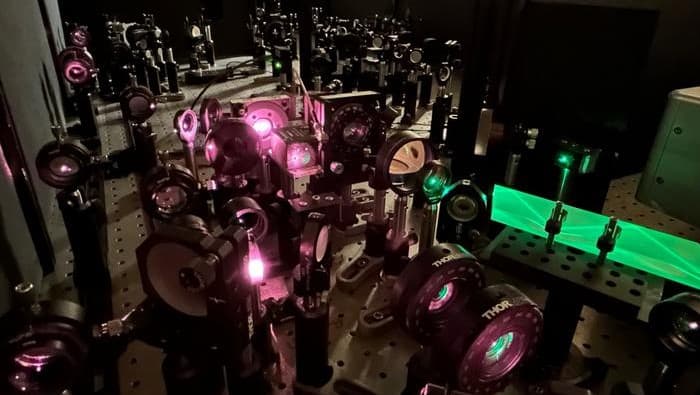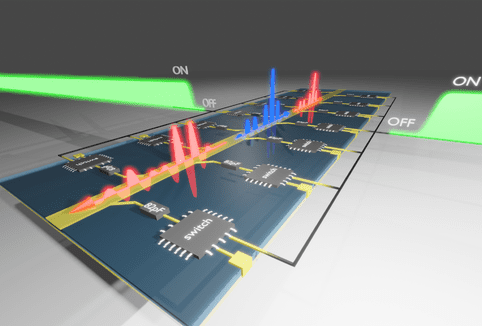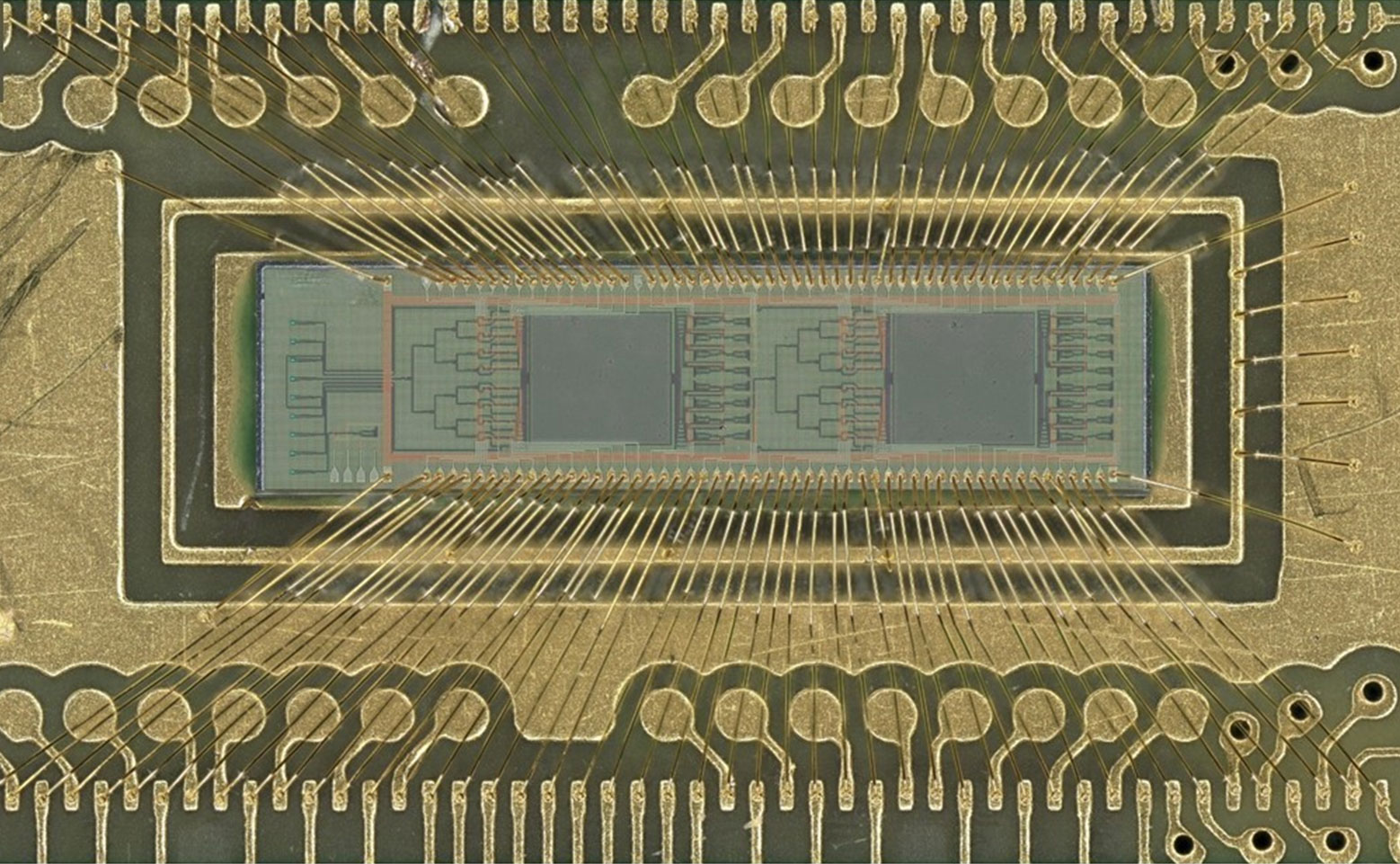
Light-Based Computing Revolutionizes AI Efficiency and Innovation
A new light-based AI chip significantly boosts efficiency—by 10 to 100 times—by using integrated lasers and tiny lenses for optical calculations, matching traditional performance while drastically reducing energy consumption, potentially transforming future AI hardware.