Spain to Launch Nationwide Climate Shelters to Combat Summer Heat
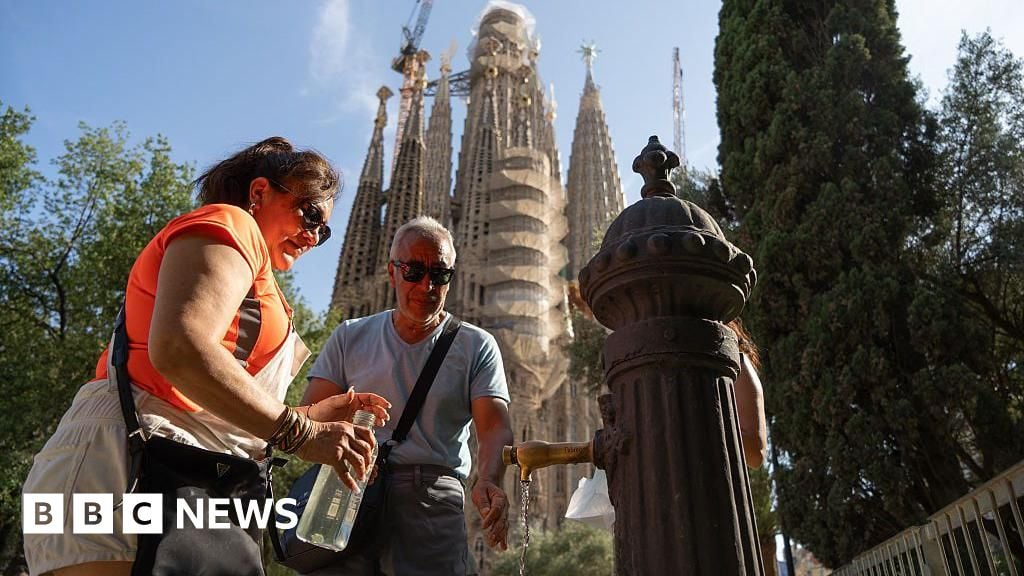
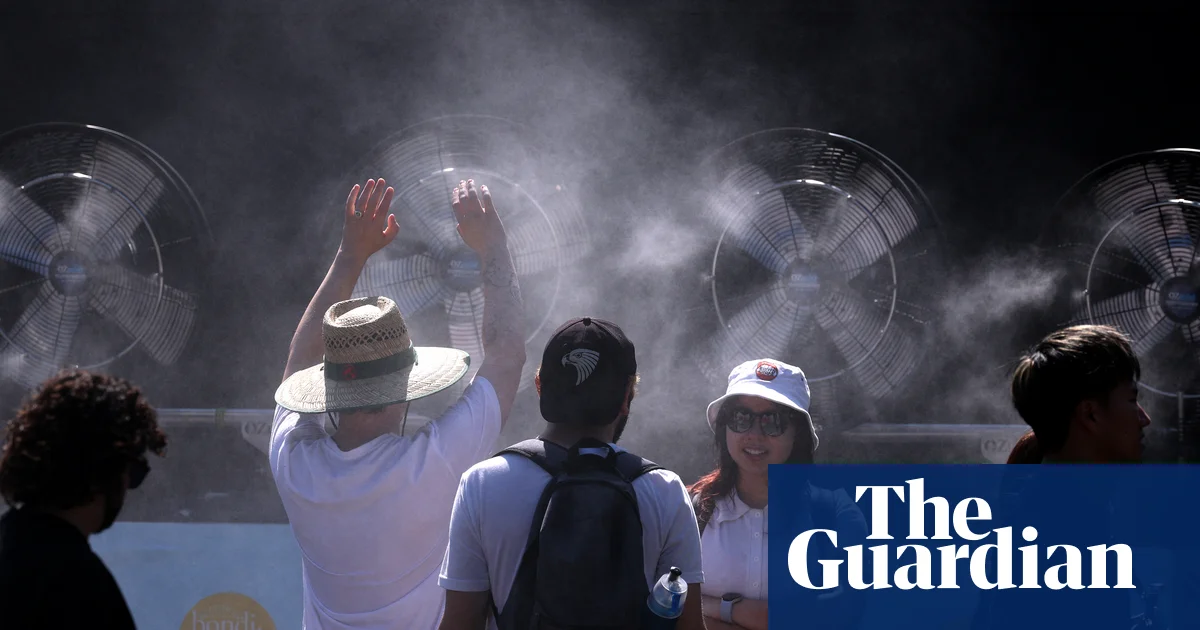
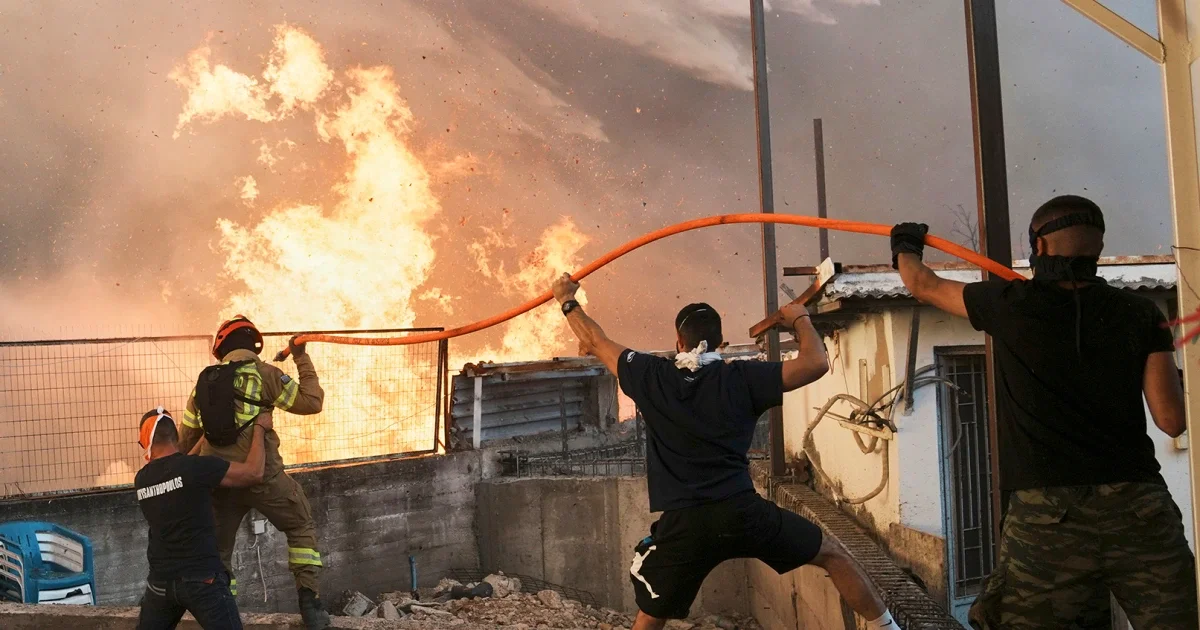
