Understanding Trypophobia: The Brain's Reaction to Tiny Holes
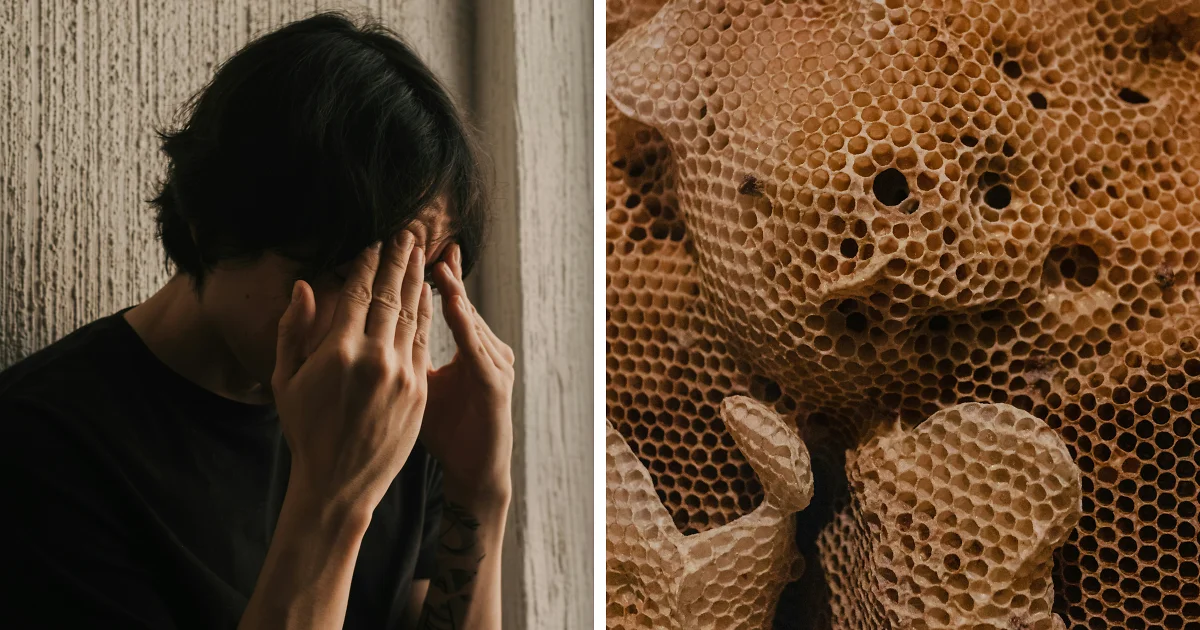
Trypophobia is an aversion to clustered holes or bumps, often driven by disgust and evolutionary disease-avoidance instincts, but it is not officially recognized as a clinical phobia. Reactions include discomfort, physical sensations, and avoidance, triggered by visual patterns resembling parasites or diseased skin. While many experience symptoms similar to phobias, it generally lacks the impairment required for diagnosis. Treatments like therapy and relaxation techniques can help manage symptoms.