From plushie to psychology: Punch and the roots of attachment theory
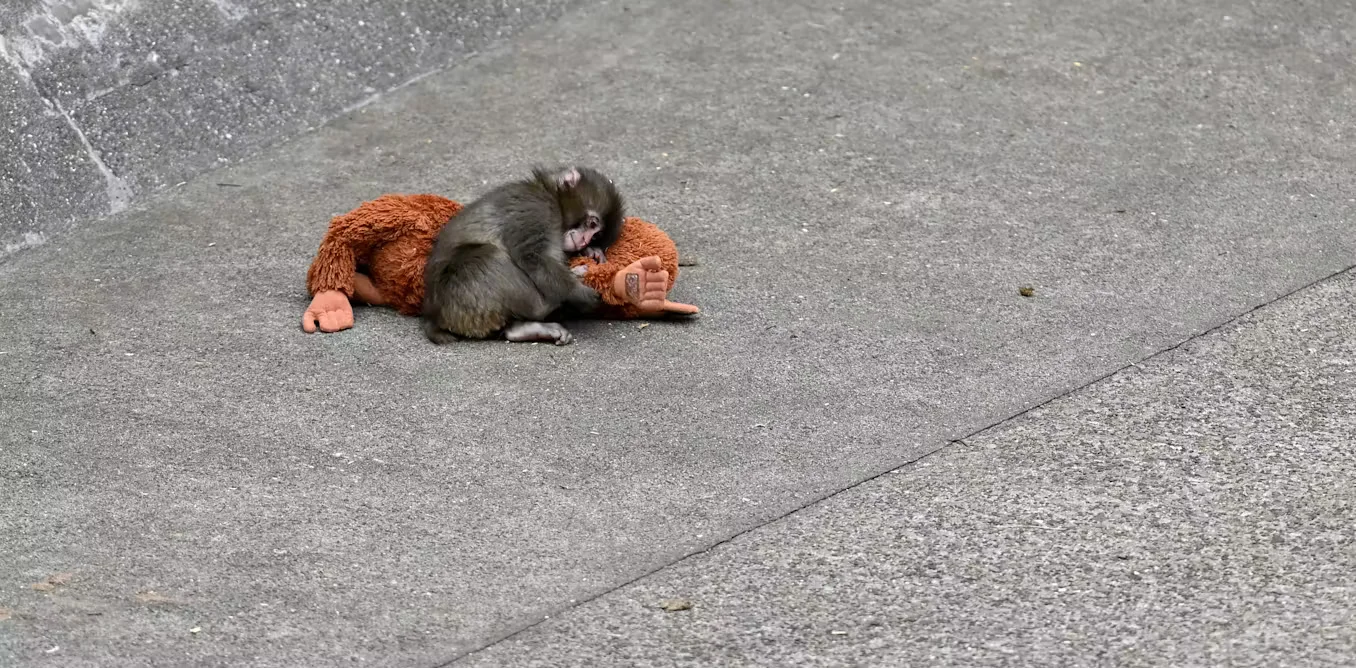
A viral video of Punch the baby macaque clinging to a soft plush toy echoes Harry Harlow’s 1950s experiments, illustrating that emotional nourishment and caregiving shape attachment more than food alone; the piece ties this to modern attachment theory and reflects on the ethical considerations of early primate research.