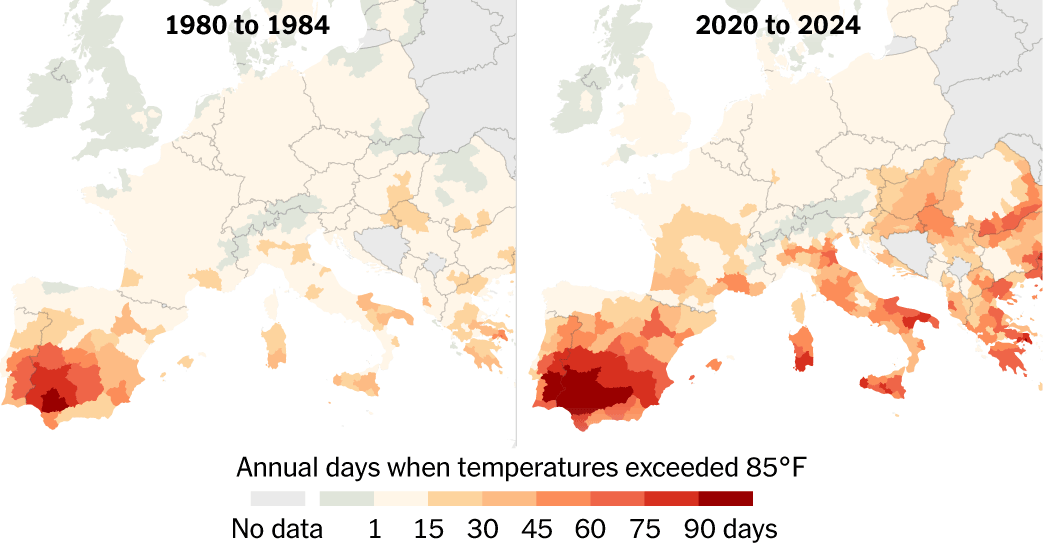
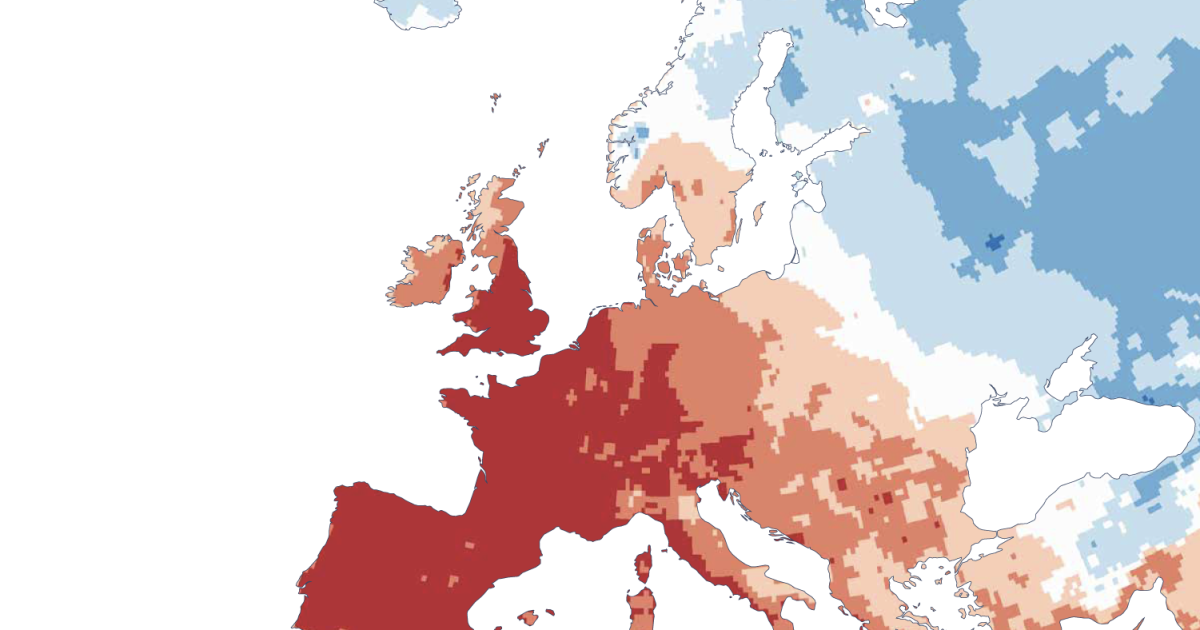
Spain plans to establish a national network of climate shelters in public buildings to protect people from intense heat, as part of broader efforts to combat the increasing frequency and severity of heatwaves and climate-related disasters, following a record hot summer and devastating wildfires in 2025.