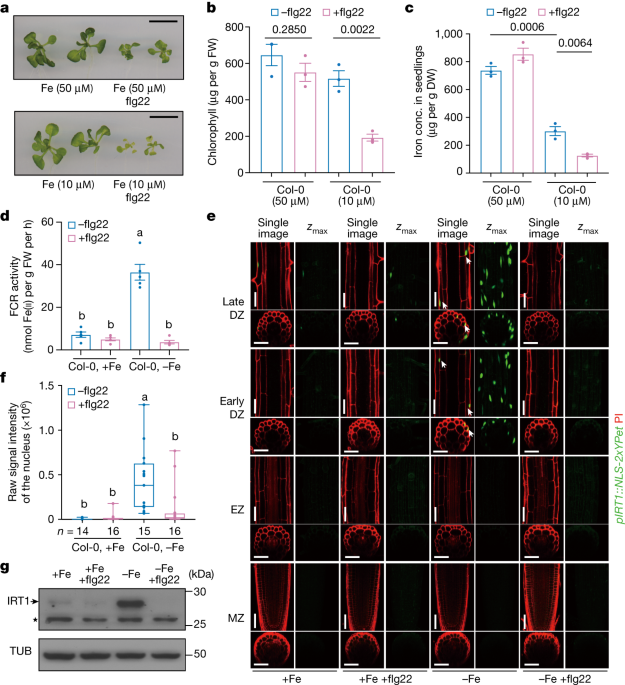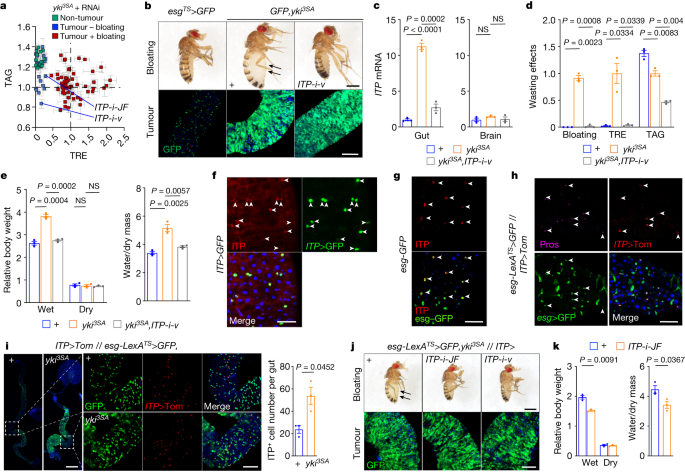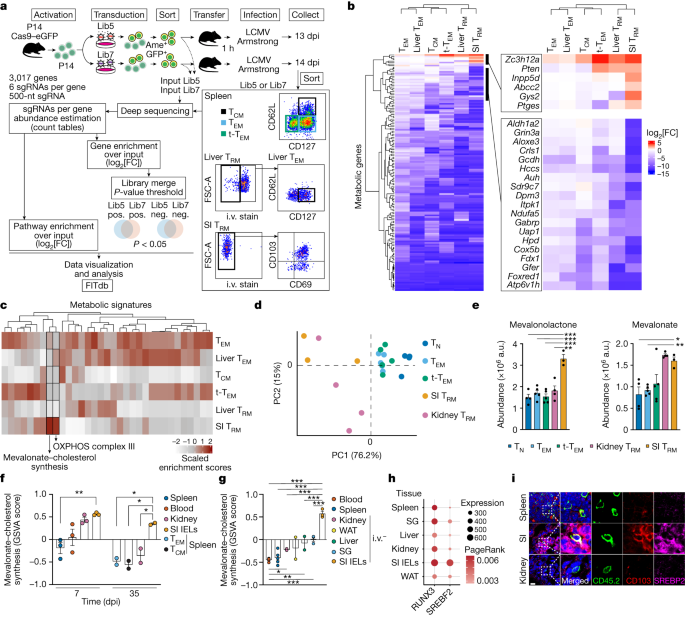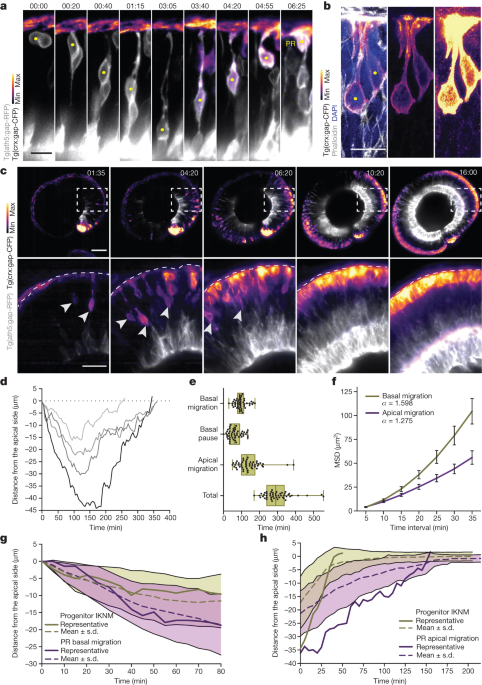
"SOX17's Role in Immune Evasion of Colorectal Adenomas and Cancers"
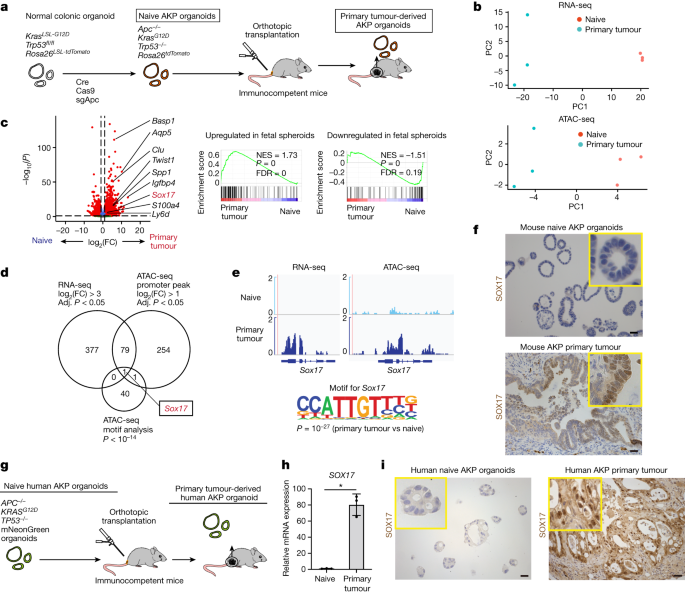
A study has found that SOX17 enables immune evasion in early colorectal adenomas and cancers. The research, which utilized RNA-seq data, ATAC-seq data, and single-cell RNA-seq data, sheds light on the role of SOX17 in immune evasion and its potential implications for colorectal cancer treatment. The findings provide valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying immune evasion in colorectal cancer and may contribute to the development of targeted therapies.