Revealing the Ultrafast Calcium Transport Mechanism of Plasma Membrane Ca2+-ATPases
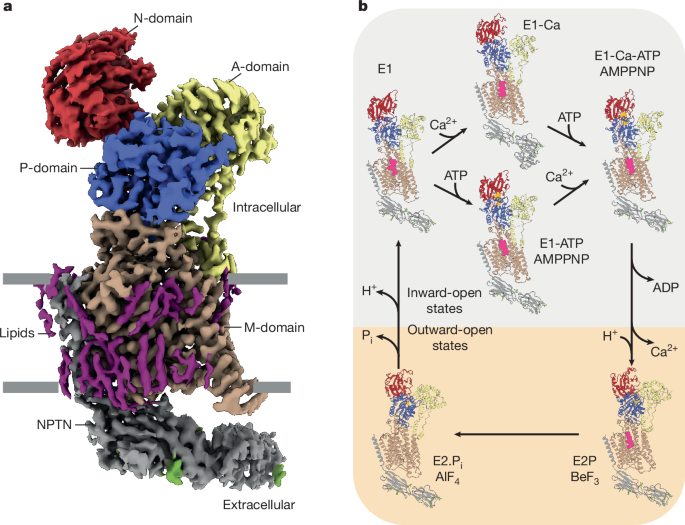
This article explores the molecular structure and function of plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPases (PMCAs), revealing how they achieve ultrafast calcium transport through specific structural features, interactions with phospholipids like PtdIns(4,5)P2, and conformational changes during their transport cycle, with implications for understanding their role in cellular calcium signaling and potential drug targeting.