Uncovering the Main Cause of Itchiness in Eczema and a Promising Breakthrough Drug
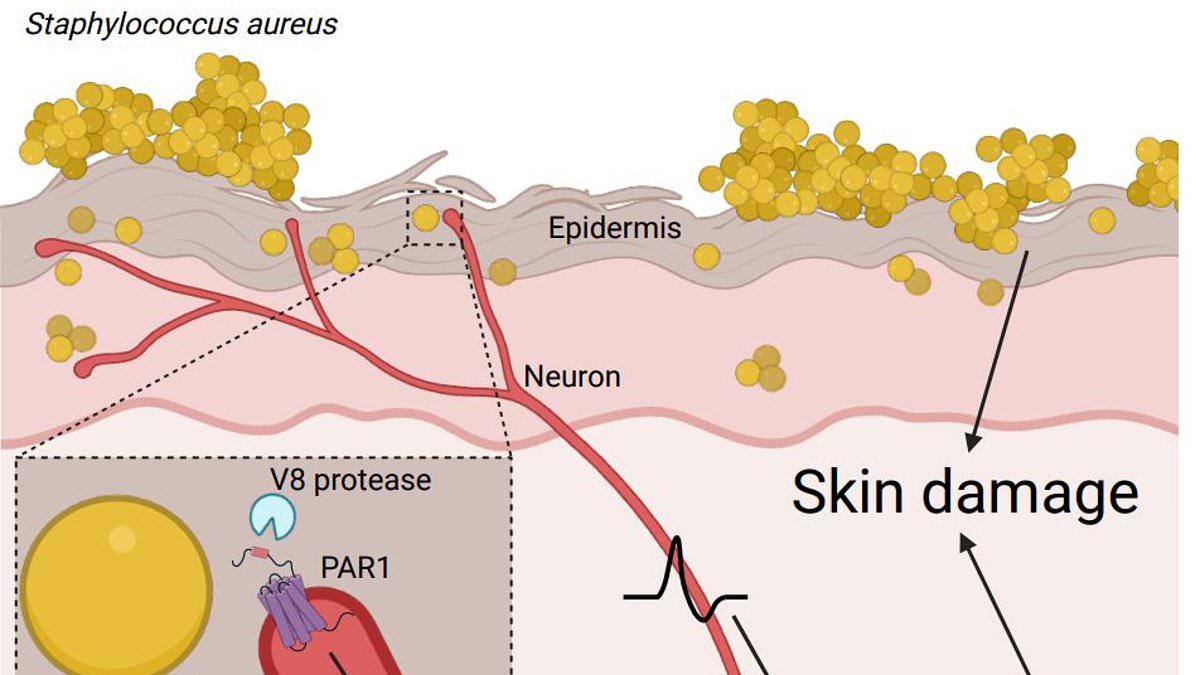
Scientists from Harvard University have discovered that the intense itchiness associated with eczema is caused by the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus, rather than inflammation of the skin itself. They identified the enzyme V8 protease as responsible for triggering the itch, and believe that the drug vorapaxar, currently used to prevent blood clots, could be modified to break the itch-scratch cycle of eczema. The researchers found that blocking the nerve receptor associated with the itch was effective in reducing itchiness in mice. Eczema affects up to 25% of the population and can have a significant impact on quality of life.