"Challenges and Opportunities: Navigating Inflation in the US Economy"
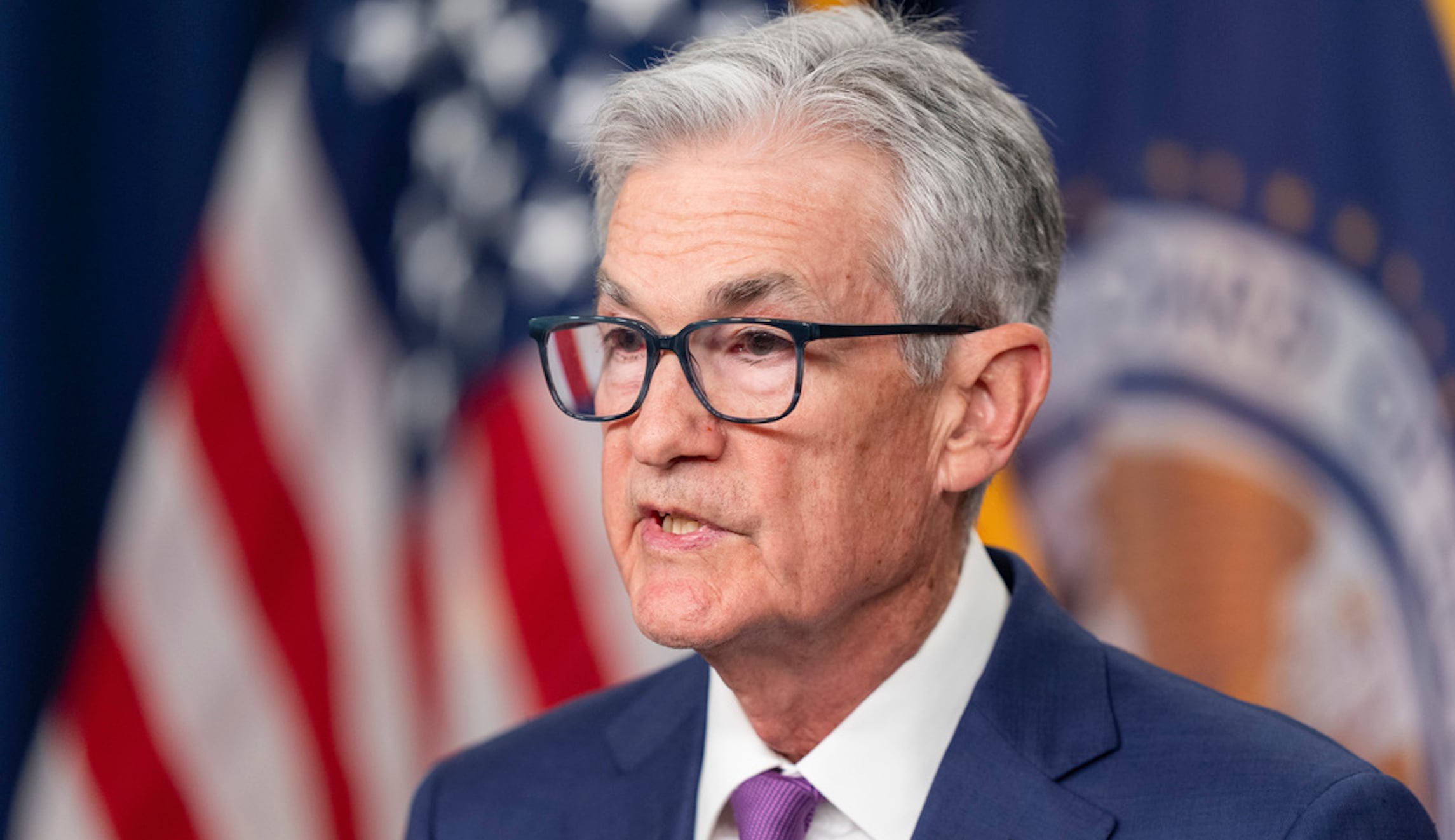
The Federal Reserve's inflation target suggests aiming for inflation below 2%, but officials have not entertained this possibility despite current inflation running well above 2%. Experts urge the Fed to clarify its target to avoid confusion. The average inflation target, adopted in 2020, may not be suited for the current surge in inflation, prompting calls for the Fed to review its longer-run goals statement. Fed Chairman Jerome Powell is expected to address questions on inflation during congressional testimony, and experts suggest the Fed should be more open about the meaning of average inflation targeting.