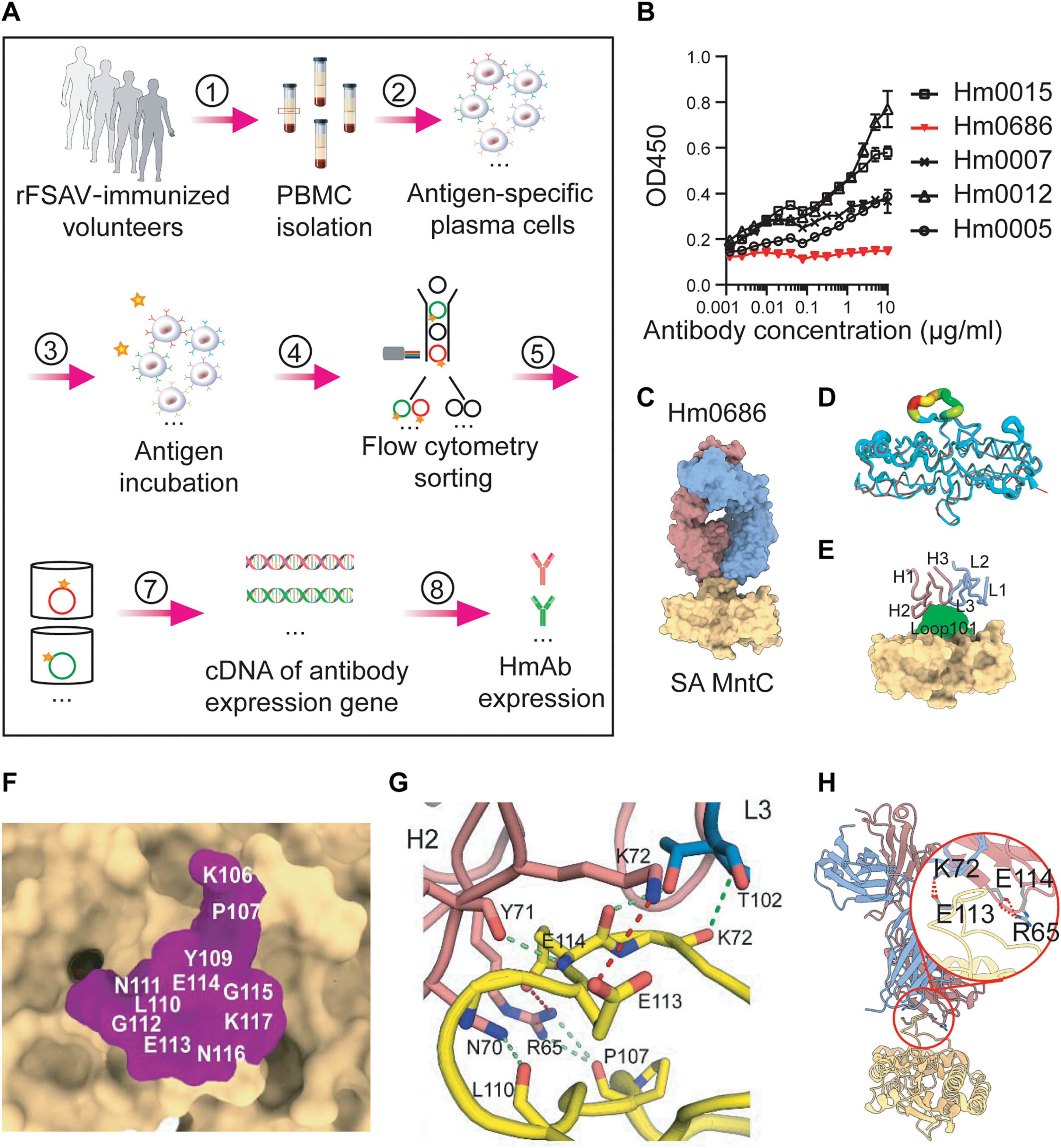
Scientists Advancing Toward Staphylococcus aureus Vaccine
Scientists in China are developing a new vaccine against drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by targeting a specific surface loop on the MntC protein, which is essential for the bacteria's survival, potentially overcoming past vaccine failures caused by the bacteria's presence as a common commensal organism.